Diana Zuckerman is president of the National Center for Health Research, a nonprofit think tank based in Washington, D.C.

Diana Zuckerman
President
National Center for Health Research
From this contributor
How the new U.S. ‘Right to Try’ law could harm people with autism
People with autism already have access to experimental treatments; the new law could make that access more dangerous.

How the new U.S. ‘Right to Try’ law could harm people with autism
Why the 21st Century Cures Act could be disastrous for medicine
A new bill threatens to lower the scientific standards that have made the Food and Drug Administration's approval the gold standard worldwide.

Why the 21st Century Cures Act could be disastrous for medicine
Explore more from The Transmitter
Shifting neural code powers speech comprehension
Dynamic coding helps explain how the brain processes multiple features of speech—from the smallest units of sounds to full sentences—simultaneously.
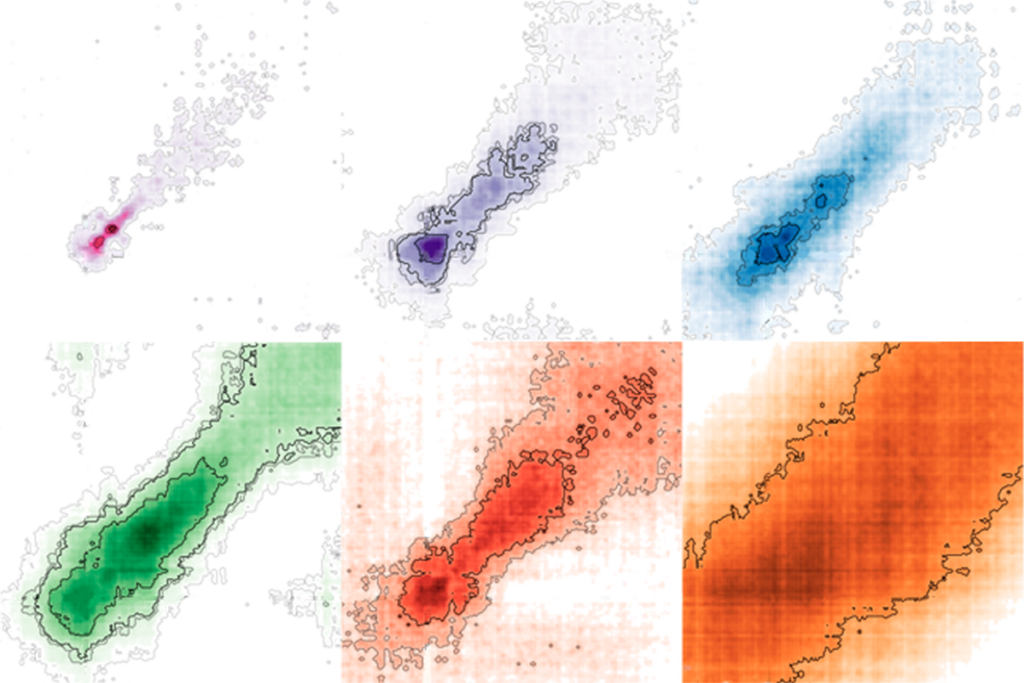
Shifting neural code powers speech comprehension
Dynamic coding helps explain how the brain processes multiple features of speech—from the smallest units of sounds to full sentences—simultaneously.
Astrocytes orchestrate oxytocin’s social effects in mice
The cells amplify oxytocin—and may be responsible for sex differences in social behavior, two preprints find.
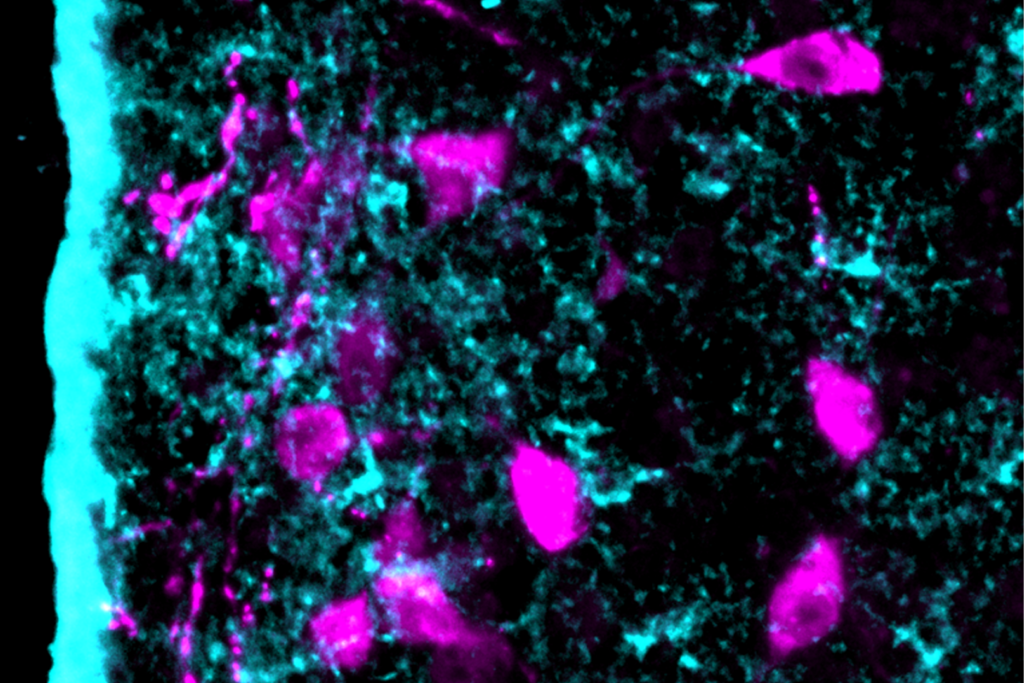
Astrocytes orchestrate oxytocin’s social effects in mice
The cells amplify oxytocin—and may be responsible for sex differences in social behavior, two preprints find.
Neuro’s ark: Spying on the secret sensory world of ticks
Carola Städele, a self-proclaimed “tick magnet,” studies the arachnids’ sensory neurobiology—in other words, how these tiny parasites zero in on their next meal.

Neuro’s ark: Spying on the secret sensory world of ticks
Carola Städele, a self-proclaimed “tick magnet,” studies the arachnids’ sensory neurobiology—in other words, how these tiny parasites zero in on their next meal.