SNPs
Null and Noteworthy: Modified MRI; father findings
This month’s newsletter tackles null findings from an attempted replication of a “revolutionary” MRI approach and an analysis of family genetics.
Null and Noteworthy: Modified MRI; father findings
This month’s newsletter tackles null findings from an attempted replication of a “revolutionary” MRI approach and an analysis of family genetics.
Genome scan spots common variant differences between autism and ADHD
Common variants in five regions of the genome may determine whether someone has one condition versus the other.

Genome scan spots common variant differences between autism and ADHD
Common variants in five regions of the genome may determine whether someone has one condition versus the other.
New resource maps gene expression, regulation in neuron subtypes
The catalog could help researchers understand the effects of autism-linked DNA variants that fall outside genes.
New resource maps gene expression, regulation in neuron subtypes
The catalog could help researchers understand the effects of autism-linked DNA variants that fall outside genes.
Information loss may weaken autism genetic scores
Even the best data practices and technology drop key variants in attempts to predict autism likelihood.

Information loss may weaken autism genetic scores
Even the best data practices and technology drop key variants in attempts to predict autism likelihood.
New resource tracks genetic variations in Han Chinese populations
An online database called NyuWa catalogs genetic variations among nearly 3,000 individuals and provides a comprehensive reference genome for the Han people.

New resource tracks genetic variations in Han Chinese populations
An online database called NyuWa catalogs genetic variations among nearly 3,000 individuals and provides a comprehensive reference genome for the Han people.
X chromosome exerts extra influence on brain development
The X chromosome holds stronger-than-expected genetic sway over the structure of several brain regions. The genes that may underlie this oversized influence have ties to autism.
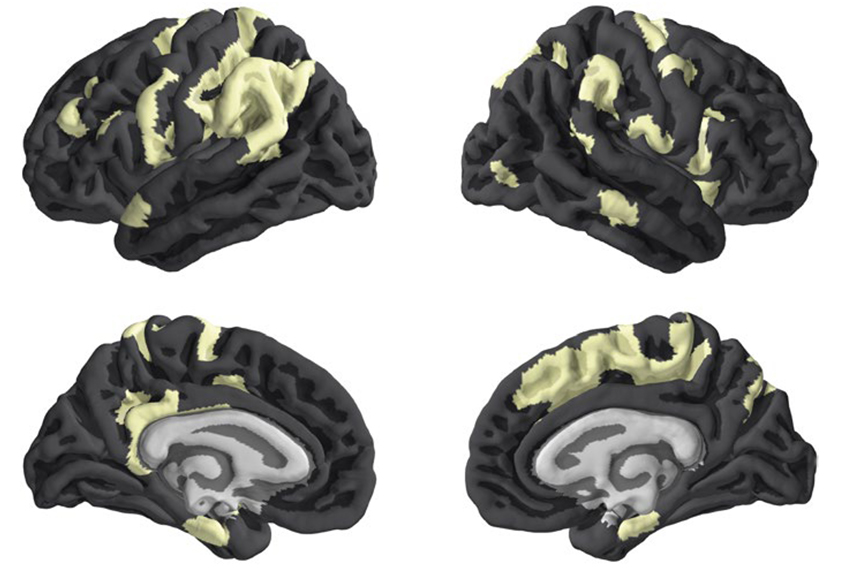
X chromosome exerts extra influence on brain development
The X chromosome holds stronger-than-expected genetic sway over the structure of several brain regions. The genes that may underlie this oversized influence have ties to autism.
Patchwork mutations present a new frontier for autism research
Mosaic mutations, which affect only some of the body’s cells, play a small but meaningful role in autism. Though they are difficult to study, researchers are working to master their complexity.

Patchwork mutations present a new frontier for autism research
Mosaic mutations, which affect only some of the body’s cells, play a small but meaningful role in autism. Though they are difficult to study, researchers are working to master their complexity.
