David Barack is a philosopher and neuroscientist who studies the neural circuits of foraging behavior and the conceptual foundations of cognitive neuroscience. He is a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Pennsylvania. After earning his B.A. in consciousness studies at Pitzer College, he received his M.A. in philosophy from the University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee and his Ph.D. in philosophy from Duke University, where he also received a certificate in cognitive neuroscience. He is currently writing a book on the neurodynamical foundations of mind.

David Barack
Research associate in neuroscience and philosophy
University of Pennsylvania
From this contributor
Must a theory be falsifiable to contribute to good science?
Four researchers debate the role that non-testable theories play in neuroscience.

Must a theory be falsifiable to contribute to good science?
Explore more from The Transmitter
Karen Adolph explains how we develop our ability to move through the world
How do babies' bodies and their environment teach them to move—and how can robots benefit from these insights?

Karen Adolph explains how we develop our ability to move through the world
How do babies' bodies and their environment teach them to move—and how can robots benefit from these insights?
Microglia’s pruning function called into question
Scientists are divided over the extent to which the cells sculpt circuits during development.
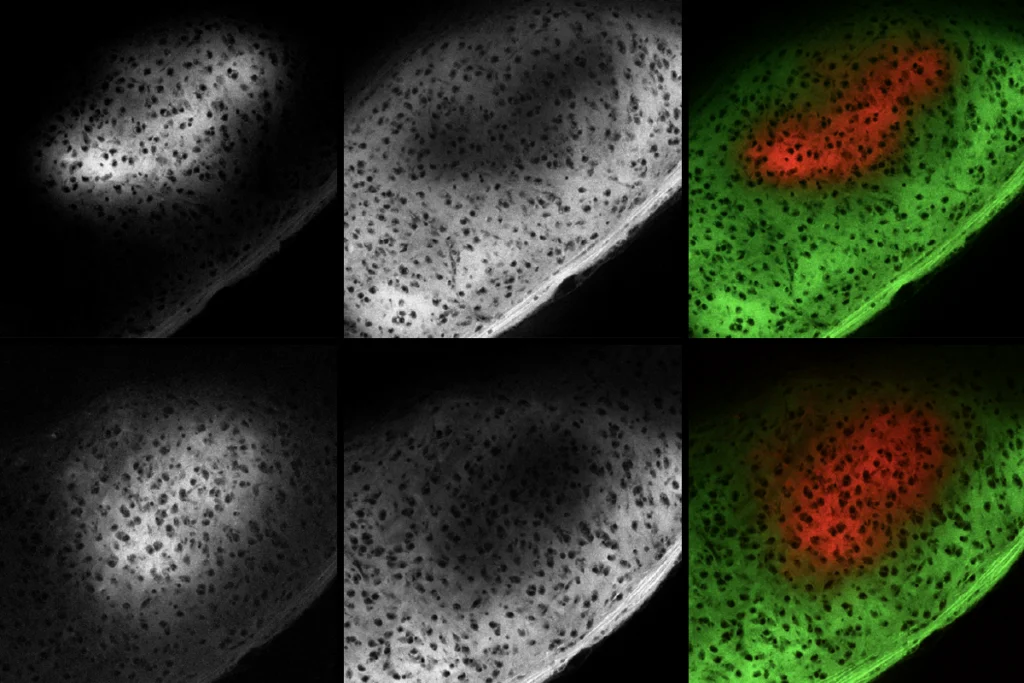
Microglia’s pruning function called into question
Scientists are divided over the extent to which the cells sculpt circuits during development.
Early trajectory of Alzheimer’s tracked in single-cell brain atlases
Inflammation in glia and the loss of certain inhibitory cells may kick off a disease cascade decades before diagnosis.
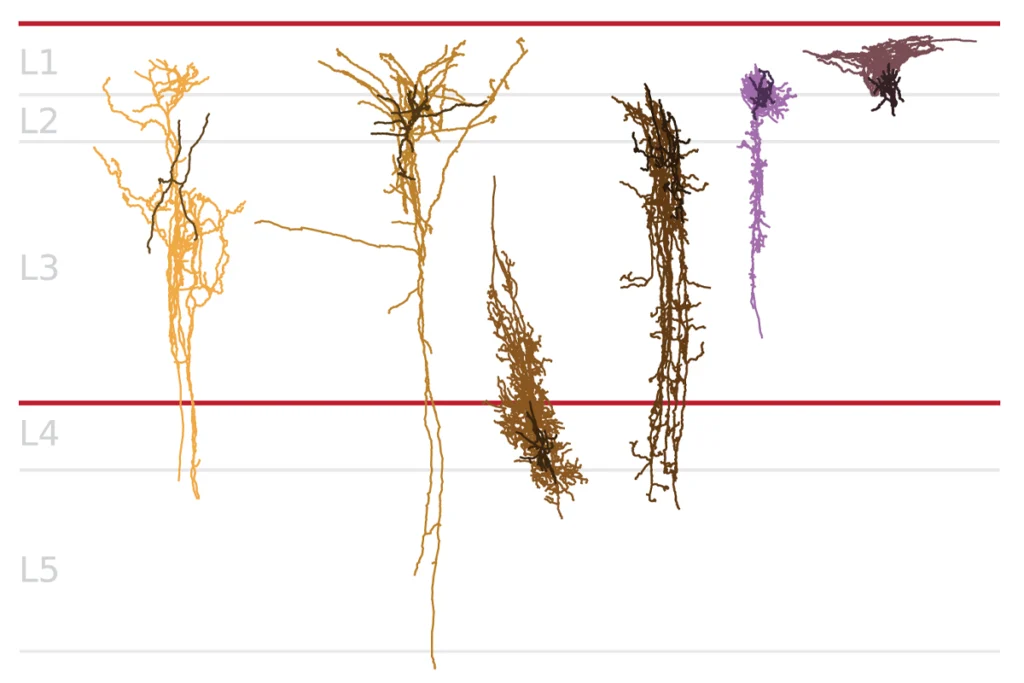

Early trajectory of Alzheimer’s tracked in single-cell brain atlases
Inflammation in glia and the loss of certain inhibitory cells may kick off a disease cascade decades before diagnosis.