Tara Santora is a former intern at Spectrum and a freelance journalist based in New York City. Tara has written about health and the environment for publications such as Psychology Today and Audubon magazine. They are also a graduate student at New York University’s Science, Health & Environmental Reporting Program.

Tara Santora
From this contributor
U.S. authorizes rapid blood test for fragile X syndrome
A new blood test can identify within seven hours whether a person carries the genetic mutation underlying fragile X syndrome.
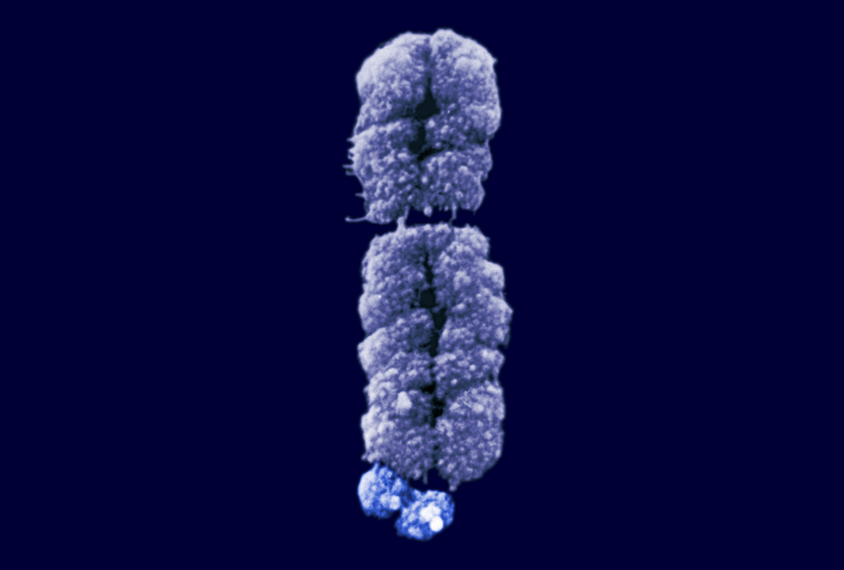
U.S. authorizes rapid blood test for fragile X syndrome
New analysis of brain activity could identify signal for autism
A new technique allows researchers to analyze raw data across multiple studies that use electroencephalography.
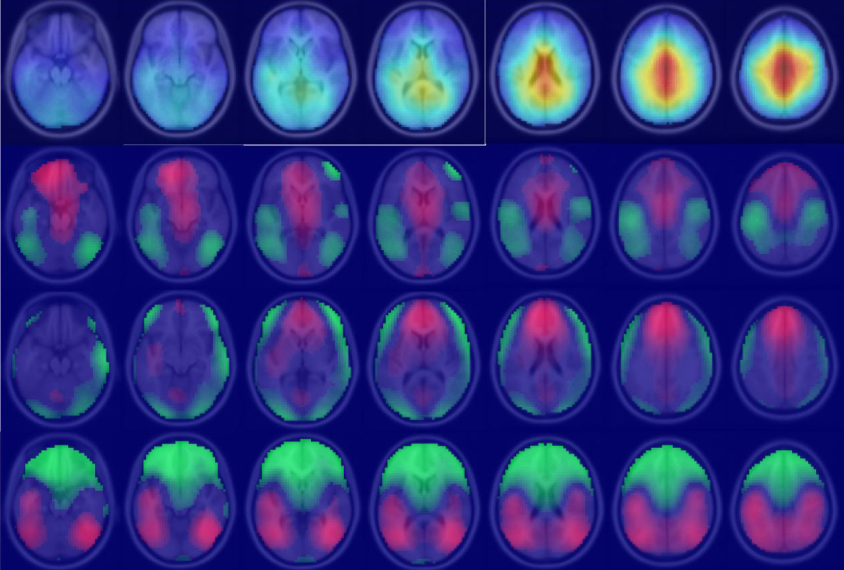
New analysis of brain activity could identify signal for autism
Machine learning flags ‘mosaic’ mutations that may contribute to autism
A new technique detects rare mutations that occur in only a subset of the body's cells.

