Emily writes frequently about autism and related issues, and her work has appeared in print or online at Discover, New York Times, Slate, Washington Post, San Francisco Chronicle, and others. Emily has a B.A. in English with minors in German and History and a Ph.D. in biological sciences, both from The University of Texas at Austin. She also completed postdoctoral work at the University of California, San Francisco and has taught graduate and undergraduate biology for many years.

Emily Willingham
Science writer
Spectrum
From this contributor
Spotted around the web: Week of 29 October 2018
Here is a roundup of news and research for the week of 29 October.
Spotted around the web: Week of 29 October 2018
Book Review: A mother finds reward in risk
In “The Boy Who Loved Too Much,” a woman tries to cocoon her son, who has Williams syndrome, from life’s insults but later realizes her protective instincts carry dangers of their own.

Book Review: A mother finds reward in risk
Spotted around the web: Week of 22 October 2018
Here is a roundup of news and research for the week of 22 October.
Spotted around the web: Week of 22 October 2018
Spotted around the web: Week of 15 October 2018
Here is a roundup of news and research for the week of 15 October.
Spotted around the web: Week of 15 October 2018
Spotted around the web: Week of 8 October 2018
Here is a roundup of news and research for the week of 8 October.
Spotted around the web: Week of 8 October 2018
Explore more from The Transmitter
New connectomes fly beyond the brain
Researchers are mapping the neurons in Drosophila’s ventral nerve cord, where the central nervous system meets the rest of the body.
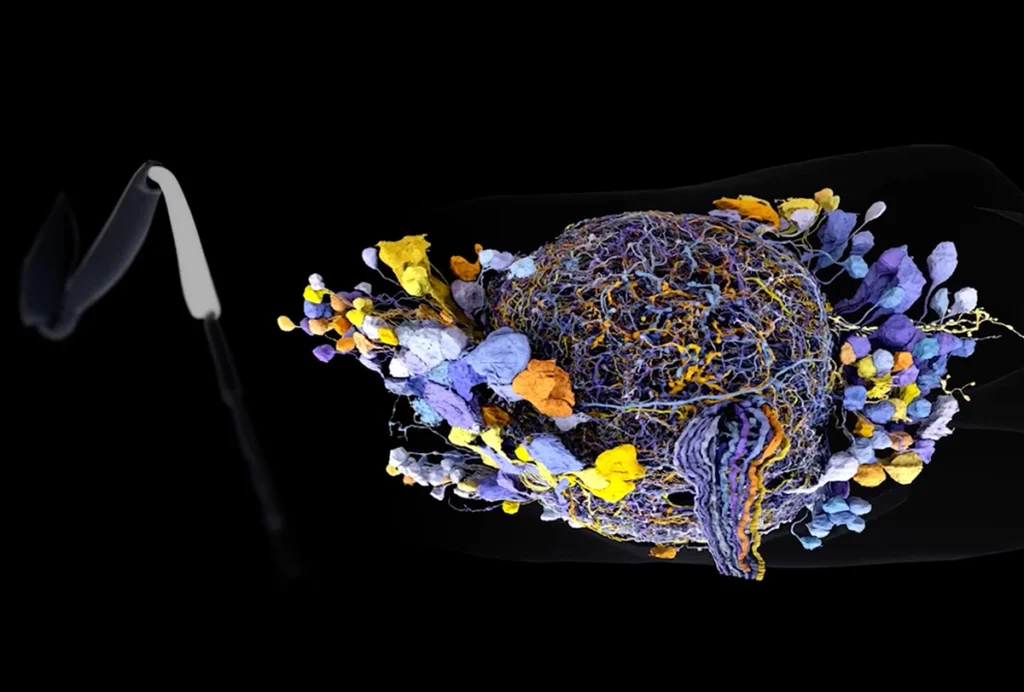
New connectomes fly beyond the brain
Researchers are mapping the neurons in Drosophila’s ventral nerve cord, where the central nervous system meets the rest of the body.
Building an autism research registry: Q&A with Tony Charman
A purpose-built database of participants who have shared genomic and behavioral data could give clinical trials a boost, Charman says.

Building an autism research registry: Q&A with Tony Charman
A purpose-built database of participants who have shared genomic and behavioral data could give clinical trials a boost, Charman says.
Cerebellar circuit may convert expected pain relief into real thing
The newly identified circuit taps into the brain’s opioid system to provide a top-down form of pain relief.
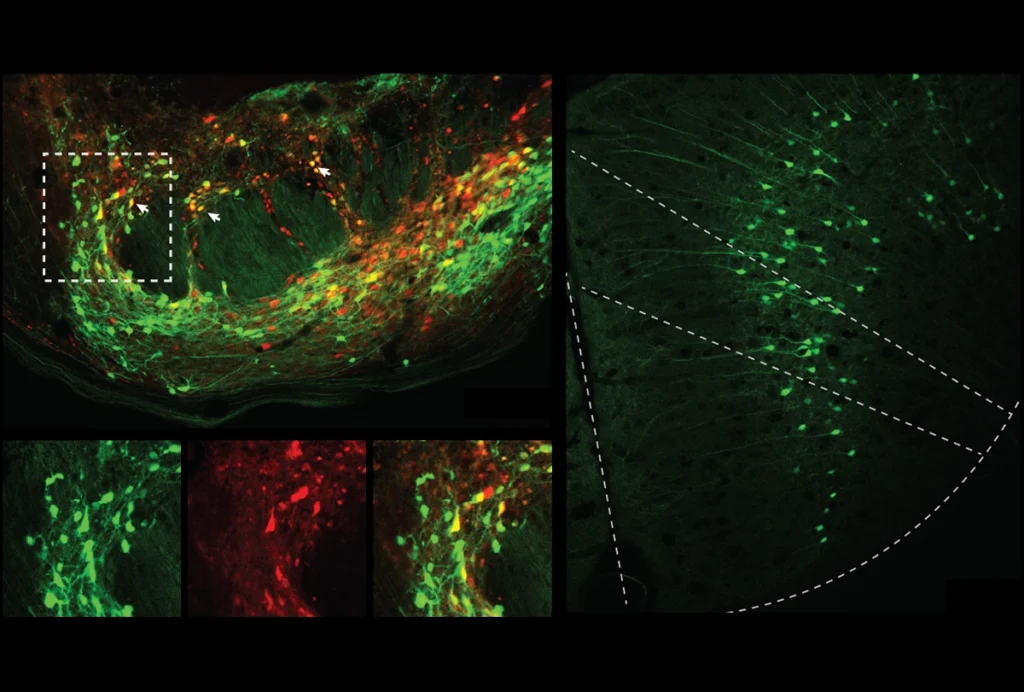
Cerebellar circuit may convert expected pain relief into real thing
The newly identified circuit taps into the brain’s opioid system to provide a top-down form of pain relief.