John N. Constantino is a board-certified child and adolescent psychiatrist and chief of behavioral and mental Health at Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta, as well as professor of psychiatry and pediatrics at Emory University School of Medicine. He is an international leader in autism trait phenotyping, sex differences in autism, and endophenotypic analyses.

John Constantino
Chief of behavioral and mental health
Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta
From this contributor
Autism is more heritable in boys than in girls
If boys have greater inherited liability for autism, the female protective effect may not fully explain the sex difference in prevalence.

Autism is more heritable in boys than in girls
Q&A with John Constantino: Solving the biomarker conundrum
Biological factors that reflect autism’s roots may differ from those that influence how severe the condition is. Failure to make a distinction has stymied the search for biomarkers.

Q&A with John Constantino: Solving the biomarker conundrum
Traits of other conditions may spur autism
Early features of other conditions may contribute to autism itself

Traits of other conditions may spur autism
Japanese spectrum
Researchers studying autism prevalence should take into account the continuous nature of autism symptoms in the general population, says John Constantino.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Machine learning spots neural progenitors in adult human brains
But the finding has not settled the long-standing debate over the existence and extent of neurogenesis during adulthood, says Yale University neuroscientist Juan Arellano.
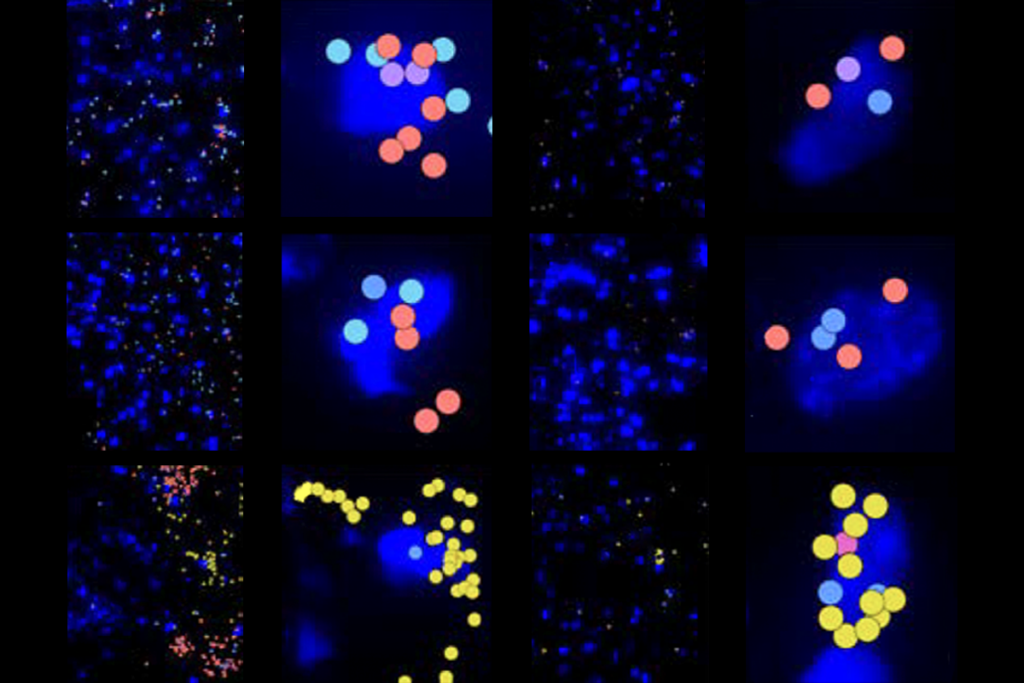
Machine learning spots neural progenitors in adult human brains
But the finding has not settled the long-standing debate over the existence and extent of neurogenesis during adulthood, says Yale University neuroscientist Juan Arellano.
Xiao-Jing Wang outlines the future of theoretical neuroscience
Wang discusses why he decided the time was right for a new theoretical neuroscience textbook and how bifurcation is a key missing concept in neuroscience explanations.
Xiao-Jing Wang outlines the future of theoretical neuroscience
Wang discusses why he decided the time was right for a new theoretical neuroscience textbook and how bifurcation is a key missing concept in neuroscience explanations.
Memory study sparks debate over statistical methods
Critics of a 2024 Nature paper suggest the authors failed to address the risk of false-positive findings. The authors argue more rigorous methods can result in missed leads.
Memory study sparks debate over statistical methods
Critics of a 2024 Nature paper suggest the authors failed to address the risk of false-positive findings. The authors argue more rigorous methods can result in missed leads.