Disrupted cell skeletons may explain brain wiring changes in autism-linked condition
Neuronal axons ignore guidance cues after a mutation in the gene TSC2 disrupts signaling through RhoA, a protein regulated by many autism-linked genes.
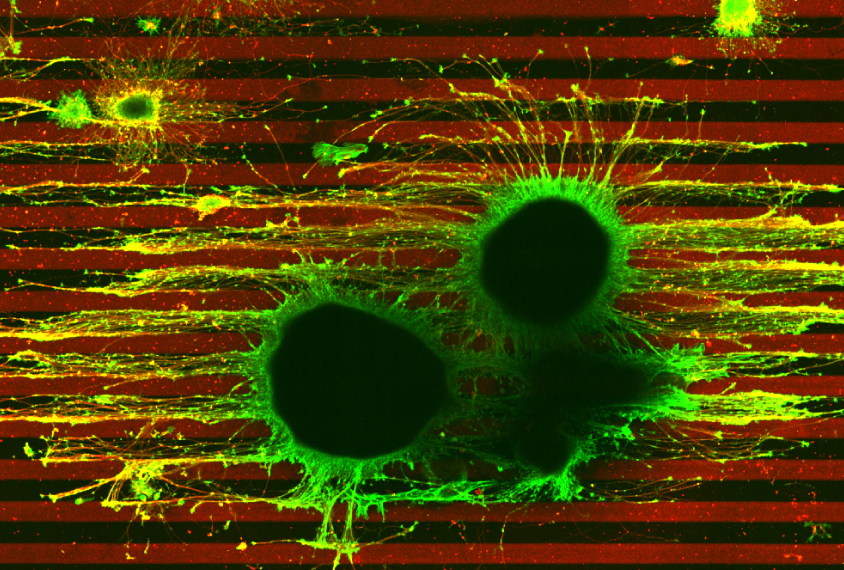
Disrupted cell skeletons may explain brain wiring changes in autism-linked condition
Neuronal axons ignore guidance cues after a mutation in the gene TSC2 disrupts signaling through RhoA, a protein regulated by many autism-linked genes.
Genetic variants in protein target sites may contribute to autism
Mutations that disrupt binding sites in RNA molecules may play a role in autism and a variety of psychiatric conditions, according to a new study.
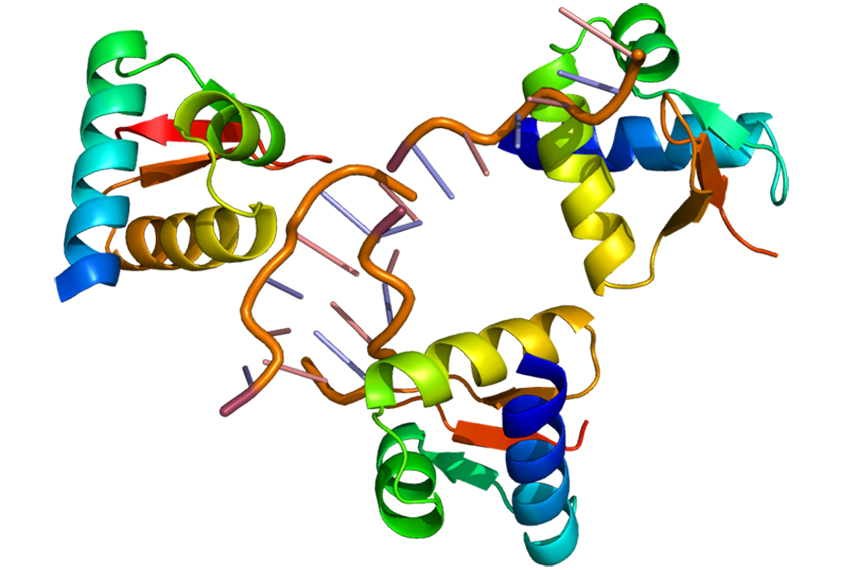
Genetic variants in protein target sites may contribute to autism
Mutations that disrupt binding sites in RNA molecules may play a role in autism and a variety of psychiatric conditions, according to a new study.
