Shweta Karikehalli is an environmental and science journalist based in New York City. Prior to joining _Spectrum_, Shweta was an editorial fellow at _Audubon_ magazine and worked for the _Daily Orange_, Syracuse University’s award-winning independent newspaper, as a copy editor and reporter. She has an M.A. in magazine, newspaper and online journalism from the S.I. Newhouse School of Public Communications and a B.S. in conservation biology from the SUNY College of Environmental Science and Forestry.

Shweta Karikehalli
From this contributor
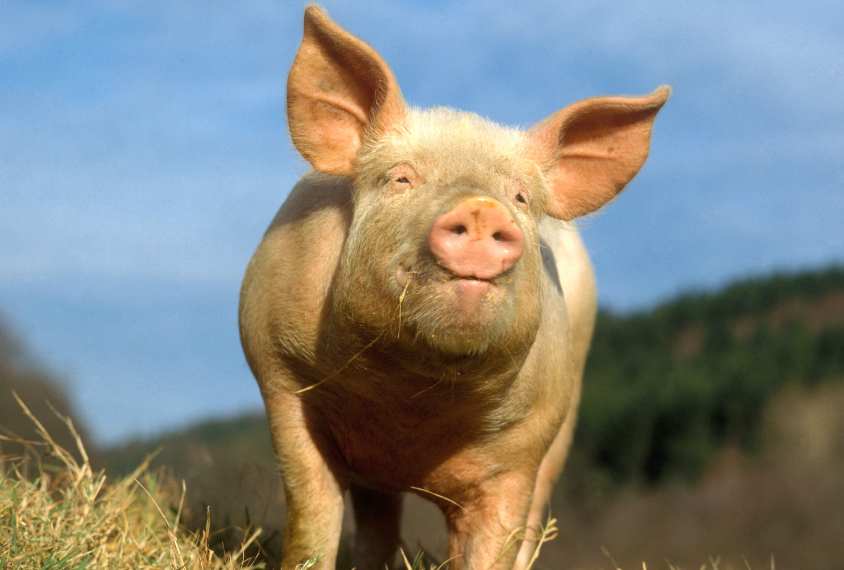
‘Zombie’ pig brains fire hours after death
A new method restores blood flow and some functions in pig brains four hours after the animals have died.
New method creates complex, long-lived brain ‘organoids’
A new method for growing brain organoids allows them to survive for up to a year — more than four times as long as is possible with other methods.
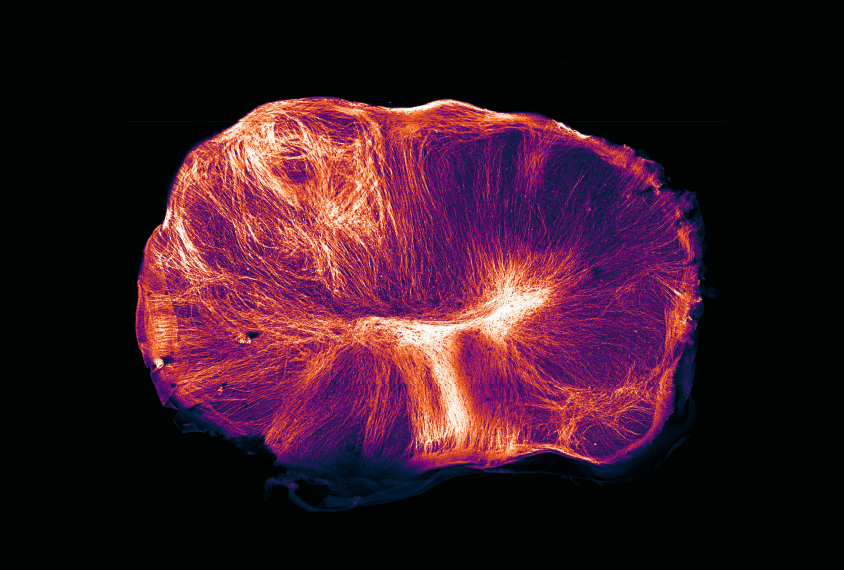
New method creates complex, long-lived brain ‘organoids’
Mighty magnet promises to render human brain in intricate detail
A new magnetic resonance imaging machine has the power to reveal the brain’s structure and activity at unprecedented resolution.
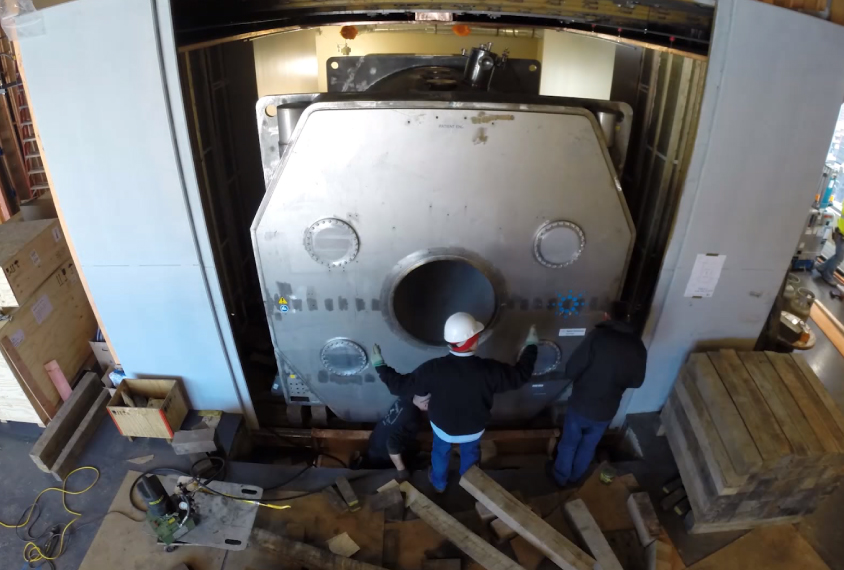

