OCD
Temperament is innate but hackable, animal studies suggest
Emotional reactivity and vulnerability to stress are largely inherited in rodents — but can be modified in early life by targeting inflammation-related cells or even just adjusting an animal’s environment.
Temperament is innate but hackable, animal studies suggest
Emotional reactivity and vulnerability to stress are largely inherited in rodents — but can be modified in early life by targeting inflammation-related cells or even just adjusting an animal’s environment.
‘Into the wild’: Moving studies of memory and learning out of the lab
People with electrodes embedded deep in their brain are collaborating with a growing posse of plucky researchers to uncover the mysteries of real-world recall.
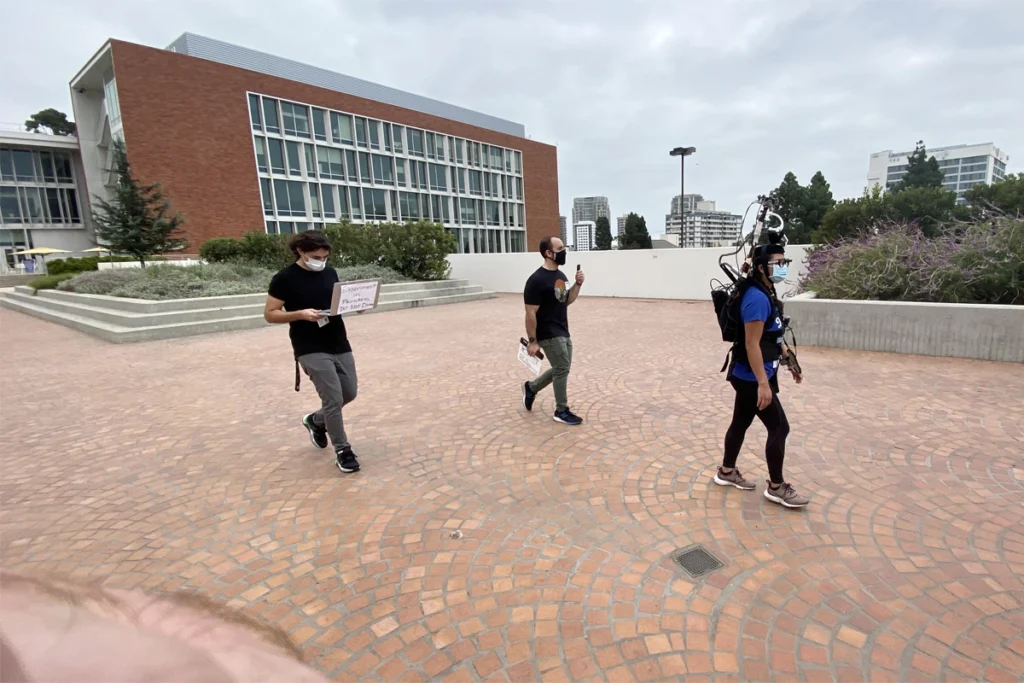

‘Into the wild’: Moving studies of memory and learning out of the lab
People with electrodes embedded deep in their brain are collaborating with a growing posse of plucky researchers to uncover the mysteries of real-world recall.
Autistic LGBTQ+ people report frequent mental health problems
The co-occurring conditions may stem from the heightened stress people in minority communities experience.

Autistic LGBTQ+ people report frequent mental health problems
The co-occurring conditions may stem from the heightened stress people in minority communities experience.
Common variants link autism, ADHD, Tourette syndrome
Genetic variants that contribute to autism may also be involved in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and Tourette syndrome, according to a new study.
Common variants link autism, ADHD, Tourette syndrome
Genetic variants that contribute to autism may also be involved in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and Tourette syndrome, according to a new study.
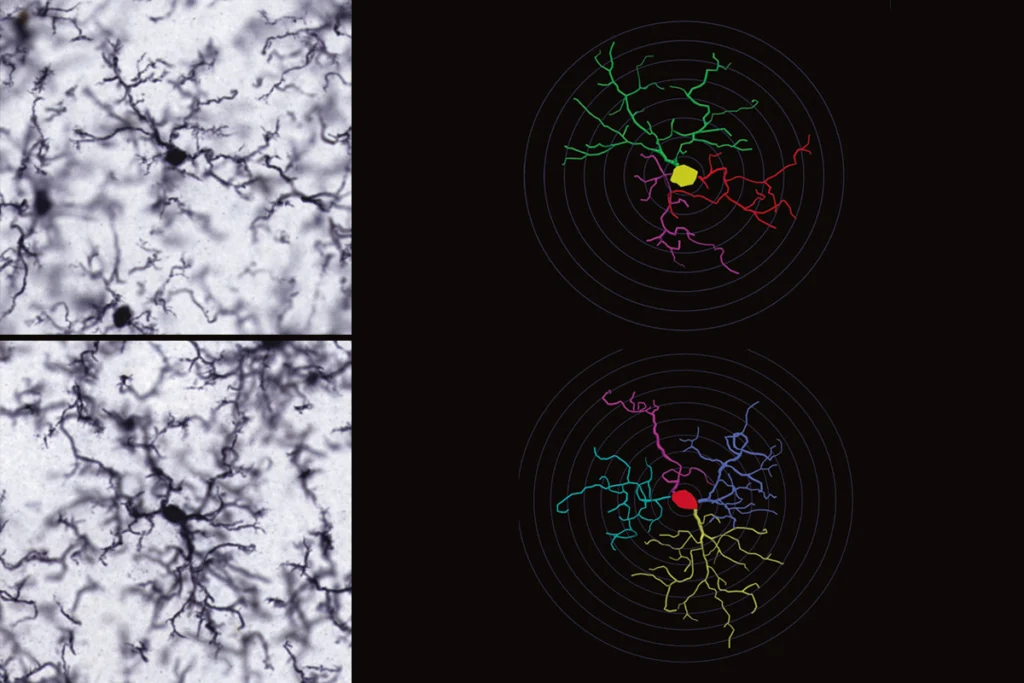
Autism shares brain structure changes with other psychiatric conditions
Atypical development of a particular type of neuron explains the structural similarities seen in the brains of people with autism, schizophrenia and other conditions, according to a new study.
Autism shares brain structure changes with other psychiatric conditions
Atypical development of a particular type of neuron explains the structural similarities seen in the brains of people with autism, schizophrenia and other conditions, according to a new study.
Repetitive behaviors and ‘stimming’ in autism, explained
Restricted interests and repetitive behaviors constitute one of two criteria that define autism in the diagnostic manual for psychiatry.
Repetitive behaviors and ‘stimming’ in autism, explained
Restricted interests and repetitive behaviors constitute one of two criteria that define autism in the diagnostic manual for psychiatry.
How a controversial condition called PANDAS is gaining ground on autism
Some scientists say an immune condition called PANDAS affects as many as 1 in 200 children who have traits similar to those of autism. But many experts contest that figure — and even the condition's very existence.

How a controversial condition called PANDAS is gaining ground on autism
Some scientists say an immune condition called PANDAS affects as many as 1 in 200 children who have traits similar to those of autism. But many experts contest that figure — and even the condition's very existence.
Rethinking repetitive behaviors in autism
Autistic people have long maintained that repetitive behaviors are beneficial. Emerging evidence in support of this idea is shaping new therapies.
Rethinking repetitive behaviors in autism
Autistic people have long maintained that repetitive behaviors are beneficial. Emerging evidence in support of this idea is shaping new therapies.
Enlarged amygdala may forecast anxiety, depression in autistic children
A tiny chunk of the brain’s emotion enter, the amygdala, is enlarged in some autistic children; the larger this piece, the more anxious and depressed the child is likely to be.
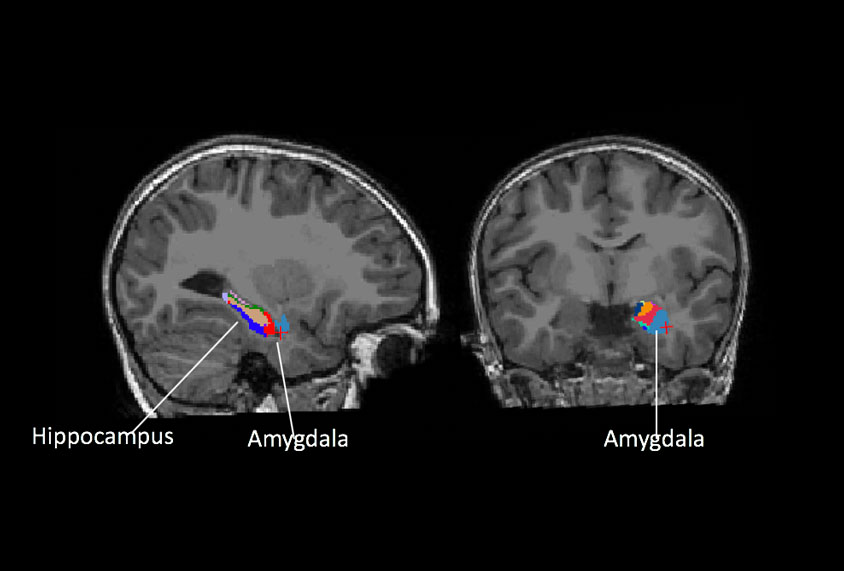
Enlarged amygdala may forecast anxiety, depression in autistic children
A tiny chunk of the brain’s emotion enter, the amygdala, is enlarged in some autistic children; the larger this piece, the more anxious and depressed the child is likely to be.
Untangling the ties between autism and obsessive-compulsive disorder
Autism and obsessive-compulsive disorder frequently accompany each other; Scientists are studying both to understand how they differ.

Untangling the ties between autism and obsessive-compulsive disorder
Autism and obsessive-compulsive disorder frequently accompany each other; Scientists are studying both to understand how they differ.
Explore more from The Transmitter
New connectomes fly beyond the brain
Researchers are mapping the neurons in Drosophila’s ventral nerve cord, where the central nervous system meets the rest of the body.
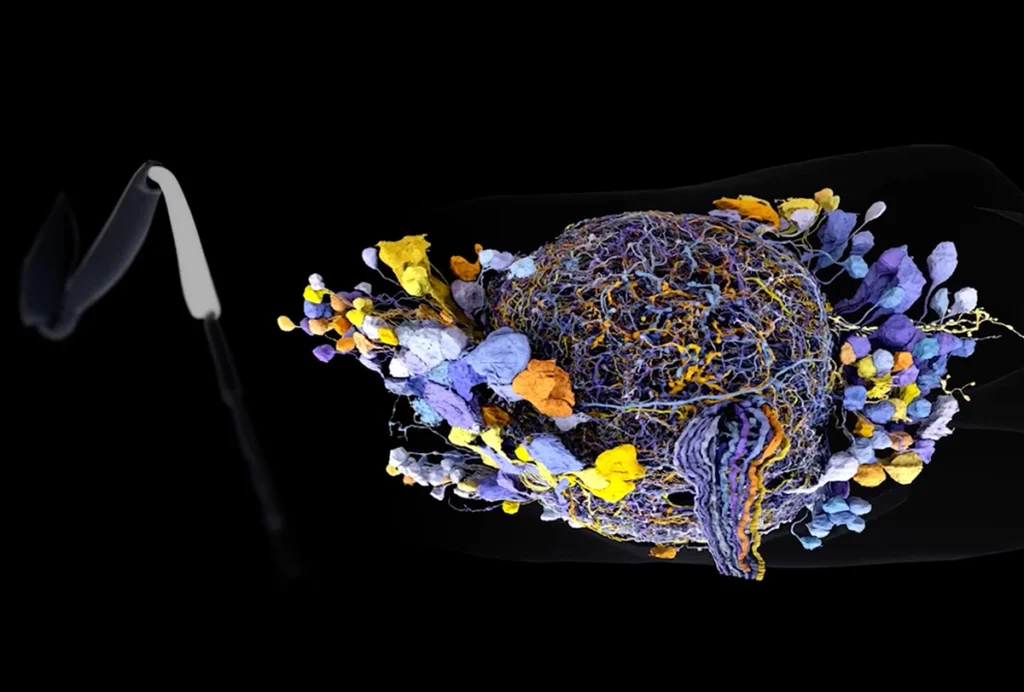
New connectomes fly beyond the brain
Researchers are mapping the neurons in Drosophila’s ventral nerve cord, where the central nervous system meets the rest of the body.
Building an autism research registry: Q&A with Tony Charman
A purpose-built database of participants who have shared genomic and behavioral data could give clinical trials a boost, Charman says.

Building an autism research registry: Q&A with Tony Charman
A purpose-built database of participants who have shared genomic and behavioral data could give clinical trials a boost, Charman says.
Cerebellar circuit may convert expected pain relief into real thing
The newly identified circuit taps into the brain’s opioid system to provide a top-down form of pain relief.
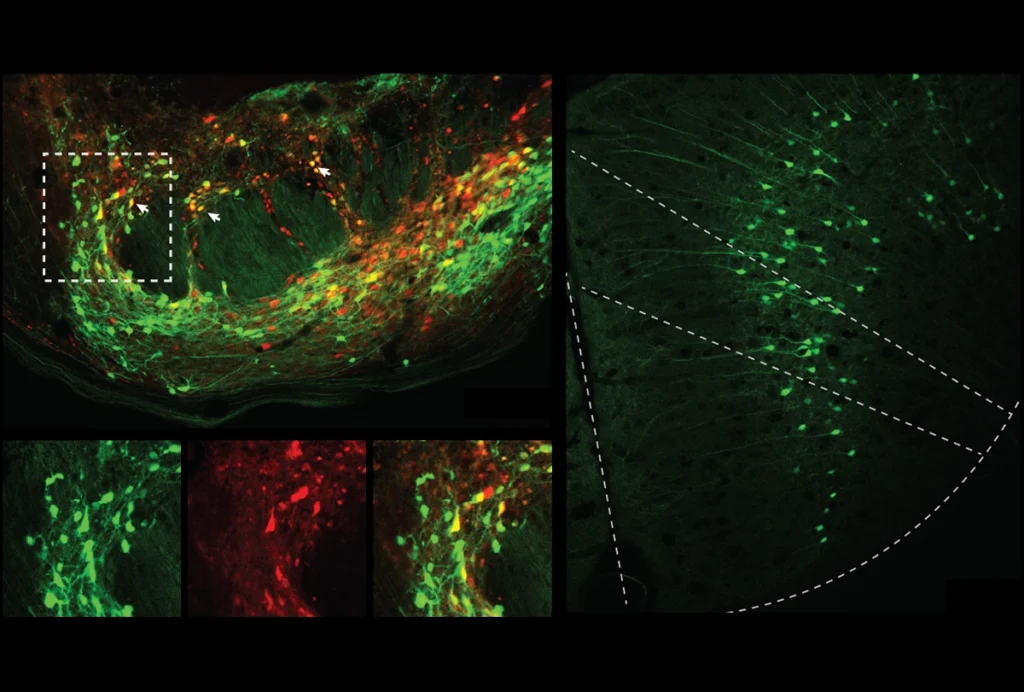
Cerebellar circuit may convert expected pain relief into real thing
The newly identified circuit taps into the brain’s opioid system to provide a top-down form of pain relief.