Andrew Meissen is a New York City-based freelance science writer specializing in neuroscience and technology. His work has appeared in publications such as BrainFacts.org, Photonics Focus and Drug Discovery News.

Andrew Meissen
Contributing Writer
Spectrum
From this contributor
Sequencing trick identifies brain cells affected by large autism-linked mutation
The method, called Orgo-Seq, reveals that a deletion of genes on chromosome 16 increases the proportion of immature neurons and neural precursors in brain organoids derived from people with the mutation.
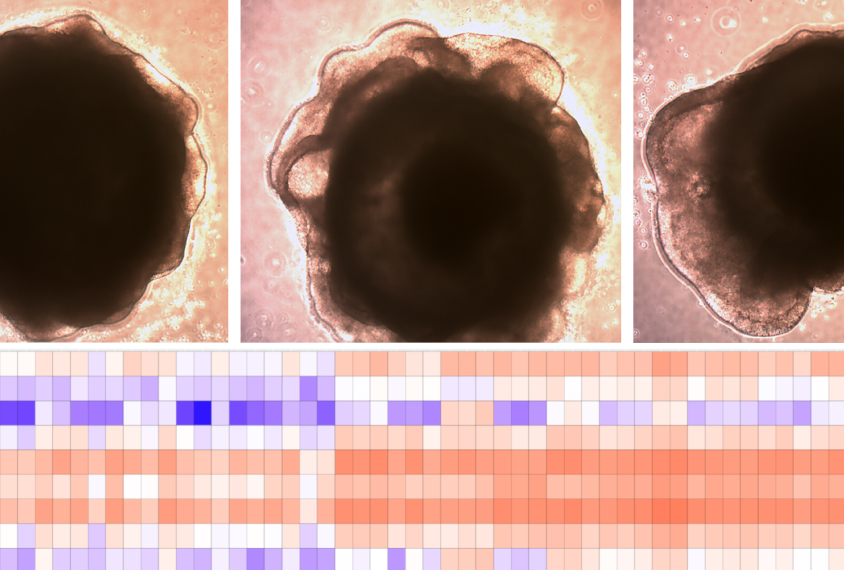
Sequencing trick identifies brain cells affected by large autism-linked mutation
Explore more from The Transmitter
Remembering Annette Dolphin, who helped explain gabapentin’s effects
The "intuitive" neuropharmacologist pushed against the status quo.

Remembering Annette Dolphin, who helped explain gabapentin’s effects
The "intuitive" neuropharmacologist pushed against the status quo.
Revised statistical bar extracts less-common variants from autism genetics studies
Adjusting genetic analyses could help plug autism’s heritability gap, according to a new preprint.

Revised statistical bar extracts less-common variants from autism genetics studies
Adjusting genetic analyses could help plug autism’s heritability gap, according to a new preprint.
Tom Griffiths describes how neural networks, logic and probability theory together explain cognition
In his new book, “The Laws of Thought,” Griffiths shows how these three pillars of study complement one another and together form a solid foundation to eventually explain all of our cognition, from brain to mind.
Tom Griffiths describes how neural networks, logic and probability theory together explain cognition
In his new book, “The Laws of Thought,” Griffiths shows how these three pillars of study complement one another and together form a solid foundation to eventually explain all of our cognition, from brain to mind.