Mighty magnet promises to render human brain in intricate detail
Genome catalog bolsters global microbiome research
The largest-yet attempt to characterize the global diversity of the human microbiome — the population of microbes that live in our bodies — has found 4,930 species, 77 percent of which were previously unknown.
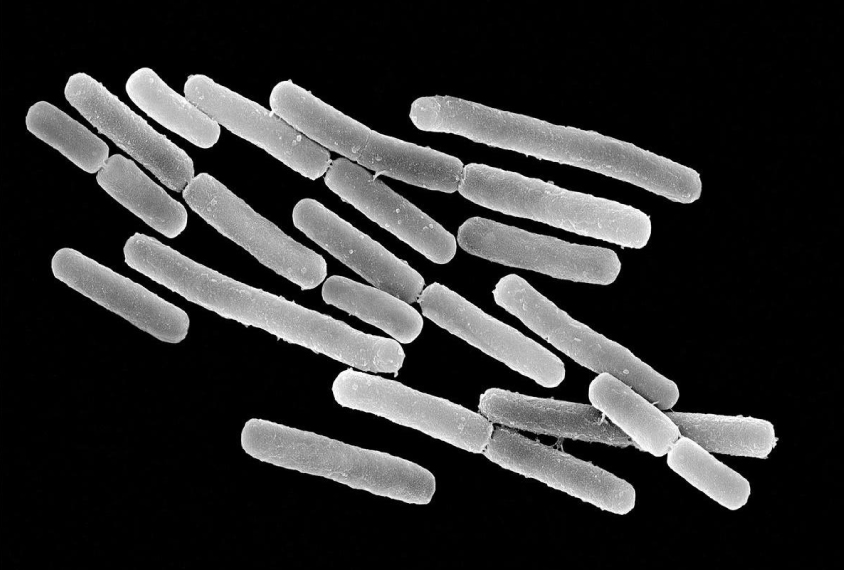
Genome catalog bolsters global microbiome research
Explore more from The Transmitter
Revised statistical bar extracts less-common variants from autism genetics studies
Adjusting genetic analyses could help plug autism’s heritability gap, according to a new preprint.

Revised statistical bar extracts less-common variants from autism genetics studies
Adjusting genetic analyses could help plug autism’s heritability gap, according to a new preprint.
Tom Griffiths describes how neural networks, logic and probability theory together explain cognition
In his new book, “The Laws of Thought,” Griffiths shows how these three pillars of study complement one another and together form a solid foundation to eventually explain all of our cognition, from brain to mind.
Tom Griffiths describes how neural networks, logic and probability theory together explain cognition
In his new book, “The Laws of Thought,” Griffiths shows how these three pillars of study complement one another and together form a solid foundation to eventually explain all of our cognition, from brain to mind.
This paper changed my life: Talia Lerner reflects on dopamine neuron diversity and the value of simple experiments
In a 2011 Neuron study, Stephan Lammel and his colleagues showed that dopamine neurons with different projections have different physiological properties. The work inspired Lerner to think about how to challenge widely held assumptions in the field.

This paper changed my life: Talia Lerner reflects on dopamine neuron diversity and the value of simple experiments
In a 2011 Neuron study, Stephan Lammel and his colleagues showed that dopamine neurons with different projections have different physiological properties. The work inspired Lerner to think about how to challenge widely held assumptions in the field.
