SALK 2013
Recent articles
Network of protein variants suggests new autism genes
Researchers have created a network of various forms of many proteins linked to autism, revealing new molecular interactions that may play a role in the disorder. The unpublished work was presented in a poster last week at the Salk Institute, Fondation IPSEN and Nature Symposium on Biological Complexity in La Jolla, California.

Network of protein variants suggests new autism genes
Researchers have created a network of various forms of many proteins linked to autism, revealing new molecular interactions that may play a role in the disorder. The unpublished work was presented in a poster last week at the Salk Institute, Fondation IPSEN and Nature Symposium on Biological Complexity in La Jolla, California.
Fragile X mice show brain-wave abnormalities during sleep
Neurons in mice that model fragile X syndrome show immature, overexcitable firing patterns, particularly during sleep, according to unpublished research presented last week at the Salk Institute, Fondation IPSEN and Nature Symposium on Biological Complexity in La Jolla, California.

Fragile X mice show brain-wave abnormalities during sleep
Neurons in mice that model fragile X syndrome show immature, overexcitable firing patterns, particularly during sleep, according to unpublished research presented last week at the Salk Institute, Fondation IPSEN and Nature Symposium on Biological Complexity in La Jolla, California.
Eye movement, motor difficulties linked in autism
Problems with eye movements in people with autism are part of their motor difficulties and may contribute to the social deficits characteristic of the disorder, according to unpublished research presented last week at the Salk Institute, Fondation IPSEN and Nature Symposium on Biological Complexity in La Jolla, California.

Eye movement, motor difficulties linked in autism
Problems with eye movements in people with autism are part of their motor difficulties and may contribute to the social deficits characteristic of the disorder, according to unpublished research presented last week at the Salk Institute, Fondation IPSEN and Nature Symposium on Biological Complexity in La Jolla, California.
Autism-linked protein differs in male and female brains
The autism-linked protein MET is expressed at lower levels in the brains of men with autism than in control brains, according to unpublished research presented Thursday at the Salk Institute, Fondation IPSEN and Nature Symposium on Biological Complexity in La Jolla, California. Women with autism do not differ from healthy controls, however.

Autism-linked protein differs in male and female brains
The autism-linked protein MET is expressed at lower levels in the brains of men with autism than in control brains, according to unpublished research presented Thursday at the Salk Institute, Fondation IPSEN and Nature Symposium on Biological Complexity in La Jolla, California. Women with autism do not differ from healthy controls, however.
Alzheimer’s drug aids autism mouse model
Memantine, a drug used to treat Alzheimer’s disease, can reverse autism-like features in mice lacking one copy of the MEF2C gene, according to a poster presented last week at the Salk Institute, Fondation IPSEN and Nature Symposium on Biological Complexity in La Jolla, California.

Alzheimer’s drug aids autism mouse model
Memantine, a drug used to treat Alzheimer’s disease, can reverse autism-like features in mice lacking one copy of the MEF2C gene, according to a poster presented last week at the Salk Institute, Fondation IPSEN and Nature Symposium on Biological Complexity in La Jolla, California.
Childhood-onset schizophrenia, autism share genetic links
Individuals who have childhood-onset schizophrenia carry more DNA deletions and duplications associated with other disorders, such as autism, than their unaffected siblings do. The unpublished research was presented 16 January at the Salk Institute, Fondation IPSEN and Nature Symposium on Biological Complexity in La Jolla, California.

Childhood-onset schizophrenia, autism share genetic links
Individuals who have childhood-onset schizophrenia carry more DNA deletions and duplications associated with other disorders, such as autism, than their unaffected siblings do. The unpublished research was presented 16 January at the Salk Institute, Fondation IPSEN and Nature Symposium on Biological Complexity in La Jolla, California.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Dendrites help neuroscientists see the forest for the trees
Dendritic arbors provide just the right scale to study how individual neurons reciprocally interact with their broader circuitry—and are our best bet to bridge cellular and systems neuroscience.

