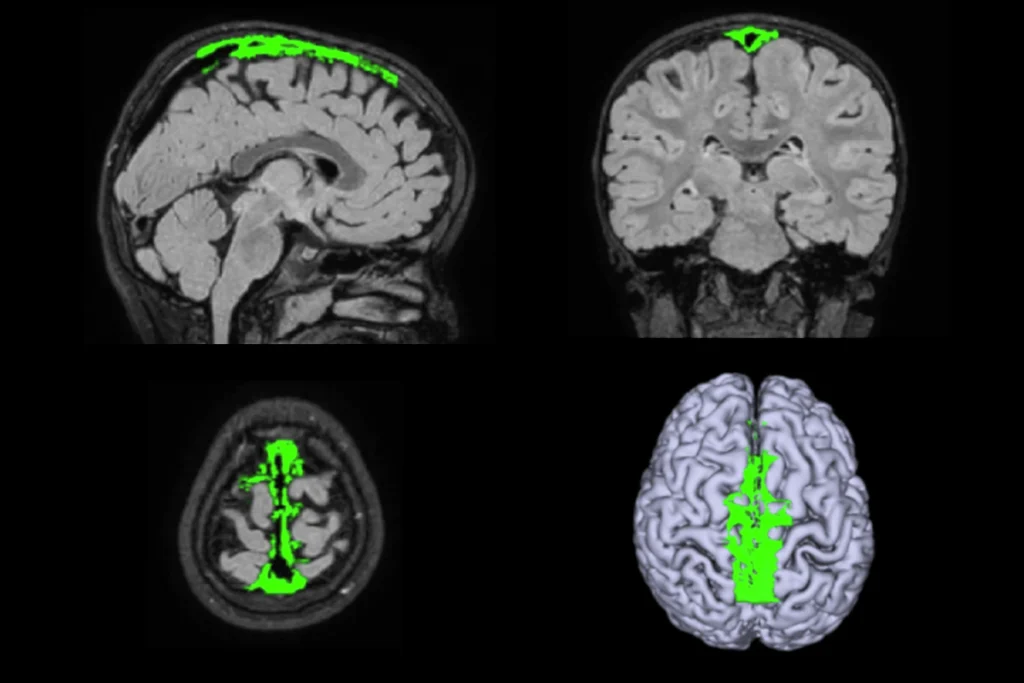
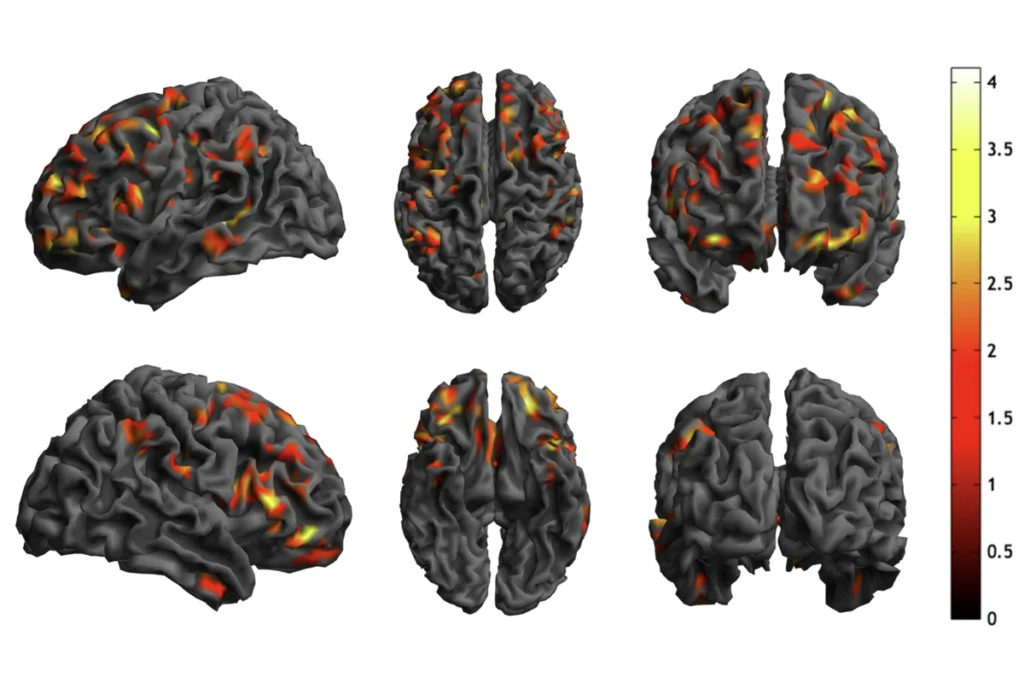
- Structural differences in temporal, fusiform and inferior frontal regions of the brain—assessed with MRI—appear to be predictive of later language skills in autistic toddlers. Nature Communications
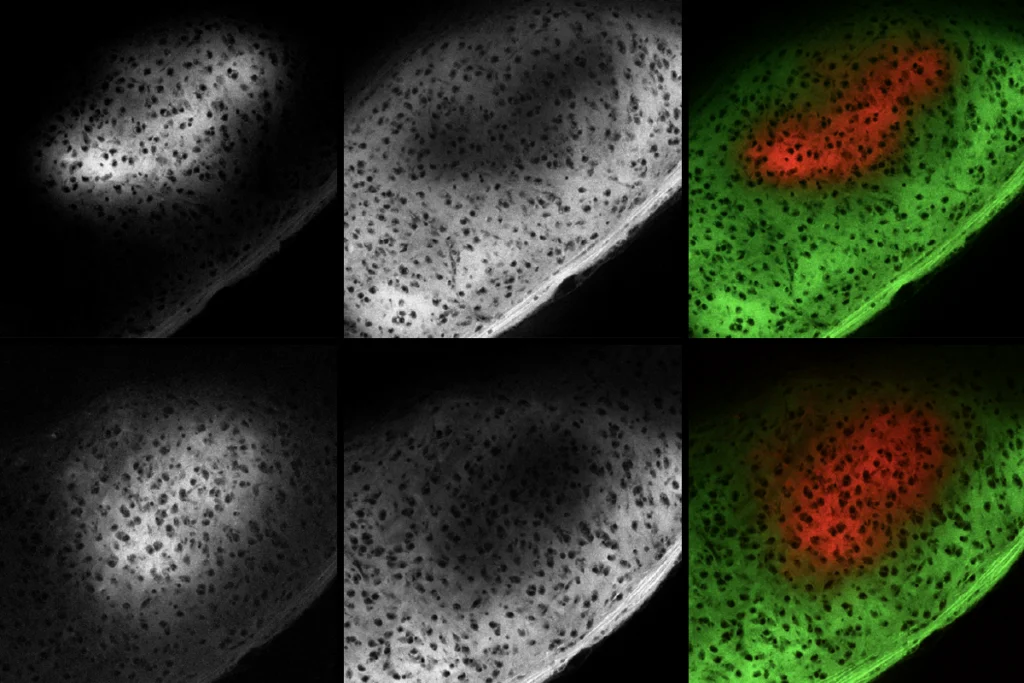
- Mice missing the autism-linked gene FOXP1 display altered cell maturation and cell cycling during early development, which may explain resulting changes in cortical structures, according to a preprint. bioRxiv
- Children with more than one neurodevelopmental condition generally have more attention, social and functional difficulties than their peers with one diagnosis. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research
