Peter Hess was a reporter for Spectrum from 2019 to 2023, where he covered cannabinoids, autism prevalence, social hormones and other topics. Before joining Spectrum in 2019, he was associate science editor at Inverse, where he wrote and edited stories for a broad audience on a wide range of scientific topics, including drugs, evolution and environmental science. His work has also appeared in The Washington Post, New Scientist, Popular Science and Motherboard. Peter has an M.A. in science journalism from New York University’s Science, Health and Environmental Reporting Program. Find him on Twitter at @PeterNHess.

Peter Hess
Former news writer
Spectrum
From this contributor
Capturing autism’s sleep problems with devices nearable and wearable
Next-generation trackers could realize a long-standing research dream: conducting sleep studies in large numbers of autistic people.
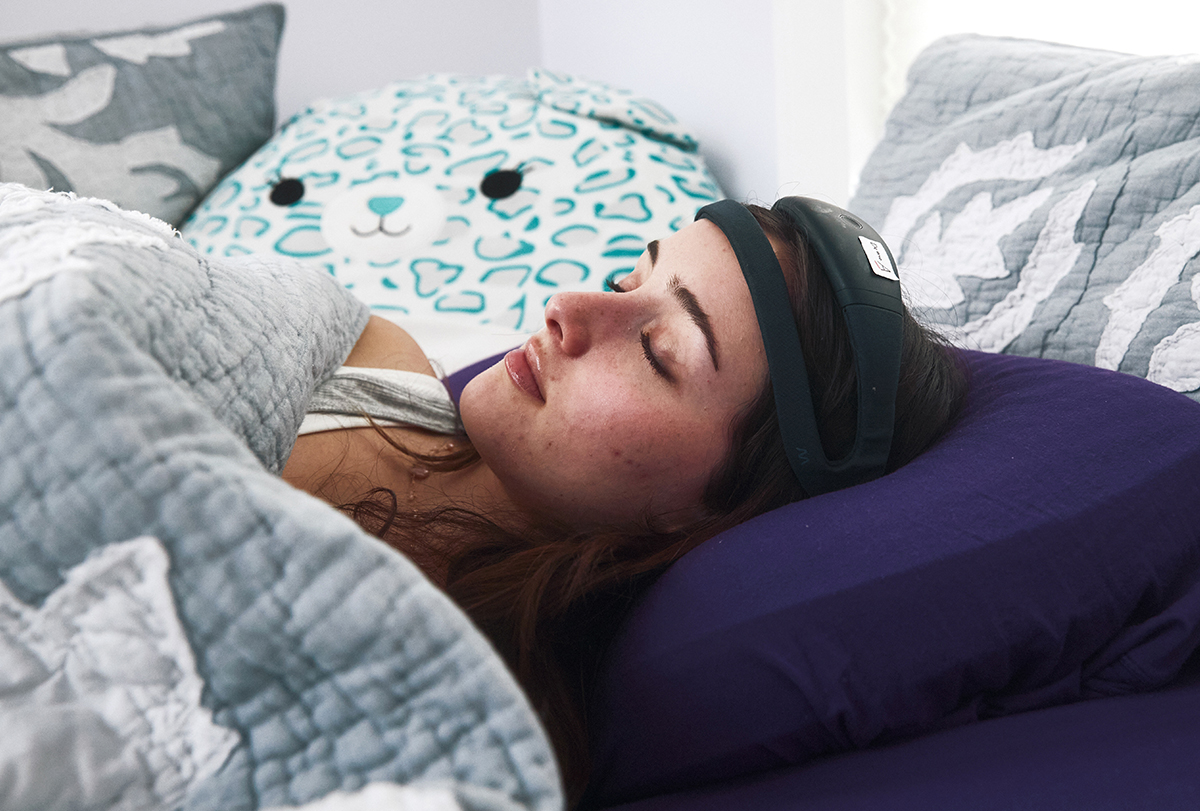

Capturing autism’s sleep problems with devices nearable and wearable
Going on Trial: Epidiolex for autism; arbaclofen tests; pain monitoring
This month’s issue of Going on Trial takes a sneak peek at some early null results from a small trial of a cannabidiol-based drug for autism, among other recent drug developments.
Going on Trial: Epidiolex for autism; arbaclofen tests; pain monitoring
Swings and misses with Jeremy Veenstra-VanderWeele
A careful clinician who prizes evidence, Jeremy Veenstra-VanderWeele is happy to embrace trial failures, as long as he learns from them.
Ruth Carper: Imaging the aging brain in autistic adults
Few studies have tracked how brain structure and function change across adulthood in people with autism. Carper and her colleagues are collecting data to fill this gap.
Ruth Carper: Imaging the aging brain in autistic adults
Autism-related genes converge on microglia and dopamine in zebrafish
The findings add to the growing evidence that genes with disparate functions can play similar roles in brain development.
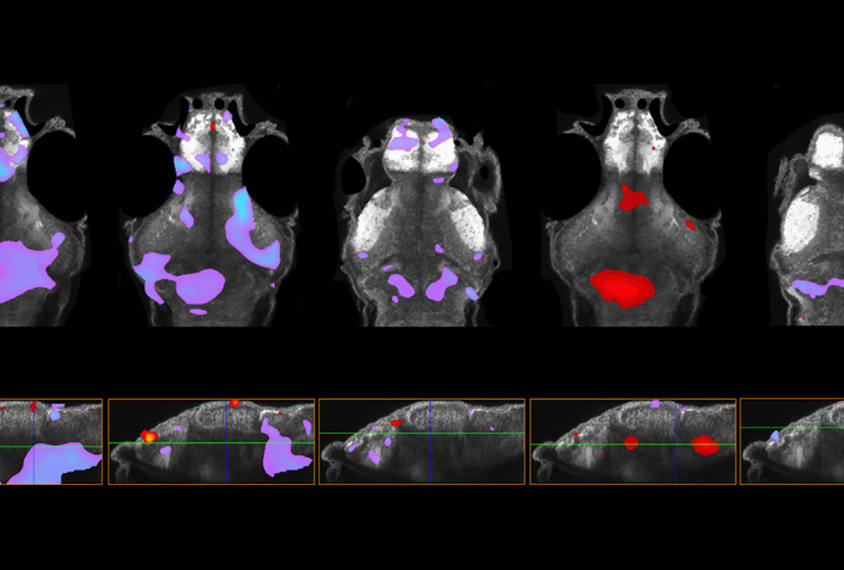
Autism-related genes converge on microglia and dopamine in zebrafish
Explore more from The Transmitter
New connectomes fly beyond the brain
Researchers are mapping the neurons in Drosophila’s ventral nerve cord, where the central nervous system meets the rest of the body.
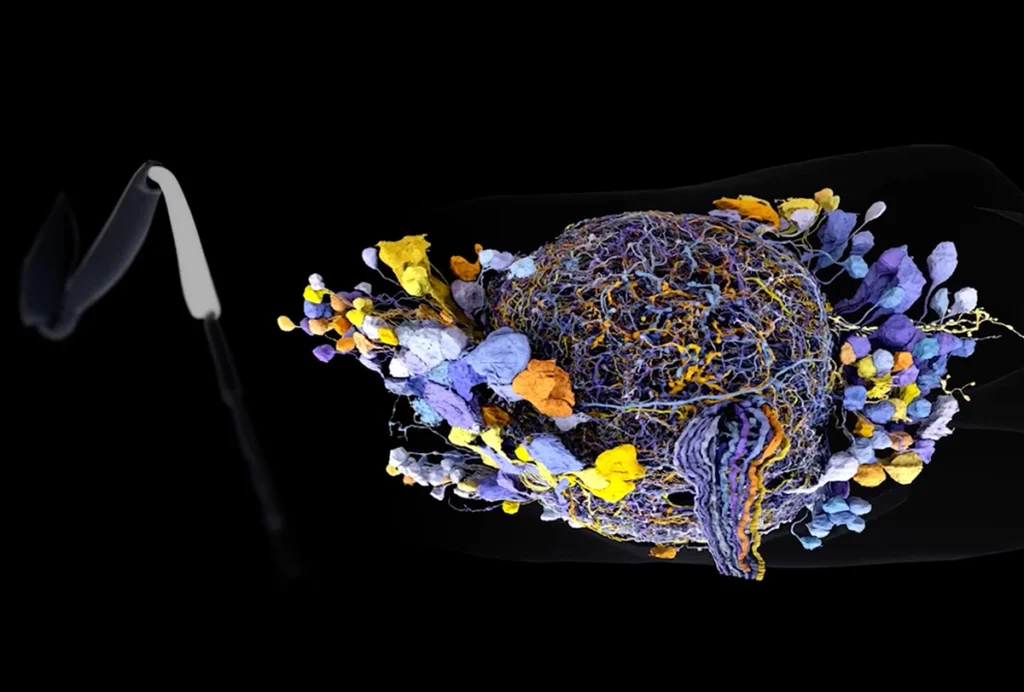
New connectomes fly beyond the brain
Researchers are mapping the neurons in Drosophila’s ventral nerve cord, where the central nervous system meets the rest of the body.
Building an autism research registry: Q&A with Tony Charman
A purpose-built database of participants who have shared genomic and behavioral data could give clinical trials a boost, Charman says.

Building an autism research registry: Q&A with Tony Charman
A purpose-built database of participants who have shared genomic and behavioral data could give clinical trials a boost, Charman says.
Cerebellar circuit may convert expected pain relief into real thing
The newly identified circuit taps into the brain’s opioid system to provide a top-down form of pain relief.
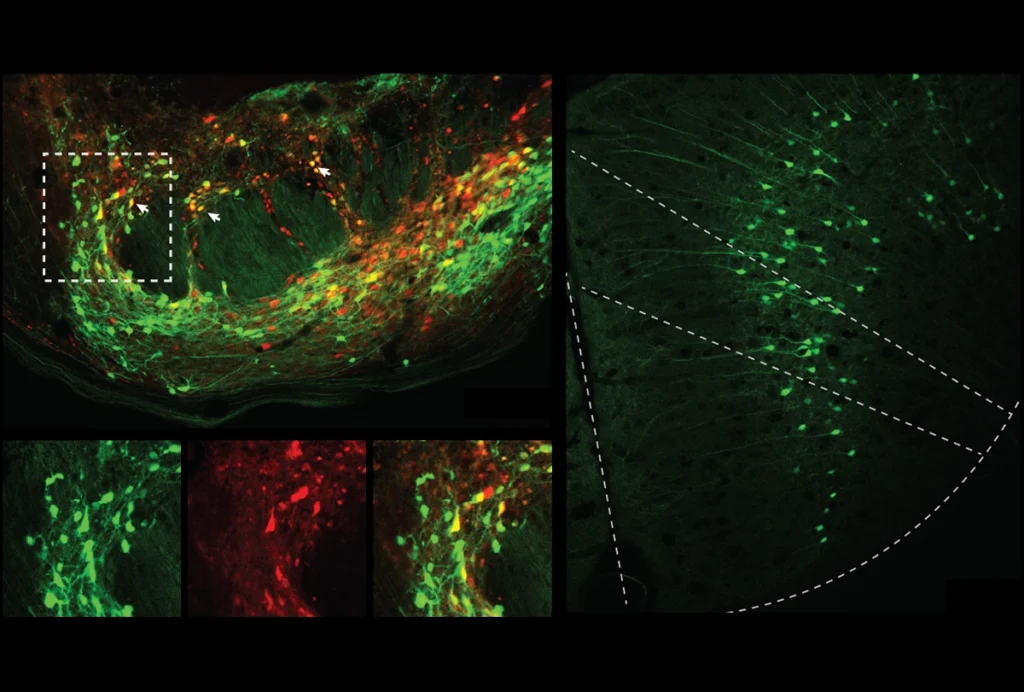
Cerebellar circuit may convert expected pain relief into real thing
The newly identified circuit taps into the brain’s opioid system to provide a top-down form of pain relief.