Scan of genomes for inherited variants lays bare new autism candidate
Lowered expression of a gene called DDHD2 may increase a person's likelihood of having autism, according to a new analysis.
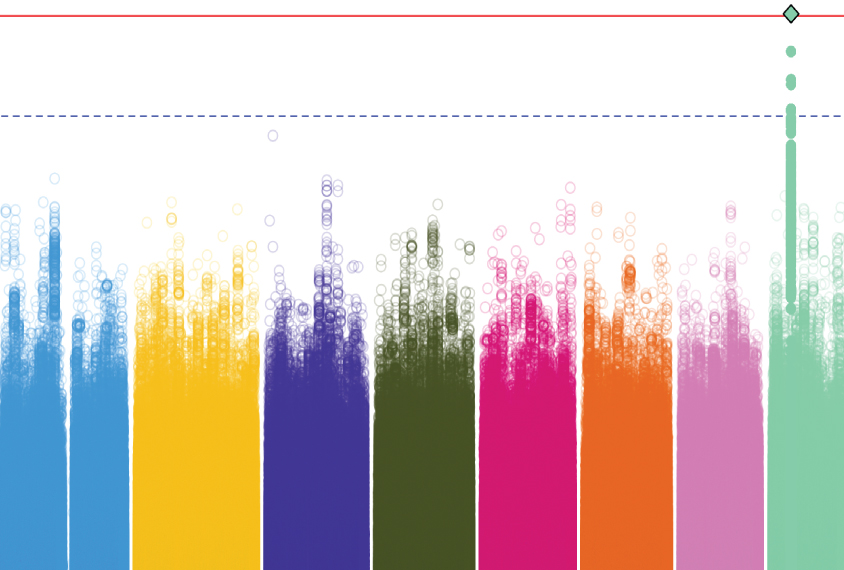
Scan of genomes for inherited variants lays bare new autism candidate
Lowered expression of a gene called DDHD2 may increase a person's likelihood of having autism, according to a new analysis.
Explore more from The Transmitter
New connectomes fly beyond the brain
Researchers are mapping the neurons in Drosophila’s ventral nerve cord, where the central nervous system meets the rest of the body.
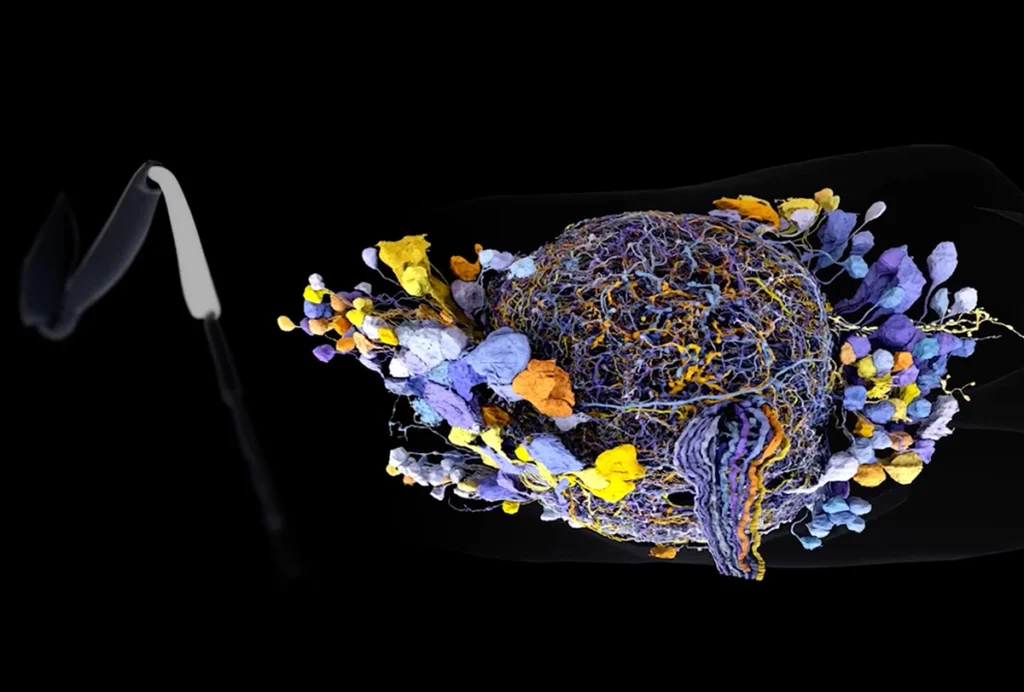
New connectomes fly beyond the brain
Researchers are mapping the neurons in Drosophila’s ventral nerve cord, where the central nervous system meets the rest of the body.
Building an autism research registry: Q&A with Tony Charman
A purpose-built database of participants who have shared genomic and behavioral data could give clinical trials a boost, Charman says.

Building an autism research registry: Q&A with Tony Charman
A purpose-built database of participants who have shared genomic and behavioral data could give clinical trials a boost, Charman says.
Cerebellar circuit may convert expected pain relief into real thing
The newly identified circuit taps into the brain’s opioid system to provide a top-down form of pain relief.
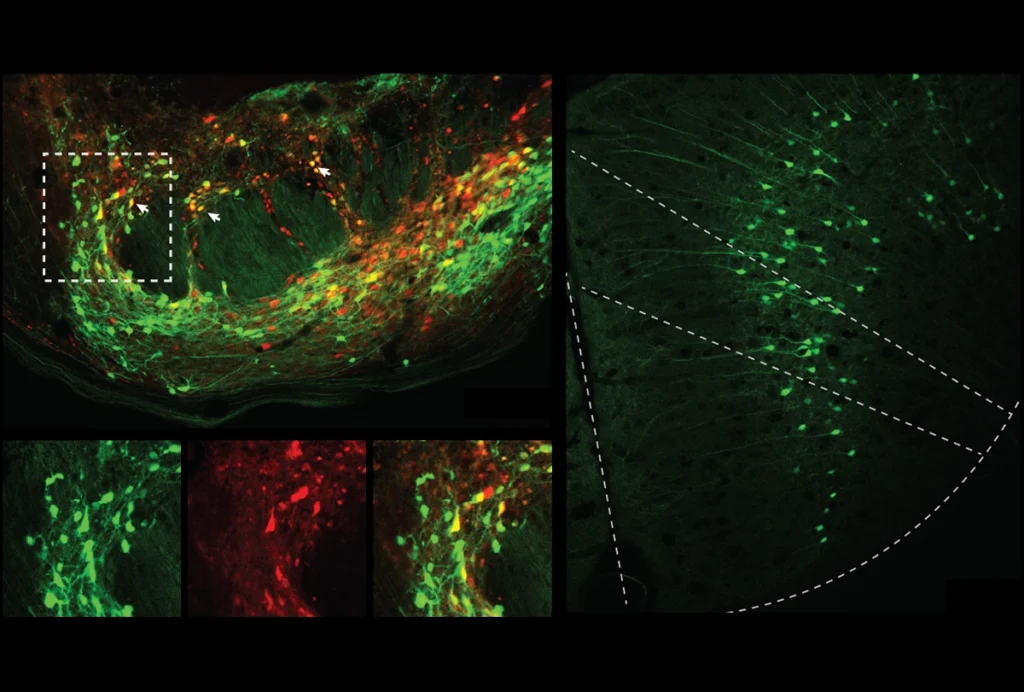
Cerebellar circuit may convert expected pain relief into real thing
The newly identified circuit taps into the brain’s opioid system to provide a top-down form of pain relief.