Machine learning flags ‘mosaic’ mutations that may contribute to autism
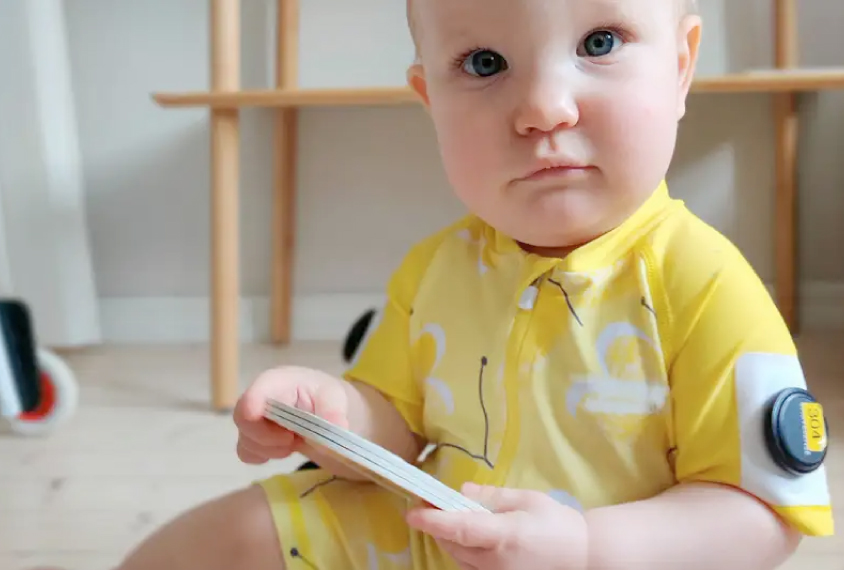
Smart jumpsuit may help test motor skills in infants with autism
A new jumpsuit is fitted with sensors that can track and classify an infant's posture and movements.

Smart jumpsuit may help test motor skills in infants with autism
Artificial neurons may repair damaged cells and circuits
Electronic neurons made from silicon mimic brain cells and could be used to treat conditions such as autism.
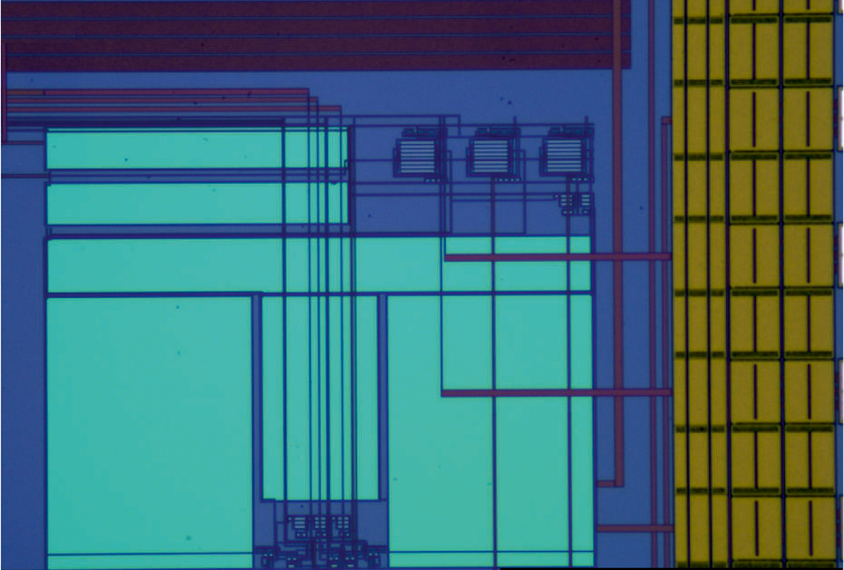
Artificial neurons may repair damaged cells and circuits
Explore more from The Transmitter
Revised statistical bar extracts less-common variants from autism genetics studies
Adjusting genetic analyses could help plug autism’s heritability gap, according to a new preprint.

Revised statistical bar extracts less-common variants from autism genetics studies
Adjusting genetic analyses could help plug autism’s heritability gap, according to a new preprint.
Tom Griffiths describes how neural networks, logic and probability theory together explain cognition
In his new book, “The Laws of Thought,” Griffiths shows how these three pillars of study complement one another and together form a solid foundation to eventually explain all of our cognition, from brain to mind.
Tom Griffiths describes how neural networks, logic and probability theory together explain cognition
In his new book, “The Laws of Thought,” Griffiths shows how these three pillars of study complement one another and together form a solid foundation to eventually explain all of our cognition, from brain to mind.
This paper changed my life: Talia Lerner reflects on dopamine neuron diversity and the value of simple experiments
In a 2011 Neuron study, Stephan Lammel and his colleagues showed that dopamine neurons with different projections have different physiological properties. The work inspired Lerner to think about how to challenge widely held assumptions in the field.

This paper changed my life: Talia Lerner reflects on dopamine neuron diversity and the value of simple experiments
In a 2011 Neuron study, Stephan Lammel and his colleagues showed that dopamine neurons with different projections have different physiological properties. The work inspired Lerner to think about how to challenge widely held assumptions in the field.