Emily Singer commissions and edits scientist-written content and develops new resources for the community. She joined The Transmitter in 2023 and has previously held a variety of editorial roles at the Simons Foundation, including editor for neuroscience collaborations, and senior biology writer and contributing editor at Quanta Magazine. Before joining the foundation, she was biomedical editor at Technology Review.

Emily Singer
Opinion and community editor
The Transmitter
From this contributor

Parents turn their skills to furthering autism research

Gender differences take center stage at autism conference
Education
- Certificate in science communication, University of California, Santa Cruz
- B.A. in biology, University of California, Santa Cruz
Fellowships
- AAAS Mass Media Fellowship
Explore more from The Transmitter
New connectomes fly beyond the brain
Researchers are mapping the neurons in Drosophila’s ventral nerve cord, where the central nervous system meets the rest of the body.
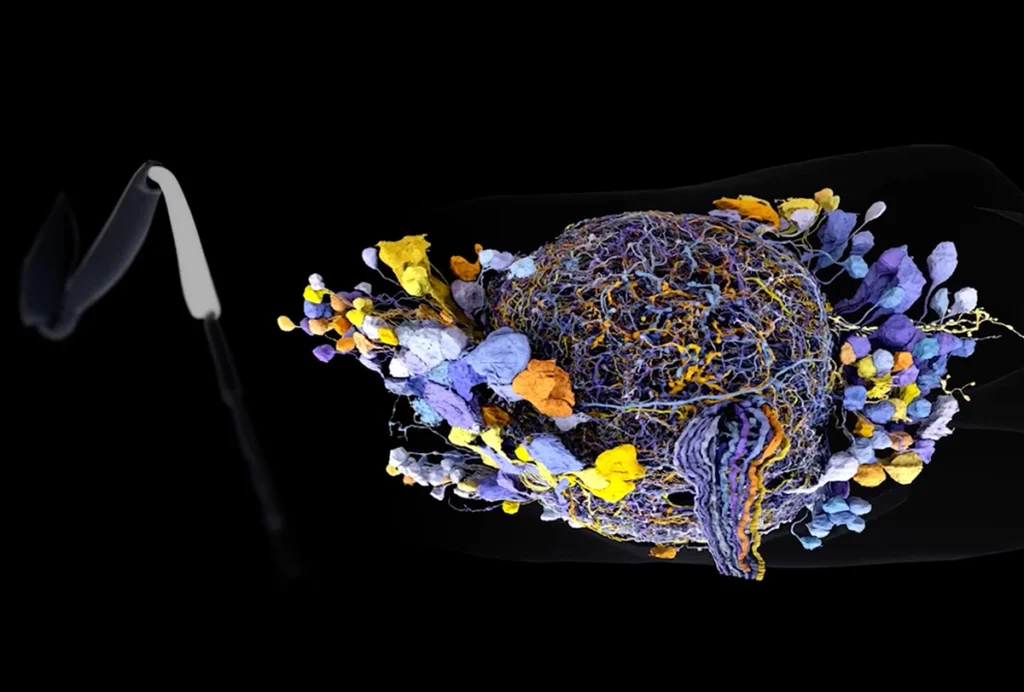
New connectomes fly beyond the brain
Researchers are mapping the neurons in Drosophila’s ventral nerve cord, where the central nervous system meets the rest of the body.
Building an autism research registry: Q&A with Tony Charman
A purpose-built database of participants who have shared genomic and behavioral data could give clinical trials a boost, Charman says.

Building an autism research registry: Q&A with Tony Charman
A purpose-built database of participants who have shared genomic and behavioral data could give clinical trials a boost, Charman says.
Cerebellar circuit may convert expected pain relief into real thing
The newly identified circuit taps into the brain’s opioid system to provide a top-down form of pain relief.
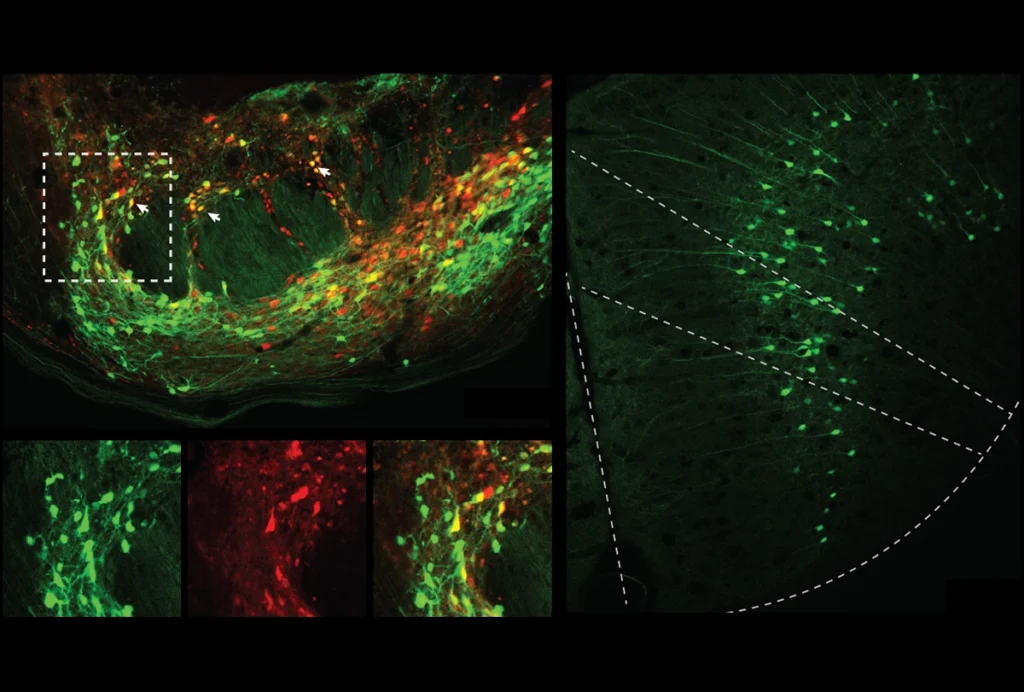
Cerebellar circuit may convert expected pain relief into real thing
The newly identified circuit taps into the brain’s opioid system to provide a top-down form of pain relief.


