Morton Ann Gernsbacher is Vilas Research Professor and Sir Frederic Bartlett Professor of Psychology at the University of Wisconsin–Madison. She is a specialist in autism and psycholinguistics and has written and edited professional and lay books and over 100 peer-reviewed articles and book chapters on these subjects. She currently serves as co-editor of the journal Psychological Science in the Public Interest and associate editor for Cognitive Psychology, and she has previously held editorial positions for Memory & Cognition and Language and Cognitive Processes. She was also president of the Association for Psychological Science in 2007.
Morton Ann Gernsbacher
Professor
University of Wisconsin - Madison
From this contributor
Book review: “Neurotribes” recovers lost history of autism
Steve Silberman’s new book, “Neurotribes,” recounts his 15-year quest to understand “the legacy of autism.”

Book review: “Neurotribes” recovers lost history of autism
Explore more from The Transmitter
Portfolio of SCN2A gene variants, and more
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 9 March.
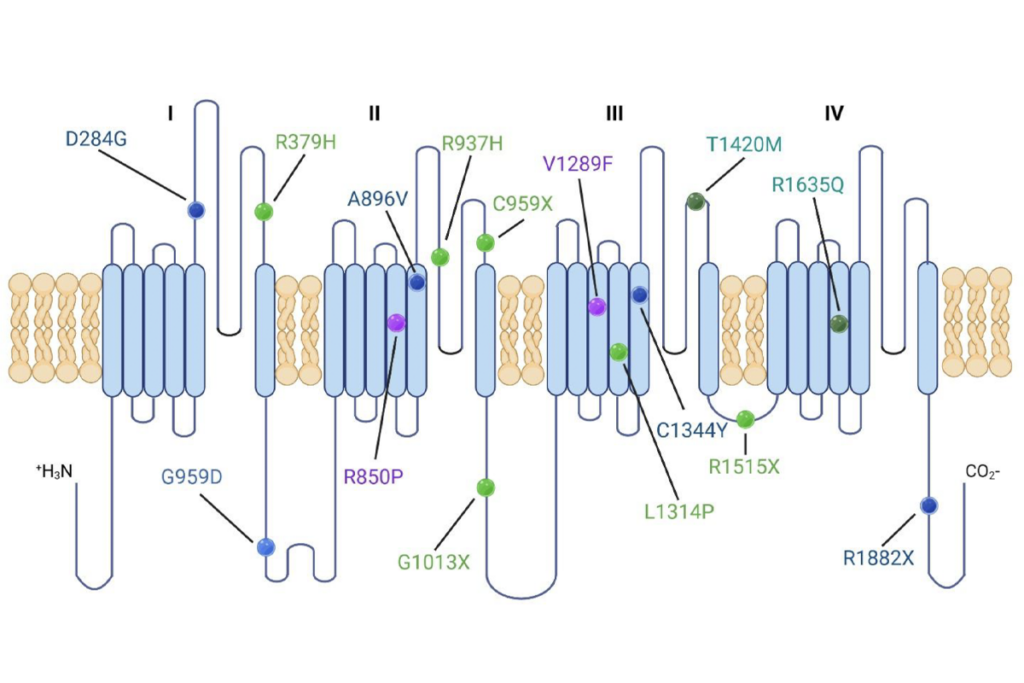
Portfolio of SCN2A gene variants, and more
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 9 March.
Hippocampus builds reputation as ‘general-purpose statistical learning machine’
New cross-species findings may help settle a long-standing debate about whether the hippocampus is required for passive learning.
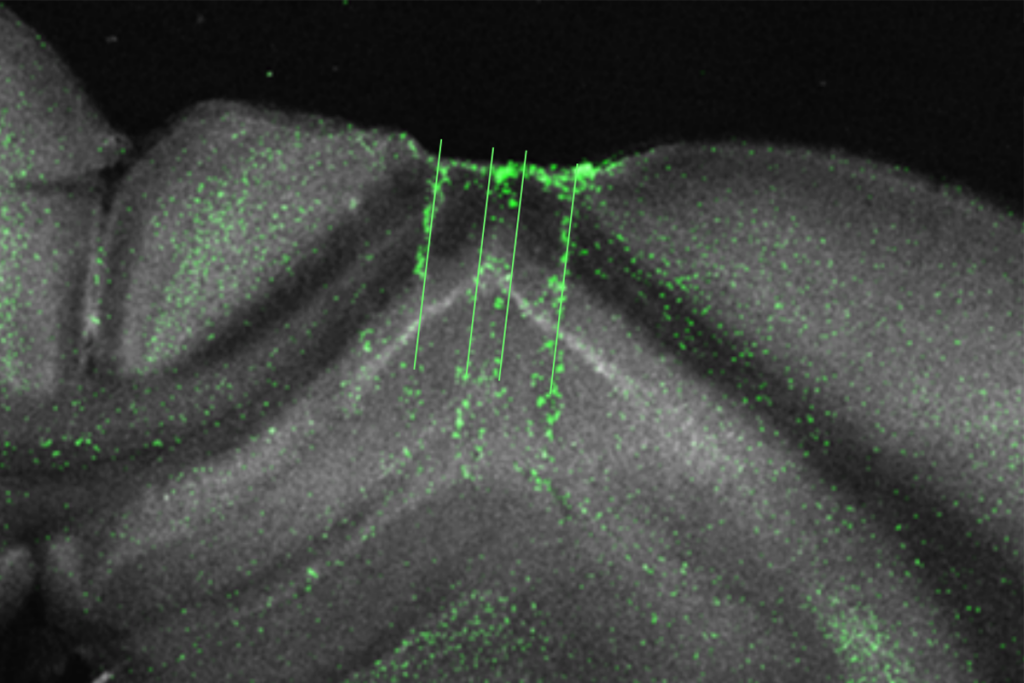
Hippocampus builds reputation as ‘general-purpose statistical learning machine’
New cross-species findings may help settle a long-standing debate about whether the hippocampus is required for passive learning.
‘The Fox, the Shrew, and You: How Brains Evolved,’ an excerpt
In his new book, Rogier Mars provides a detailed account of animal and human brain evolution. In this excerpt from Chapter 1, he starts with the sea squirt—and why it needs the brain it eats after its larval stage.

‘The Fox, the Shrew, and You: How Brains Evolved,’ an excerpt
In his new book, Rogier Mars provides a detailed account of animal and human brain evolution. In this excerpt from Chapter 1, he starts with the sea squirt—and why it needs the brain it eats after its larval stage.