Mu Yang is a behavioral neuroscientist and the director of the Mouse NeuroBehavior Core at Columbia University Medical Center. She received training in animal behavior and neuroethology in the lab of the late Robert Blanchard at the University of Hawaii, where she earned her Ph.D. In 2006, she joined the lab of Jacqueline Crawley at the National Institute of Mental Health for postdoctoral training. She spent 2012 to 2016 as an assistant professor in the department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences and a faculty member at the MIND Institute at the University California, Davis. In 2016, she joined Columbia’s Institute for Genomic Medicine to lead the university’s first centralized state-of-the-art mouse behavior phenotyping facility. Since summer 2017, her team has provided testing and data analysis services to over 30 Columbia research groups.

Mu Yang
Director of the Mouse NeuroBehavior Core
Columbia University Medical Center
Explore more from The Transmitter
Okur-Chung neurodevelopmental syndrome; excess CSF; autistic girls
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 21 October.
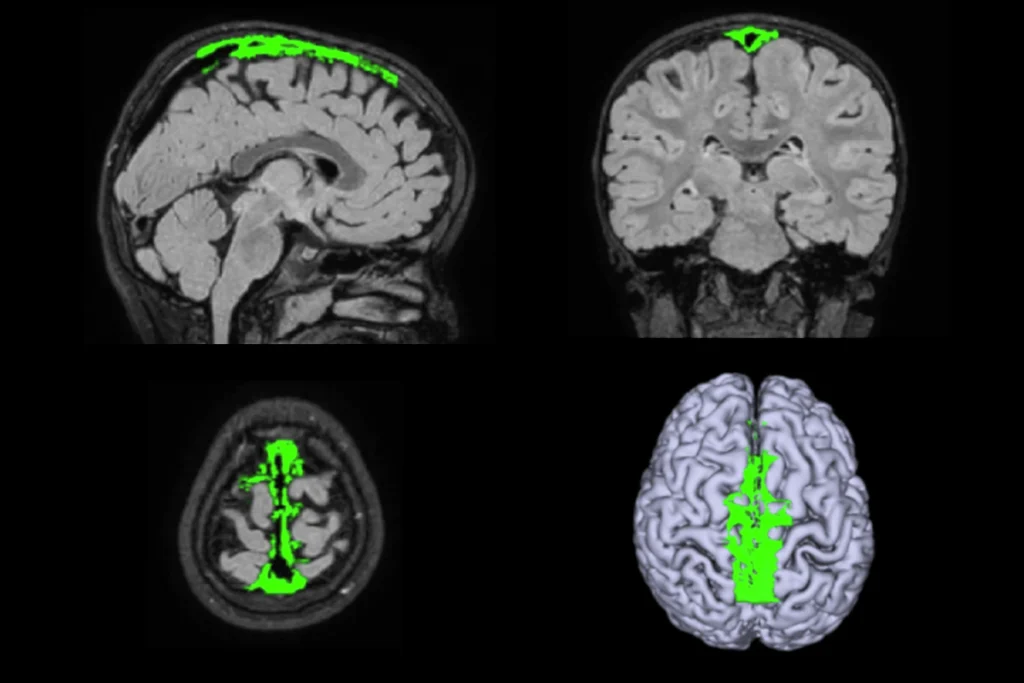
Okur-Chung neurodevelopmental syndrome; excess CSF; autistic girls
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 21 October.
Brains, biases and amyloid beta: Why the female brain deserves a closer look in Alzheimer’s research
New results suggest the disease progresses differently in women, but we need more basic science to unpack the mechanisms involved.

Brains, biases and amyloid beta: Why the female brain deserves a closer look in Alzheimer’s research
New results suggest the disease progresses differently in women, but we need more basic science to unpack the mechanisms involved.
Are brains and AI converging?—an excerpt from ‘ChatGPT and the Future of AI: The Deep Language Revolution’
In his new book, to be published next week, computational neuroscience pioneer Terrence Sejnowski tackles debates about AI’s capacity to mirror cognitive processes.
Are brains and AI converging?—an excerpt from ‘ChatGPT and the Future of AI: The Deep Language Revolution’
In his new book, to be published next week, computational neuroscience pioneer Terrence Sejnowski tackles debates about AI’s capacity to mirror cognitive processes.