Monica Coenraads’ involvement with Rett syndrome began the day her then-2-year-old daughter was diagnosed with the disorder. A year later, in 1999, she co-founded the Rett Syndrome Research Foundation (RSRF) and held the position of scientific director during the eight years of the foundation’s drive to stimulate scientific interest and research in Rett syndrome. This culminated in the groundbreaking work in 2007 that demonstrated the first global reversal of symptoms in preclinical models of the disorder. Coenraads co-founded the Rett Syndrome Research Trust (RSRT) in late 2007 to pursue the next steps from that milestone. Under her leadership at RSRF and RSRT, $36 million has been raised for research. In 2010 she co-founded the Rett Syndrome Research Trust UK, now called Reverse Rett, and currently serves as a trustee.
Monica Coenraads
Executive Director
Rett Syndrome Research Trust
Explore more from The Transmitter
Machine learning spots neural progenitors in adult human brains
But the finding has not settled the long-standing debate over the existence and extent of neurogenesis during adulthood, says Yale University neuroscientist Juan Arellano.
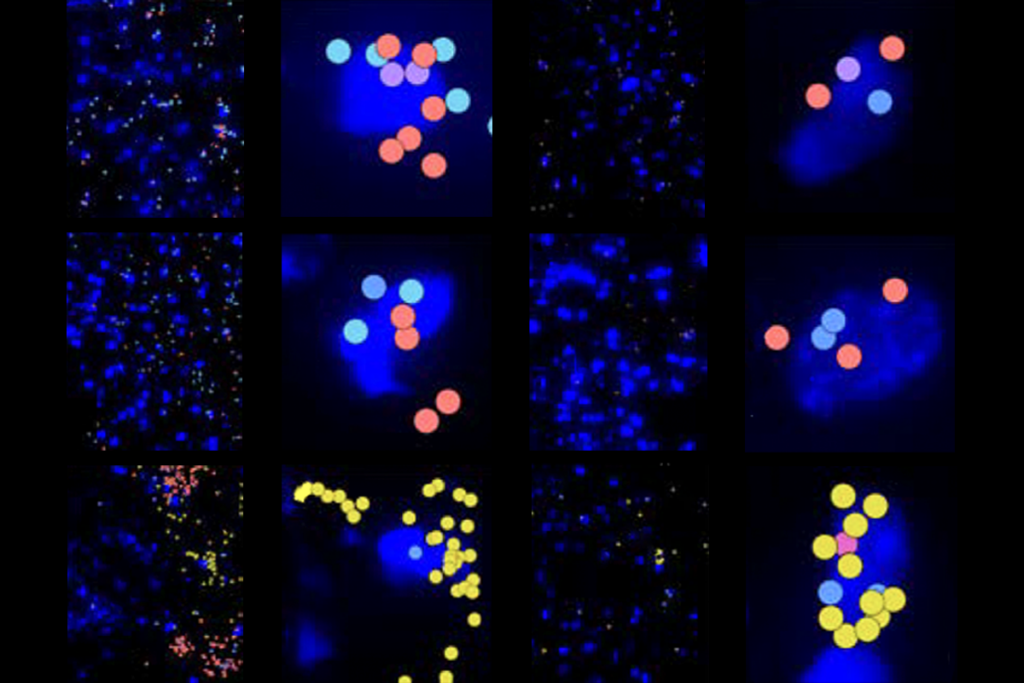
Machine learning spots neural progenitors in adult human brains
But the finding has not settled the long-standing debate over the existence and extent of neurogenesis during adulthood, says Yale University neuroscientist Juan Arellano.
Xiao-Jing Wang outlines the future of theoretical neuroscience
Wang discusses why he decided the time was right for a new theoretical neuroscience textbook and how bifurcation is a key missing concept in neuroscience explanations.
Xiao-Jing Wang outlines the future of theoretical neuroscience
Wang discusses why he decided the time was right for a new theoretical neuroscience textbook and how bifurcation is a key missing concept in neuroscience explanations.
Memory study sparks debate over statistical methods
Critics of a 2024 Nature paper suggest the authors failed to address the risk of false-positive findings. The authors argue more rigorous methods can result in missed leads.
Memory study sparks debate over statistical methods
Critics of a 2024 Nature paper suggest the authors failed to address the risk of false-positive findings. The authors argue more rigorous methods can result in missed leads.