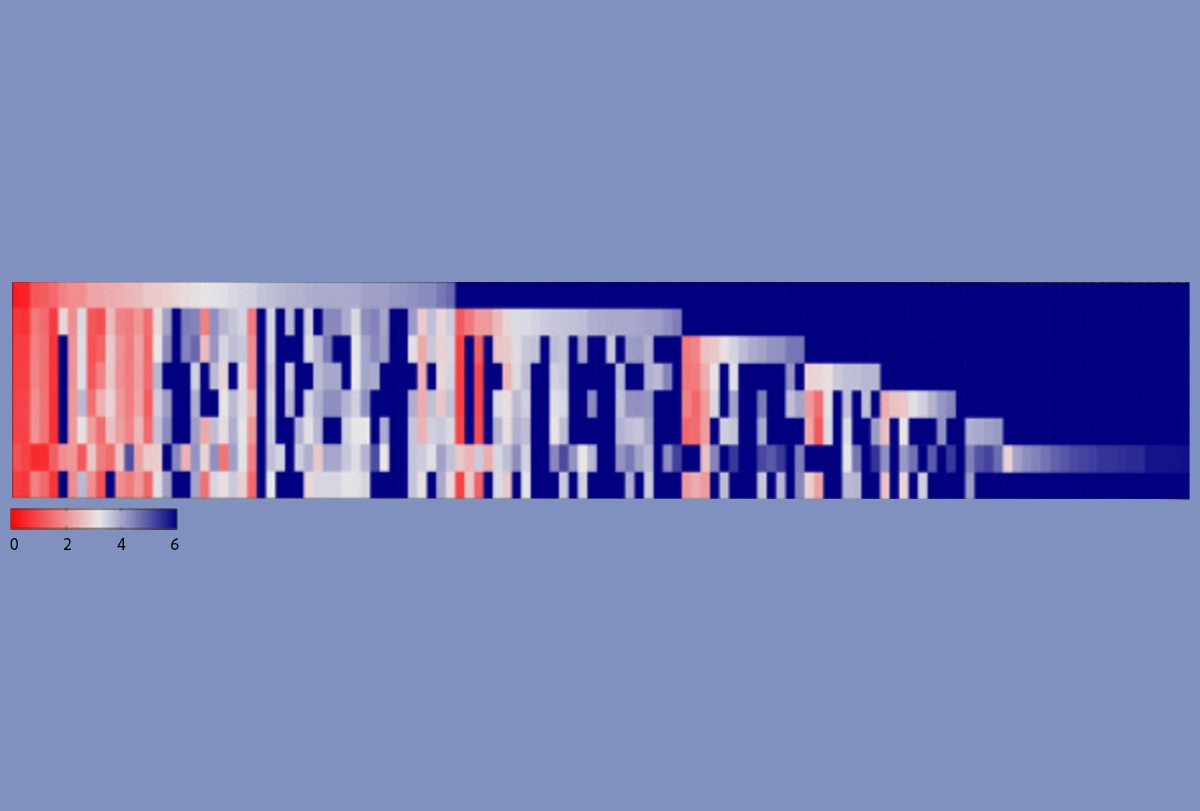
Dynamic development: The number of distinct SHANK3 transcripts (columns) in mice peaks at postnatal day 56 (second to bottom row); the timeline goes from embryonic day 14 (top row) to postnatal day 180 (bottom row).
- Transcriptomes from mice carrying variants of the SHANK3 gene, a model of autism, and postmortem brains from autistic people show “unprecedented” diversity. Cell Reports
- Neural stem cells can model the dynamics of gene expression very early in development and can show how genes linked to neurodevelopmental conditions alter those dynamics, according to a preprint. bioRxiv