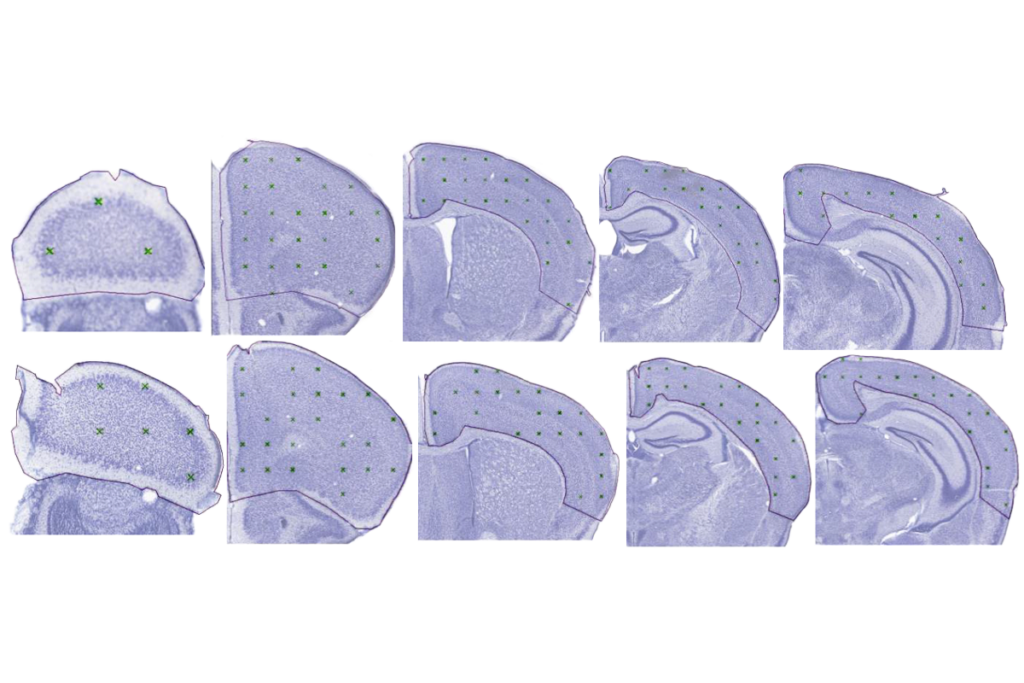
- Oxytocin exposure during birth alters oxytocin signaling and communication in rat pups; in males, it also alters functional connectivity and empathy-like behaviors. iScience
- Alpha activity in the brains of 1-year-old children later diagnosed with autism is related to restricted and repetitive behaviors at 2 years old, according to a preprint. Research Square
- Mice missing the interleukin-1 receptor show autism-like behaviors and an unusually high number of synapses, suggesting the cytokine mediates microglial pruning of neuronal connections during development. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity
Oxytocin during labor; infant brain activity; interleukin-1
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 12 February.
By
Jill Adams
13 February 2024 | 1 min read
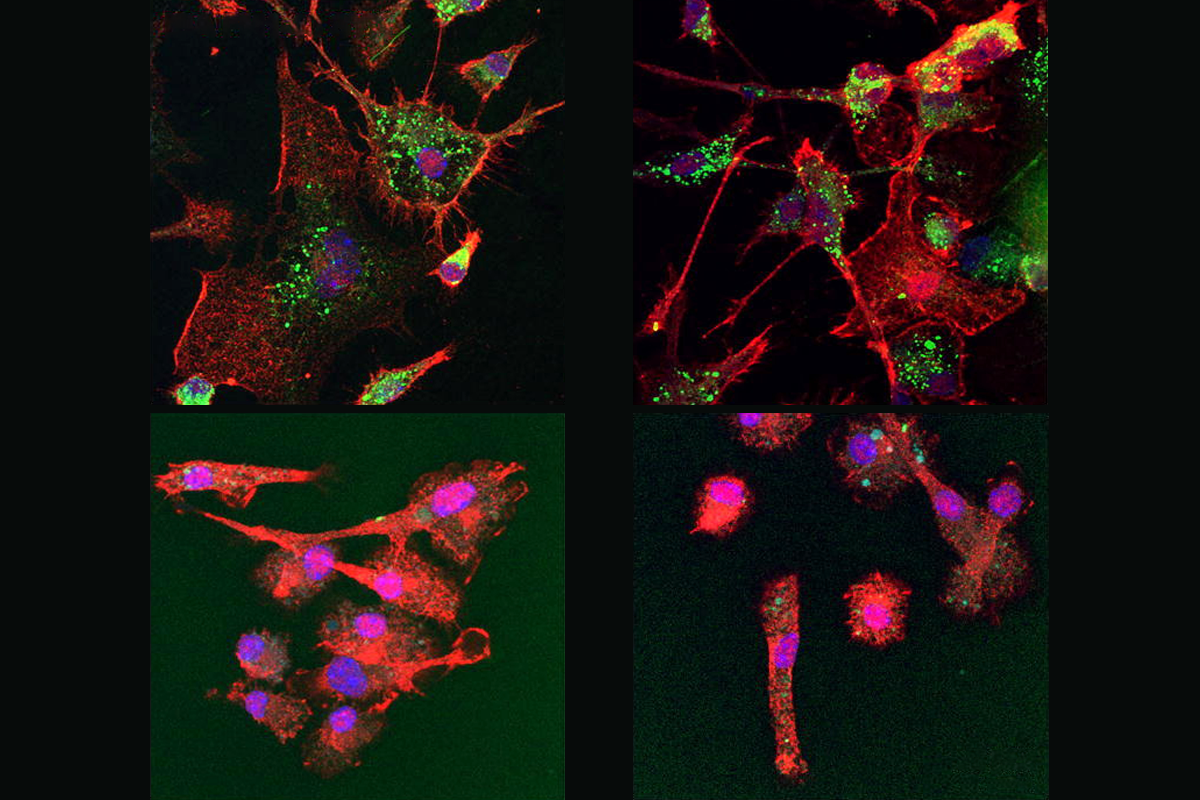
Pruning maneuvers: Microglia missing the interleukin-1 receptor gene (bottom panels) show deficits in engulfing synaptosomes (green) compared with wildtype cells (top panels).
- The link between pragmatic language difficulties and repetitive behaviors observed in autistic children also occurs in non-autistic children. Autism Research
- A machine-learning strategy can distinguish patterns of neural activity for autistic versus non-autistic adults who are engaging in eye contact with another person. Scientific Reports
- Preterm infants display altered functional connectivity that is associated with social and sensory difficulties and repetitive behaviors in an autism screen at 18 months of age. Nature Communications
tags:
Recommended reading

INSAR takes ‘intentional break’ from annual summer webinar series
By
Lauren Schenkman
30 June 2025 | 4 min read

Dosage of X or Y chromosome relates to distinct outcomes; and more
By
Daisy Yuhas
24 June 2025 | 2 min read
Explore more from The Transmitter
Machine learning spots neural progenitors in adult human brains
By
Claudia López Lloreda
3 July 2025 | 7 min listen
Xiao-Jing Wang outlines the future of theoretical neuroscience
By
Paul Middlebrooks
2 July 2025 | 112 min listen
Memory study sparks debate over statistical methods
By
Katie Moisse
2 July 2025 | 5 min read
Cite this article: