Tony Charman
Chair of clinical child psychology
King's College London
From this contributor
Building an autism research registry: Q&A with Tony Charman
A purpose-built database of participants who have shared genomic and behavioral data could give clinical trials a boost, Charman says.

Building an autism research registry: Q&A with Tony Charman
Your questions about the Lancet Commission and ‘profound autism,’ answered
Tony Charman and Catherine Lord answer questions from Spectrum’s webinar on the Lancet Commission’s recommendations for autism research.

Your questions about the Lancet Commission and ‘profound autism,’ answered
Separate thinking skills underlie autism, attention deficit
Theory of mind difficulties are likely to be more central to autism than to attention deficit hyperactive disorder, whereas executive function problems are more often associated with the latter.

Separate thinking skills underlie autism, attention deficit
Tony Charman: Longitudinal studies for autism research
Clinicians and autism researchers should learn the early signs of autism and take into account an individual’s developmental trajectory, says Tony Charman.

Tony Charman: Longitudinal studies for autism research
Explore more from The Transmitter
Xiao-Jing Wang outlines the future of theoretical neuroscience
Wang discusses why he decided the time was right for a new theoretical neuroscience textbook and how bifurcation is a key missing concept in neuroscience explanations.
Xiao-Jing Wang outlines the future of theoretical neuroscience
Wang discusses why he decided the time was right for a new theoretical neuroscience textbook and how bifurcation is a key missing concept in neuroscience explanations.
Memory study sparks debate over statistical methods
Critics of a 2024 Nature paper suggest the authors failed to address the risk of false-positive findings. The authors argue more rigorous methods can result in missed leads.
Memory study sparks debate over statistical methods
Critics of a 2024 Nature paper suggest the authors failed to address the risk of false-positive findings. The authors argue more rigorous methods can result in missed leads.
Attention not necessary for visual awareness, large study suggests
People can perceive some visual information even if they do not pay direct attention to it.
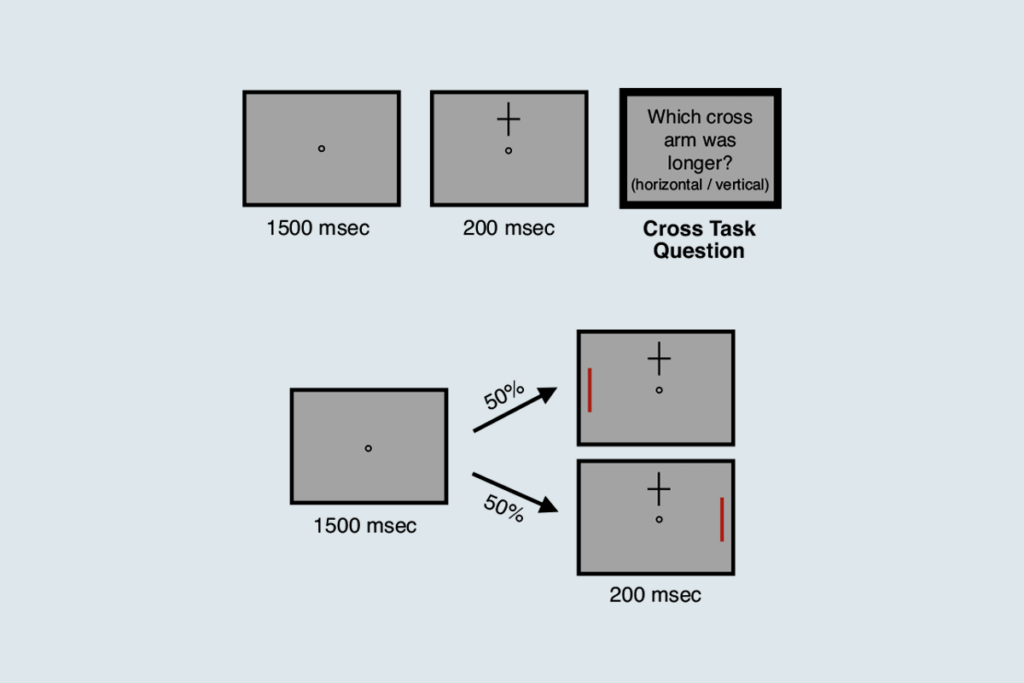
Attention not necessary for visual awareness, large study suggests
People can perceive some visual information even if they do not pay direct attention to it.