- Cortical gamma-band oscillations in response to speech, which are thought to be related to the excitatory-inhibitory balance in the brain, are greater in autistic people than in non-autistic people. Molecular Autism
- Maternal immune activation in mice, a model of autism and other neurodevelopmental conditions, spurs more cytokine release in male offspring than in female ones. Journal of Neuroinflammation
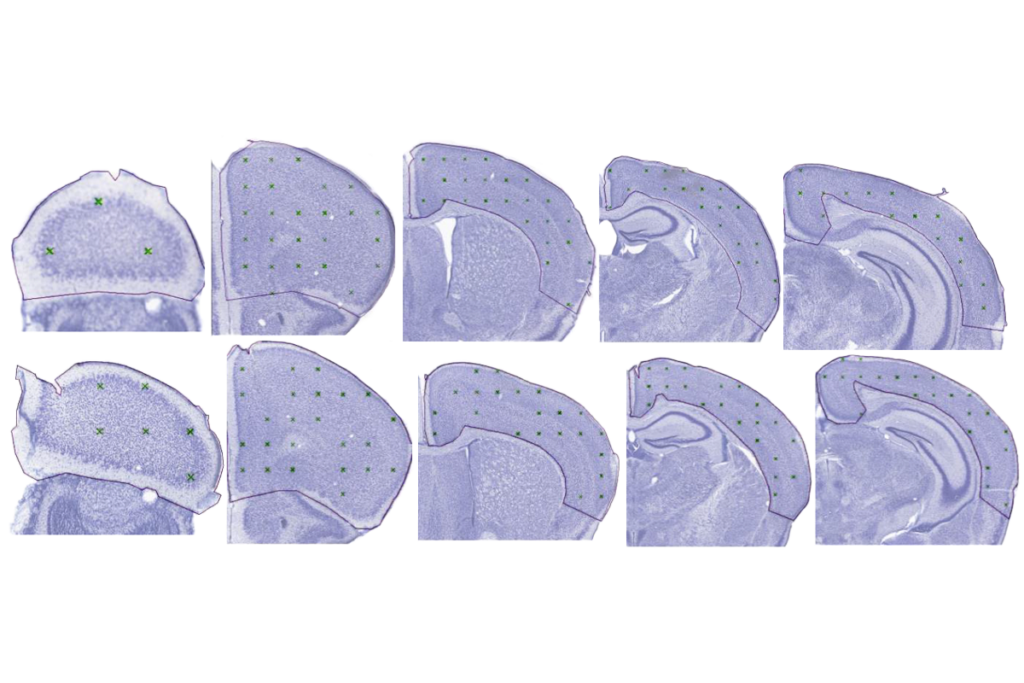
- Mice missing KATNAL2, an autism-linked gene, have altered social-communication behaviors and enlarged brain ventricles, which appear to be triggered by glial ciliary action. PLOS Biology
Sex-dependent cytokine release; KATNAL2 gene; auditory processing in fragile X syndrome
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 20 May.
By
Jill Adams
21 May 2024 | 1 min read
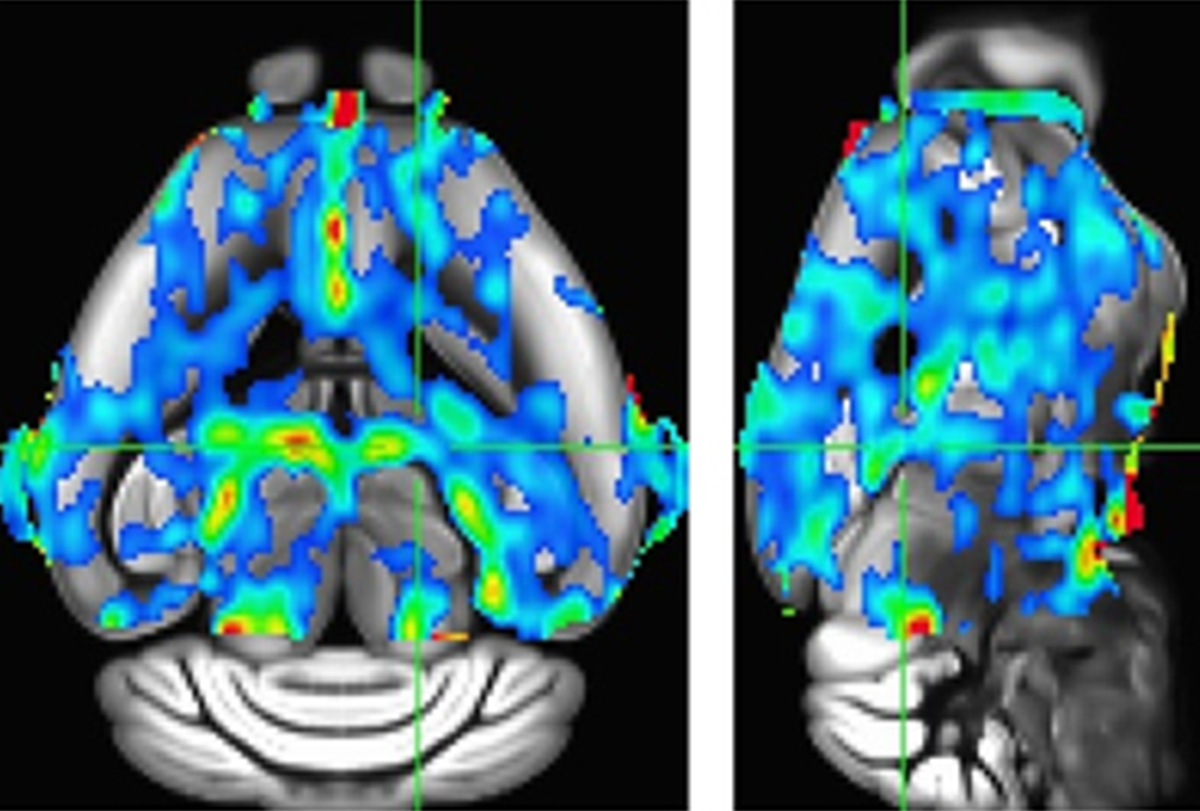
Low flow: Cerebral blood volume is decreased in many brain areas (red, orange, yellow) in mice missing the autism-linked gene KATNAL2.
- Mice missing the FMR1 gene, a model of fragile X syndrome, show enhanced auditory event response potentials and sex-based differences in the maturation of temporal processing. Journal of Neurodevelopmental Disorders
- A novel statistical method called CWAS-Plus links noncoding variants to functional outputs. The technique has identified transcription factor binding sites associated with autism, according to a preprint. medRxiv
tags:
Recommended reading

INSAR takes ‘intentional break’ from annual summer webinar series
By
Lauren Schenkman
30 June 2025 | 4 min read

Dosage of X or Y chromosome relates to distinct outcomes; and more
By
Daisy Yuhas
24 June 2025 | 2 min read
Explore more from The Transmitter
Machine learning spots neural progenitors in adult human brains
By
Claudia López Lloreda
3 July 2025 | 7 min listen
Xiao-Jing Wang outlines the future of theoretical neuroscience
By
Paul Middlebrooks
2 July 2025 | 112 min listen
Memory study sparks debate over statistical methods
By
Katie Moisse
2 July 2025 | 5 min read
Cite this article: