Jacob Vorstman is associate professor of psychiatry at the University of Toronto and director of the Autism Research Unit at the Hospital for Sick Children in Canada. Initially, his research focused on the psychiatric and genetic aspects of the 22q11.2 deletion. After obtaining his Ph.D. in 2008, he broadened the scope from 22q11.2 deletion syndrome to the study of genotype-phenotype relations in neurodevelopmental conditions — in particular, autism, intellectual disability and schizophrenia. His ambition is to further insights into the genetic architecture underlying these conditions as well as to improve methods to measure the associated phenotypes.

Jacob Vorstman
Professor
The Hospital for Sick Children
From this contributor
A genetics-first clinic for catching developmental conditions early: Q&A with Jacob Vorstman
A new clinic is assessing children who have a genetic predisposition for autism and other neurodevelopmental conditions—sometimes before traits appear.

A genetics-first clinic for catching developmental conditions early: Q&A with Jacob Vorstman
How polygenic scores can improve predictions about autism, schizophrenia
Jacob Vorstman wants to help people who have rare mutations tied to autism, schizophrenia and other neurodevelopmental conditions set expectations about outcomes.
How polygenic scores can improve predictions about autism, schizophrenia
Explore more from The Transmitter
Karen Adolph explains how we develop our ability to move through the world
How do babies' bodies and their environment teach them to move—and how can robots benefit from these insights?

Karen Adolph explains how we develop our ability to move through the world
How do babies' bodies and their environment teach them to move—and how can robots benefit from these insights?
Microglia’s pruning function called into question
Scientists are divided over the extent to which the cells sculpt circuits during development.
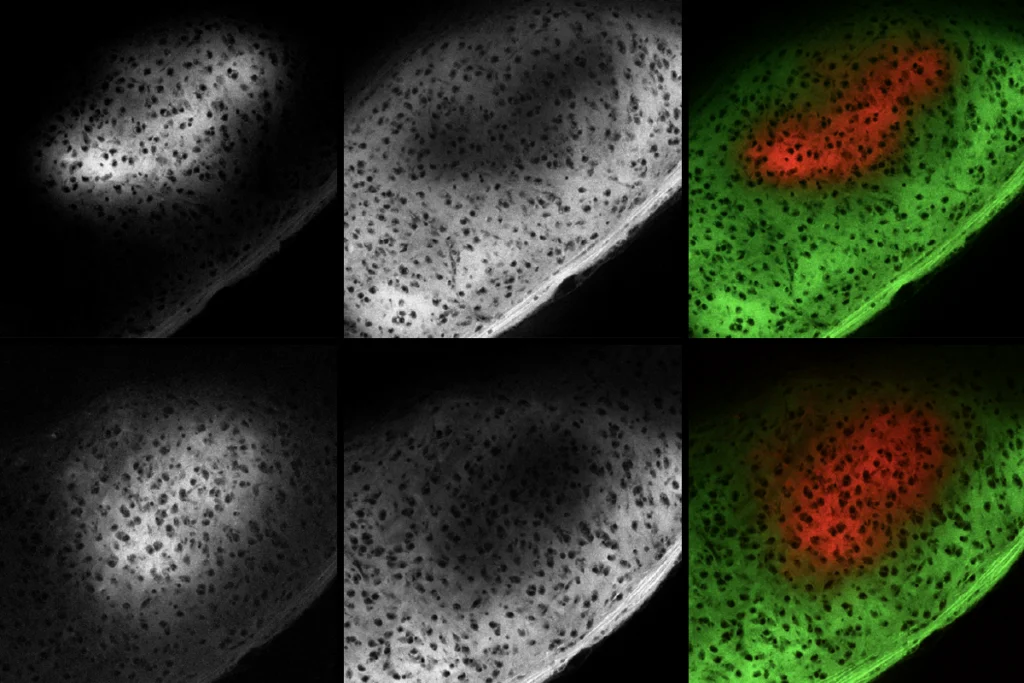
Microglia’s pruning function called into question
Scientists are divided over the extent to which the cells sculpt circuits during development.
Early trajectory of Alzheimer’s tracked in single-cell brain atlases
Inflammation in glia and the loss of certain inhibitory cells may kick off a disease cascade decades before diagnosis.
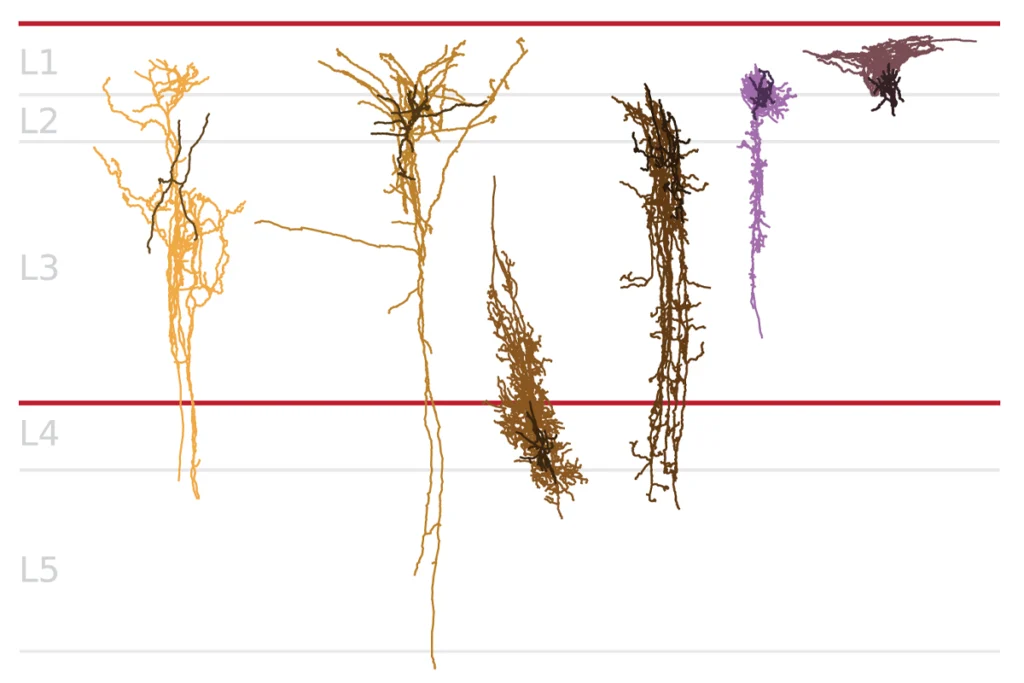

Early trajectory of Alzheimer’s tracked in single-cell brain atlases
Inflammation in glia and the loss of certain inhibitory cells may kick off a disease cascade decades before diagnosis.