SALK 2013
Recent articles
Network of protein variants suggests new autism genes
Researchers have created a network of various forms of many proteins linked to autism, revealing new molecular interactions that may play a role in the disorder. The unpublished work was presented in a poster last week at the Salk Institute, Fondation IPSEN and Nature Symposium on Biological Complexity in La Jolla, California.

Network of protein variants suggests new autism genes
Researchers have created a network of various forms of many proteins linked to autism, revealing new molecular interactions that may play a role in the disorder. The unpublished work was presented in a poster last week at the Salk Institute, Fondation IPSEN and Nature Symposium on Biological Complexity in La Jolla, California.
Fragile X mice show brain-wave abnormalities during sleep
Neurons in mice that model fragile X syndrome show immature, overexcitable firing patterns, particularly during sleep, according to unpublished research presented last week at the Salk Institute, Fondation IPSEN and Nature Symposium on Biological Complexity in La Jolla, California.

Fragile X mice show brain-wave abnormalities during sleep
Neurons in mice that model fragile X syndrome show immature, overexcitable firing patterns, particularly during sleep, according to unpublished research presented last week at the Salk Institute, Fondation IPSEN and Nature Symposium on Biological Complexity in La Jolla, California.
Eye movement, motor difficulties linked in autism
Problems with eye movements in people with autism are part of their motor difficulties and may contribute to the social deficits characteristic of the disorder, according to unpublished research presented last week at the Salk Institute, Fondation IPSEN and Nature Symposium on Biological Complexity in La Jolla, California.

Eye movement, motor difficulties linked in autism
Problems with eye movements in people with autism are part of their motor difficulties and may contribute to the social deficits characteristic of the disorder, according to unpublished research presented last week at the Salk Institute, Fondation IPSEN and Nature Symposium on Biological Complexity in La Jolla, California.
Autism-linked protein differs in male and female brains
The autism-linked protein MET is expressed at lower levels in the brains of men with autism than in control brains, according to unpublished research presented Thursday at the Salk Institute, Fondation IPSEN and Nature Symposium on Biological Complexity in La Jolla, California. Women with autism do not differ from healthy controls, however.

Autism-linked protein differs in male and female brains
The autism-linked protein MET is expressed at lower levels in the brains of men with autism than in control brains, according to unpublished research presented Thursday at the Salk Institute, Fondation IPSEN and Nature Symposium on Biological Complexity in La Jolla, California. Women with autism do not differ from healthy controls, however.
Alzheimer’s drug aids autism mouse model
Memantine, a drug used to treat Alzheimer’s disease, can reverse autism-like features in mice lacking one copy of the MEF2C gene, according to a poster presented last week at the Salk Institute, Fondation IPSEN and Nature Symposium on Biological Complexity in La Jolla, California.

Alzheimer’s drug aids autism mouse model
Memantine, a drug used to treat Alzheimer’s disease, can reverse autism-like features in mice lacking one copy of the MEF2C gene, according to a poster presented last week at the Salk Institute, Fondation IPSEN and Nature Symposium on Biological Complexity in La Jolla, California.
Childhood-onset schizophrenia, autism share genetic links
Individuals who have childhood-onset schizophrenia carry more DNA deletions and duplications associated with other disorders, such as autism, than their unaffected siblings do. The unpublished research was presented 16 January at the Salk Institute, Fondation IPSEN and Nature Symposium on Biological Complexity in La Jolla, California.

Childhood-onset schizophrenia, autism share genetic links
Individuals who have childhood-onset schizophrenia carry more DNA deletions and duplications associated with other disorders, such as autism, than their unaffected siblings do. The unpublished research was presented 16 January at the Salk Institute, Fondation IPSEN and Nature Symposium on Biological Complexity in La Jolla, California.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Machine learning spots neural progenitors in adult human brains
But the finding has not settled the long-standing debate over the existence and extent of neurogenesis during adulthood, says Yale University neuroscientist Juan Arellano.
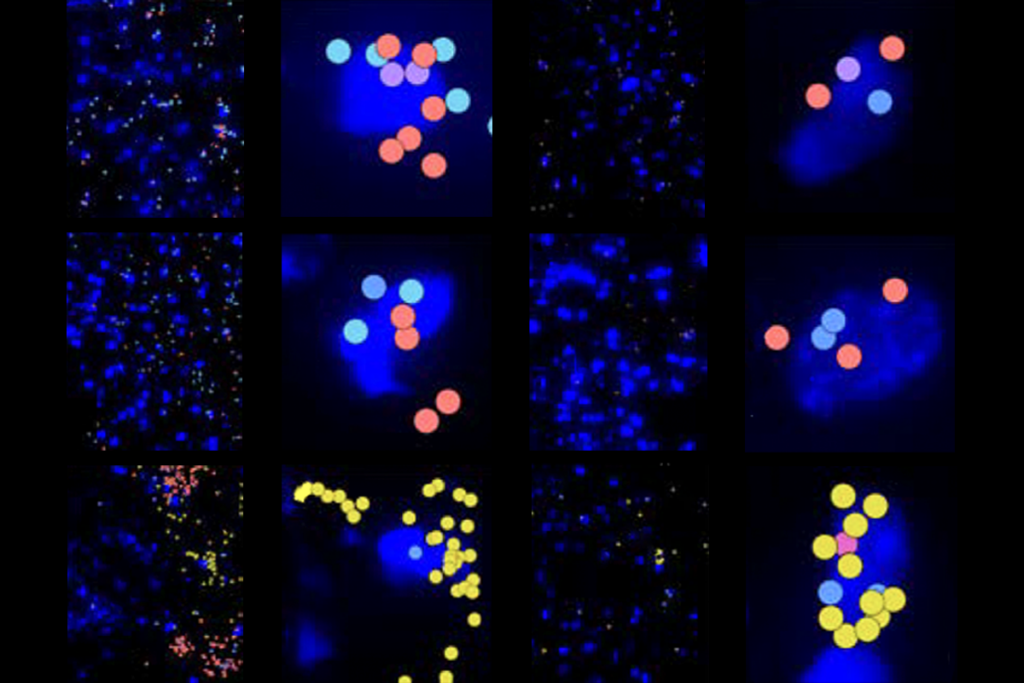
Machine learning spots neural progenitors in adult human brains
But the finding has not settled the long-standing debate over the existence and extent of neurogenesis during adulthood, says Yale University neuroscientist Juan Arellano.
Xiao-Jing Wang outlines the future of theoretical neuroscience
Wang discusses why he decided the time was right for a new theoretical neuroscience textbook and how bifurcation is a key missing concept in neuroscience explanations.
Xiao-Jing Wang outlines the future of theoretical neuroscience
Wang discusses why he decided the time was right for a new theoretical neuroscience textbook and how bifurcation is a key missing concept in neuroscience explanations.
Memory study sparks debate over statistical methods
Critics of a 2024 Nature paper suggest the authors failed to address the risk of false-positive findings. The authors argue more rigorous methods can result in missed leads.
Memory study sparks debate over statistical methods
Critics of a 2024 Nature paper suggest the authors failed to address the risk of false-positive findings. The authors argue more rigorous methods can result in missed leads.