Dendrites help neuroscientists see the forest for the trees
Dendritic arbors provide just the right scale to study how individual neurons reciprocally interact with their broader circuitry—and are our best bet to bridge cellular and systems neuroscience.
Two primate centers drop ‘primate’ from their name
The Washington and Tulane National Biomedical Research Centers—formerly called National Primate Research Centers—say they made the change to better reflect the breadth of research performed at the centers.
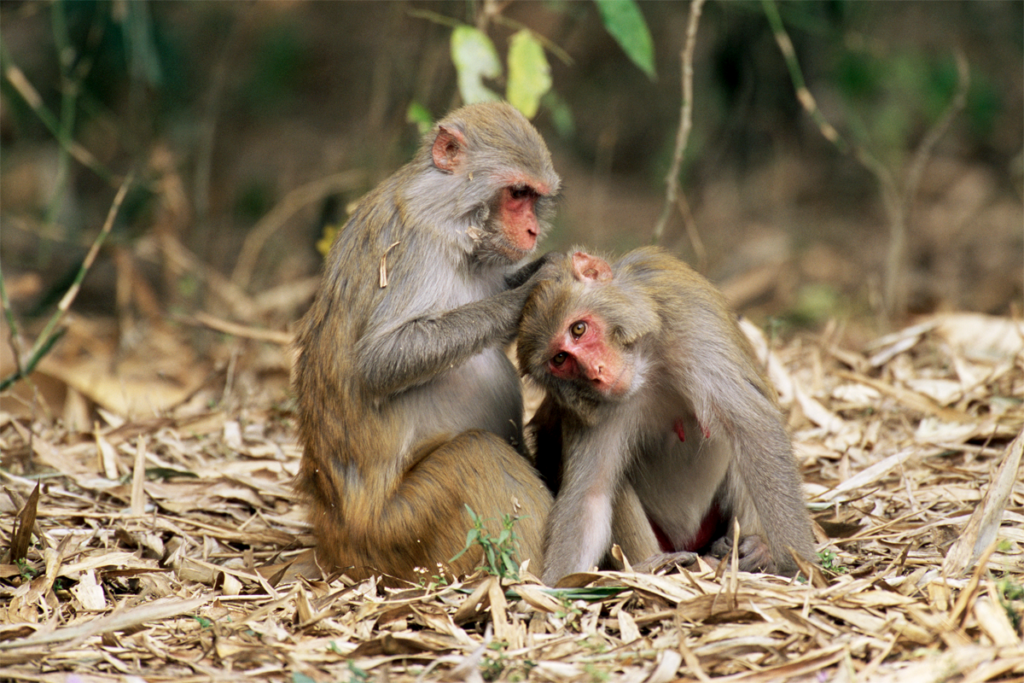

Two primate centers drop ‘primate’ from their name
The Washington and Tulane National Biomedical Research Centers—formerly called National Primate Research Centers—say they made the change to better reflect the breadth of research performed at the centers.
Post-infection immune conflict alters fetal development in some male mice
The immune conflict between dam and fetus could help explain sex differences in neurodevelopmental conditions.
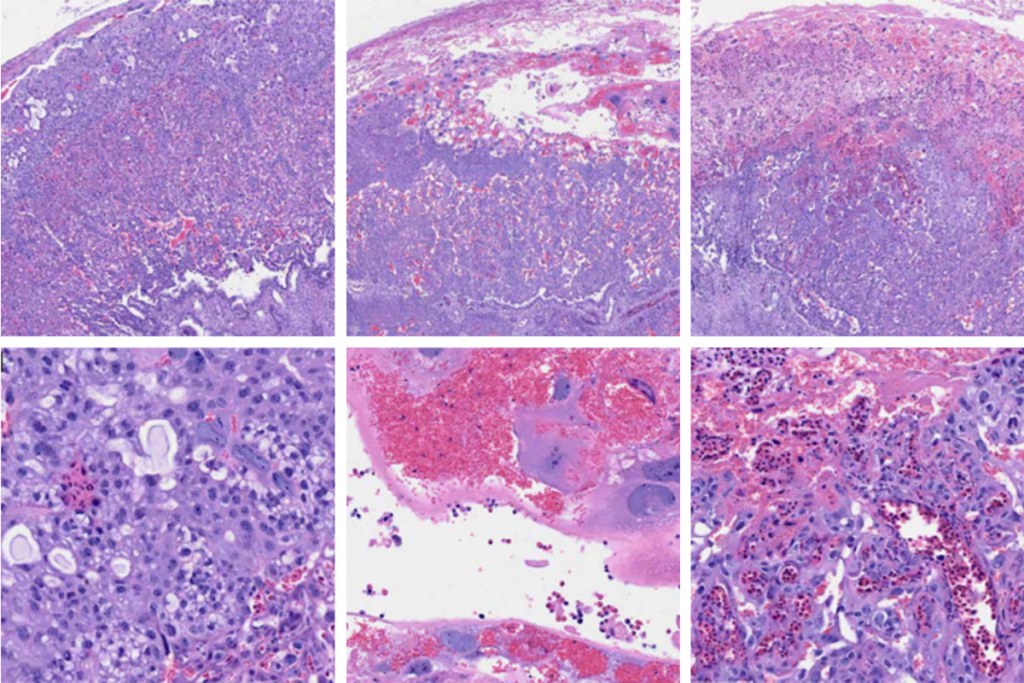
Post-infection immune conflict alters fetal development in some male mice
The immune conflict between dam and fetus could help explain sex differences in neurodevelopmental conditions.