Nico Dosenbach is associate professor of neurology at Washington University School of Medicine. His research as a systems neuroscientist is focused on pushing resting-state functional connectivity MRI (RSFC), functional MRI (fMRI) and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) to the level of individual patients. To create and annotate the connectomes of individuals he is working to improve the signal-to-noise, spatial resolution and replicability of RSFC, DTI and fMRI data.

Nico Dosenbach
Associate professor of neurology
Washington University School of Medicine
From this contributor
Breaking down the winner’s curse: Lessons from brain-wide association studies
We found an issue with a specific type of brain imaging study and tried to share it with the field. Then the backlash began.
Breaking down the winner’s curse: Lessons from brain-wide association studies
Explore more from The Transmitter
Xiao-Jing Wang outlines the future of theoretical neuroscience
Wang discusses why he decided the time was right for a new theoretical neuroscience textbook and how bifurcation is a key missing concept in neuroscience explanations.
Xiao-Jing Wang outlines the future of theoretical neuroscience
Wang discusses why he decided the time was right for a new theoretical neuroscience textbook and how bifurcation is a key missing concept in neuroscience explanations.
Memory study sparks debate over statistical methods
Critics of a 2024 Nature paper suggest the authors failed to address the risk of false-positive findings. The authors argue more rigorous methods can result in missed leads.
Memory study sparks debate over statistical methods
Critics of a 2024 Nature paper suggest the authors failed to address the risk of false-positive findings. The authors argue more rigorous methods can result in missed leads.
Attention not necessary for visual awareness, large study suggests
People can perceive some visual information even if they do not pay direct attention to it.
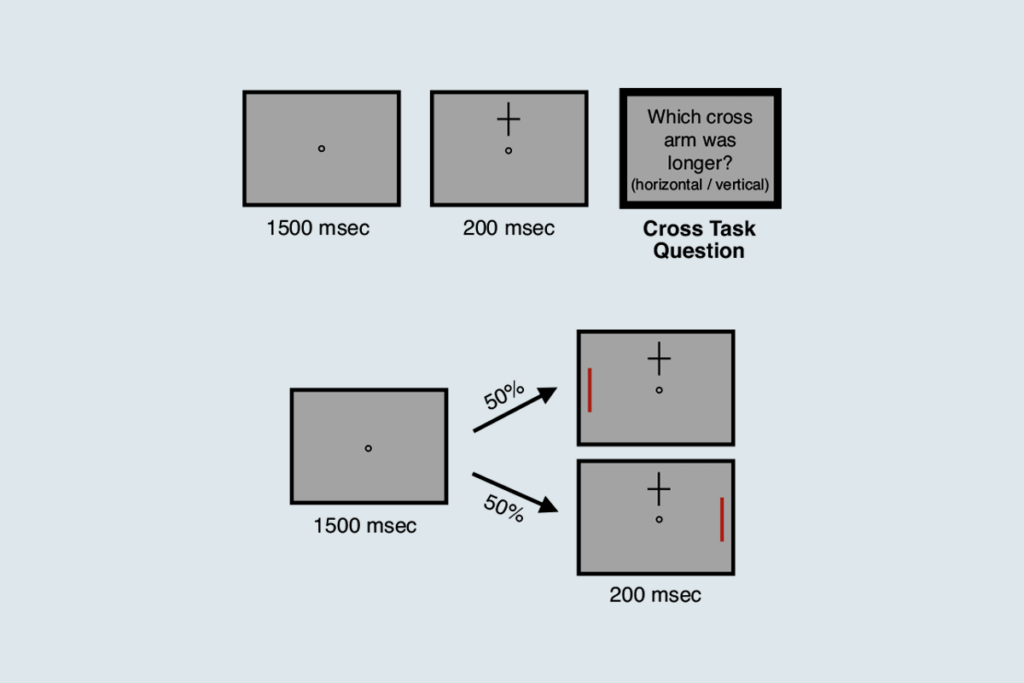
Attention not necessary for visual awareness, large study suggests
People can perceive some visual information even if they do not pay direct attention to it.