Julie Forman-Kay is program head in molecular medicine at the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto, Canada. She received her B.Sc. in chemistry from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and her Ph.D. in molecular biophysics andd biochemistry from Yale University. The major focus of her lab is to provide biological insights into how dynamic properties of proteins are related to function and methodological tools to enable better understanding of dynamic and disordered states. Most recently, her lab has probed the biophysics of protein phase separation and how it regulates cellular condensates and biological function.

Julie Forman-Kay
Program head
Hospital for Sick Children
From this contributor
How microscopic ‘condensates’ in cells might contribute to autism
A controversial idea about how cells compartmentalize their contents into droplets — like beads of oil in water — could be key to understanding autism, says Julie Forman-Kay.
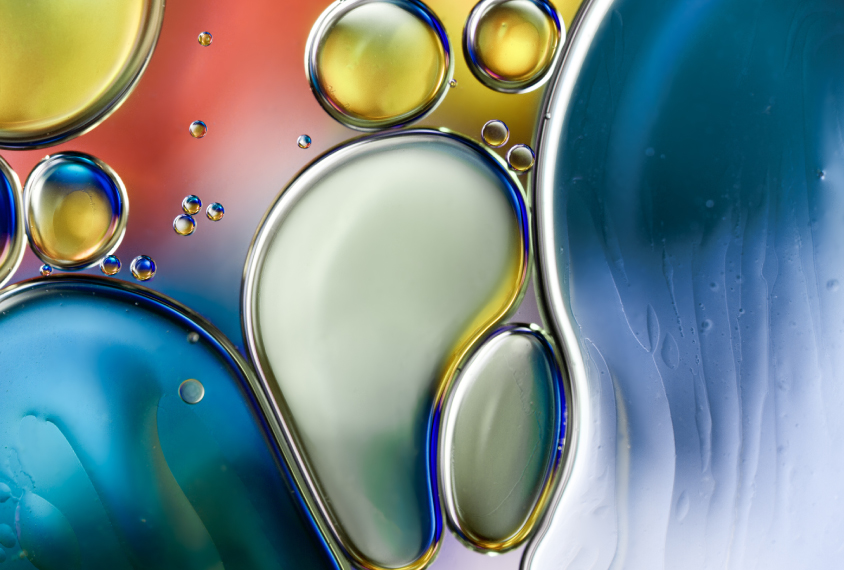
How microscopic ‘condensates’ in cells might contribute to autism
Explore more from The Transmitter
Xiao-Jing Wang outlines the future of theoretical neuroscience
Wang discusses why he decided the time was right for a new theoretical neuroscience textbook and how bifurcation is a key missing concept in neuroscience explanations.
Xiao-Jing Wang outlines the future of theoretical neuroscience
Wang discusses why he decided the time was right for a new theoretical neuroscience textbook and how bifurcation is a key missing concept in neuroscience explanations.
Memory study sparks debate over statistical methods
Critics of a 2024 Nature paper suggest the authors failed to address the risk of false-positive findings. The authors argue more rigorous methods can result in missed leads.
Memory study sparks debate over statistical methods
Critics of a 2024 Nature paper suggest the authors failed to address the risk of false-positive findings. The authors argue more rigorous methods can result in missed leads.
Attention not necessary for visual awareness, large study suggests
People can perceive some visual information even if they do not pay direct attention to it.
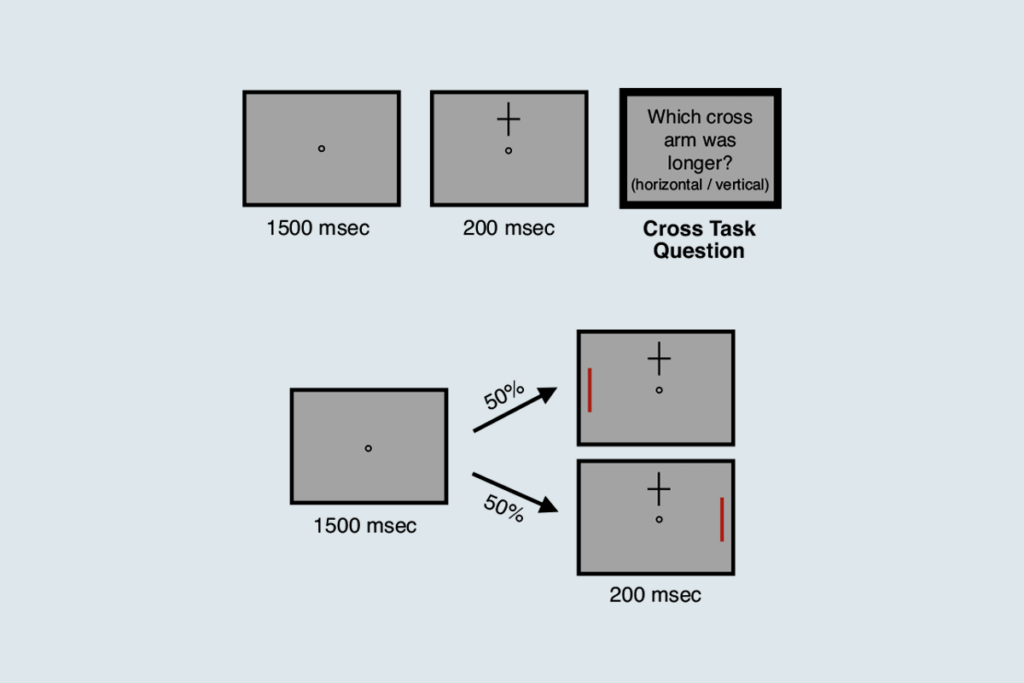
Attention not necessary for visual awareness, large study suggests
People can perceive some visual information even if they do not pay direct attention to it.