Connie Kasari is professor of human development and psychology at the University of California, Los Angeles. She is the principal investigator for several multi-site research programs and a founding member of the university’s Center for Autism Research and Treatment.

Connie Kasari
From this contributor
How much behavioral therapy does an autistic child need?
People tend to believe that, regardless of the treatment, more is always better. But is it?

How much behavioral therapy does an autistic child need?
Learning when to treat repetitive behaviors in autism
Some restricted and repetitive behaviors may have hidden benefits for people with autism, so scientists should work to find a happy medium between acceptance and change.

Learning when to treat repetitive behaviors in autism
School’s in
School-based interventions are arguably the best way to reach the truly underserved, under-represented and under-resourced children with autism, says Connie Kasari.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Karen Adolph explains how we develop our ability to move through the world
How do babies' bodies and their environment teach them to move—and how can robots benefit from these insights?

Karen Adolph explains how we develop our ability to move through the world
How do babies' bodies and their environment teach them to move—and how can robots benefit from these insights?
Microglia’s pruning function called into question
Scientists are divided over the extent to which the cells sculpt circuits during development.
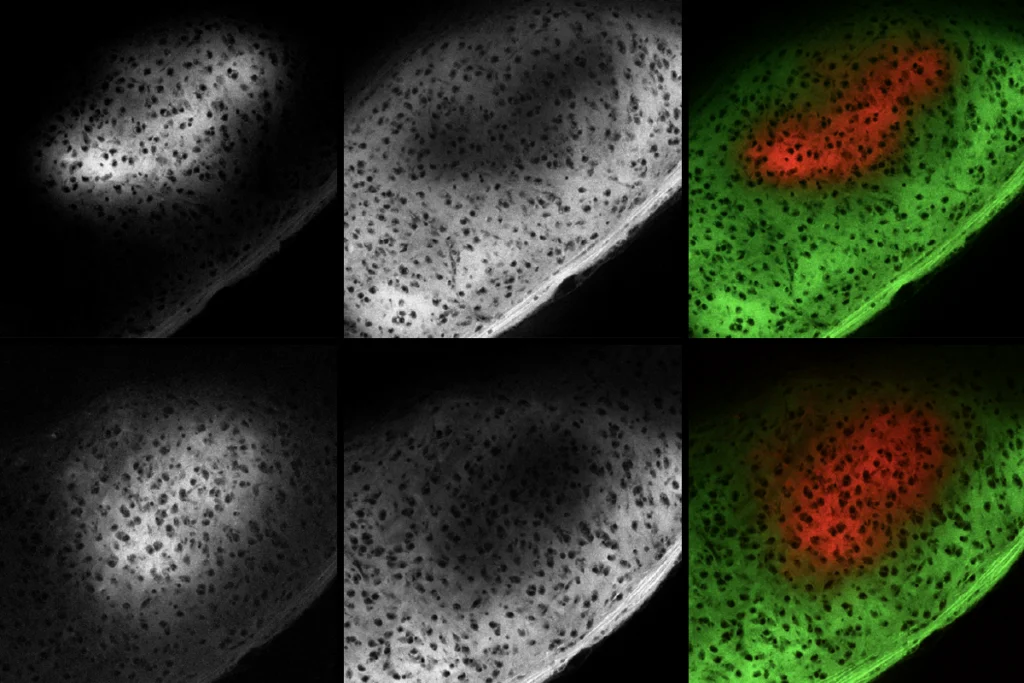
Microglia’s pruning function called into question
Scientists are divided over the extent to which the cells sculpt circuits during development.
Early trajectory of Alzheimer’s tracked in single-cell brain atlases
Inflammation in glia and the loss of certain inhibitory cells may kick off a disease cascade decades before diagnosis.
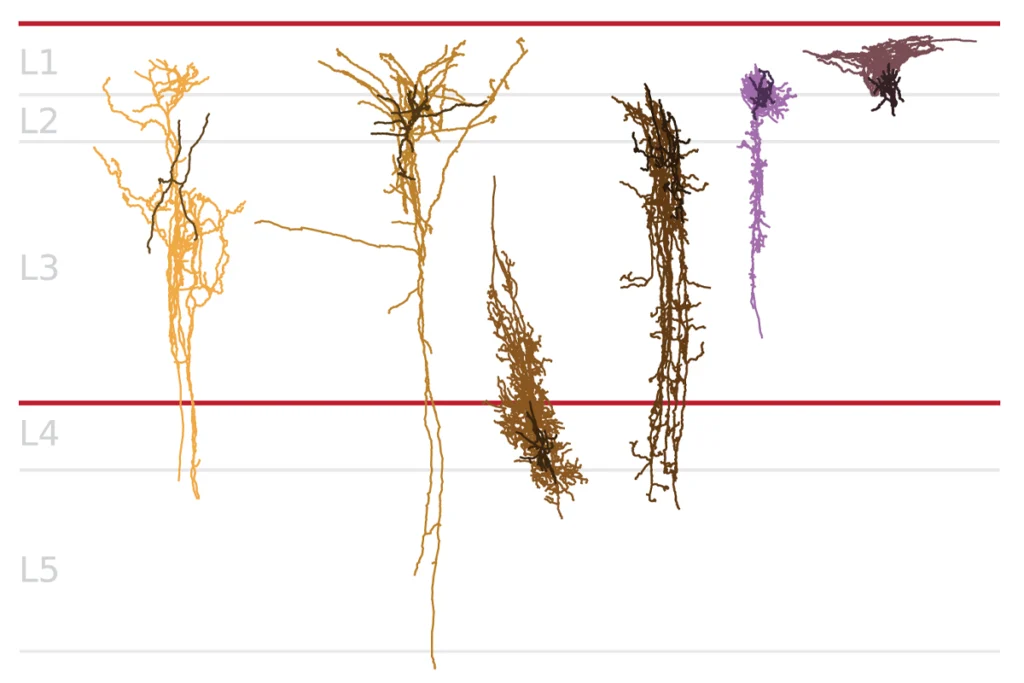

Early trajectory of Alzheimer’s tracked in single-cell brain atlases
Inflammation in glia and the loss of certain inhibitory cells may kick off a disease cascade decades before diagnosis.
