Michael E. Goldberg is David Mahoney Professor of Brain and Behavior in the departments of neuroscience, neurology, psychiatry and ophthalmology at Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons, director of the Mahoney-Keck Center for Brain and Behavior Research, and is an active clinical neurologist. His neuroscience research focuses on the physiological basis of cognitive processes such as visual attention, spatial perception and decision-making. He earned his M.D. from Harvard Medical School in 1968. From 1978 to 2001, Goldberg was a senior investigator at the Laboratory of Sensorimotor Research at the National Eye Institute in Bethesda, Maryland. He is a fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences and the American Association for the Advancement of Science, and an elected member of the National Academy of Sciences. He is a past president of the Society for Neuroscience, and now chair of the society’s Committee on Animals in Research.
Michael E. Goldberg
David Mahoney Professor of Brain and Behavior
Columbia University
Explore more from The Transmitter
Xiao-Jing Wang outlines the future of theoretical neuroscience
Wang discusses why he decided the time was right for a new theoretical neuroscience textbook and how bifurcation is a key missing concept in neuroscience explanations.
Xiao-Jing Wang outlines the future of theoretical neuroscience
Wang discusses why he decided the time was right for a new theoretical neuroscience textbook and how bifurcation is a key missing concept in neuroscience explanations.
Memory study sparks debate over statistical methods
Critics of a 2024 Nature paper suggest the authors failed to address the risk of false-positive findings. The authors argue more rigorous methods can result in missed leads.
Memory study sparks debate over statistical methods
Critics of a 2024 Nature paper suggest the authors failed to address the risk of false-positive findings. The authors argue more rigorous methods can result in missed leads.
Attention not necessary for visual awareness, large study suggests
People can perceive some visual information even if they do not pay direct attention to it.
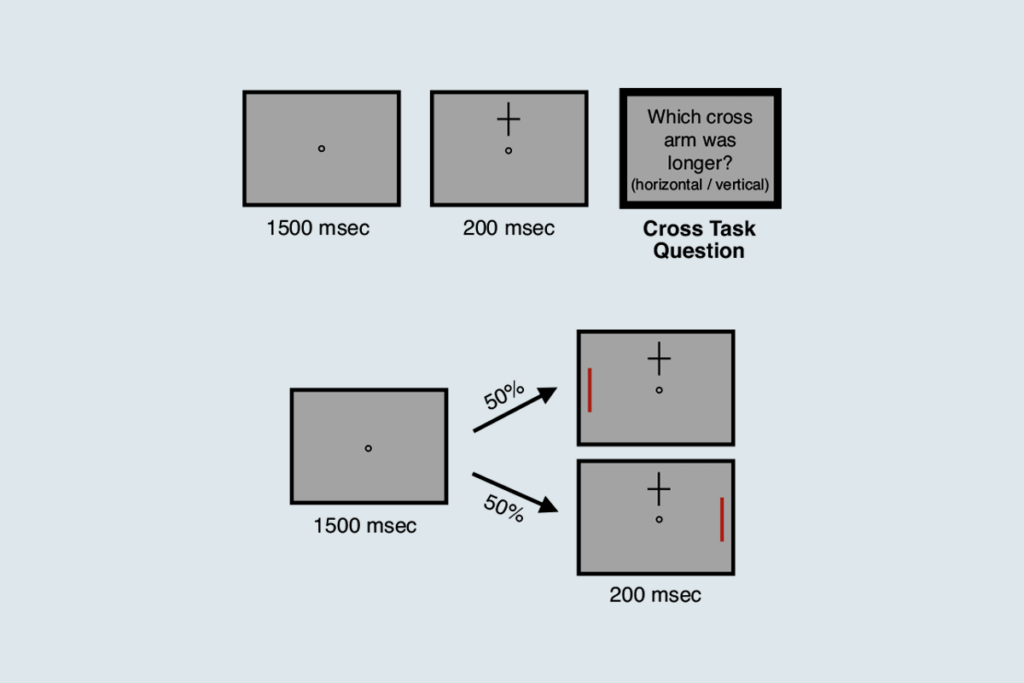
Attention not necessary for visual awareness, large study suggests
People can perceive some visual information even if they do not pay direct attention to it.