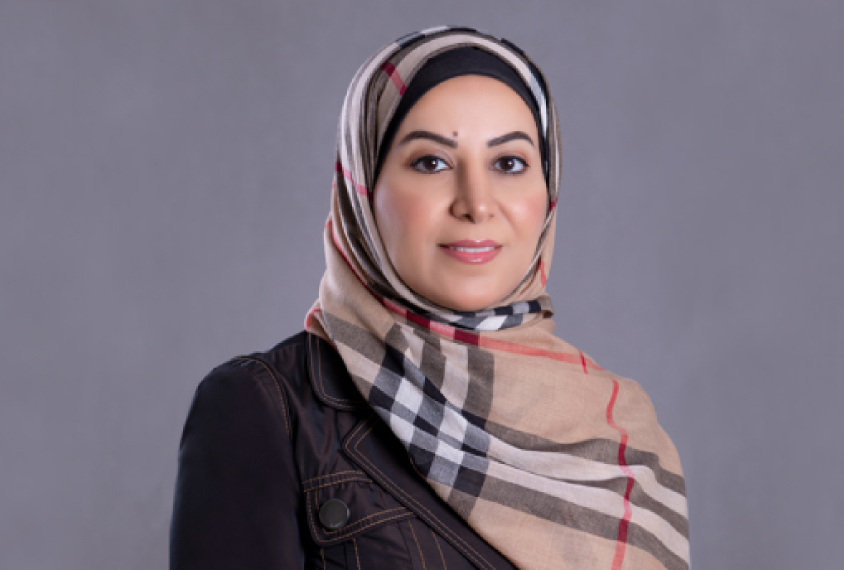
Watfa Al-Mamari is a developmental pediatrician who established the first developmental pediatric clinics in Oman in 2011. She has worked closely with academic institutions to ensure that developmental pediatrics is included in the curriculum for both undergraduate and postgraduate students. She has a special interest in autism and led the team to establish a national program in Oman to screen children for autism at 18 months of age.
Al-Mamari graduated from Sultan Qaboos University in Muscat, Oman, and later did her residency and fellowship at McGill University in Montreal, Canada.

Watfa Al-Mamari
Developmental pediatrician
Sultan Qaboos University
From this contributor
How one doctor made Oman a leader on autism in the Middle East
Developmental pediatrician Watfa Al-Mamari is building an autism program in Oman from the ground up.

How one doctor made Oman a leader on autism in the Middle East
Explore more from The Transmitter
Machine learning spots neural progenitors in adult human brains
But the finding has not settled the long-standing debate over the existence and extent of neurogenesis during adulthood, says Yale University neuroscientist Juan Arellano.
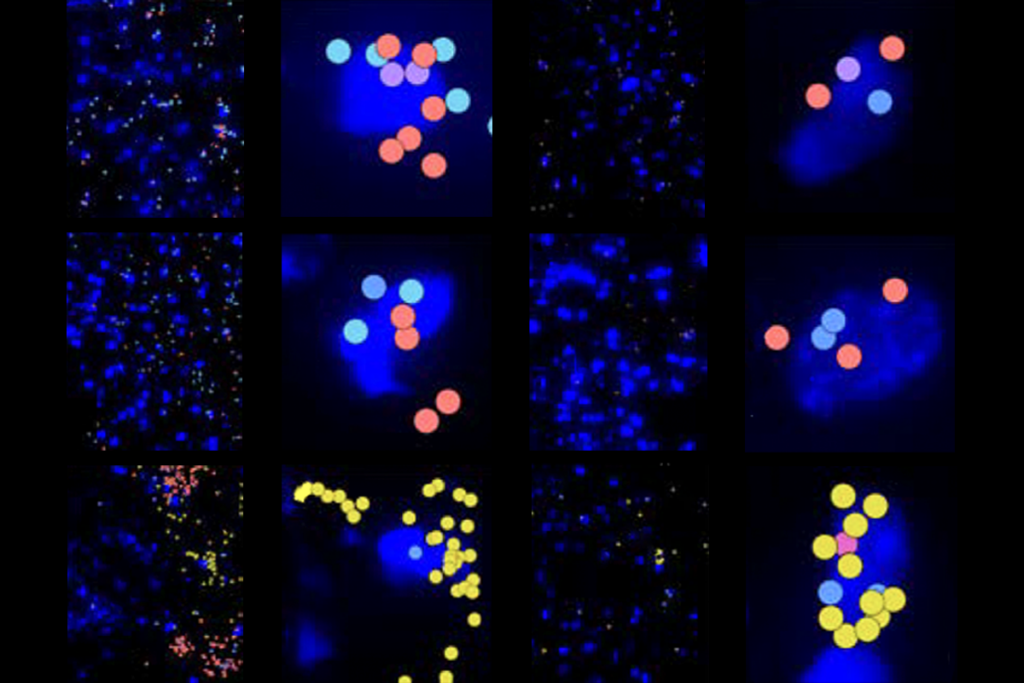
Machine learning spots neural progenitors in adult human brains
But the finding has not settled the long-standing debate over the existence and extent of neurogenesis during adulthood, says Yale University neuroscientist Juan Arellano.
Xiao-Jing Wang outlines the future of theoretical neuroscience
Wang discusses why he decided the time was right for a new theoretical neuroscience textbook and how bifurcation is a key missing concept in neuroscience explanations.
Xiao-Jing Wang outlines the future of theoretical neuroscience
Wang discusses why he decided the time was right for a new theoretical neuroscience textbook and how bifurcation is a key missing concept in neuroscience explanations.
Memory study sparks debate over statistical methods
Critics of a 2024 Nature paper suggest the authors failed to address the risk of false-positive findings. The authors argue more rigorous methods can result in missed leads.
Memory study sparks debate over statistical methods
Critics of a 2024 Nature paper suggest the authors failed to address the risk of false-positive findings. The authors argue more rigorous methods can result in missed leads.