Nicholette Zeliadt manages The Transmitters’s staff reporters and interns, and she commissions and edits news articles. She joined The Transmitter as news writer in 2014. Before that, she was a freelance writer and editor. Her work has appeared in The New York Times, Scientific American, Nature Medicine, Science and The Scientist.

Nicholette Zeliadt
Managing editor
The Transmitter
From this contributor

Leaving lasting marks with Tessa Montague
Spotted around the web: INSAR; cerebellar gene expression; pangenome
Spotted around the web: Mapping histones; COVID-19 births; acetaminophen lawsuits

New diagnostic code for PTEN syndrome may spur research
Education
- Ph.D. in environmental health, University of Minnesota
- B.A. in biochemistry, University of Iowa
Fellowships
- AAAS Mass Media Fellowship
Explore more from The Transmitter
Exclusive: Recruitment issues jeopardize ambitious plan for human brain atlas
A lack of six new brain donors may stop the project from meeting its goal to pair molecular and cellular data with the functional organization of the cortex.
Exclusive: Recruitment issues jeopardize ambitious plan for human brain atlas
A lack of six new brain donors may stop the project from meeting its goal to pair molecular and cellular data with the functional organization of the cortex.
How pragmatism and passion drive Fred Volkmar—even after retirement
Whether looking back at his career highlights or forward to his latest projects, the psychiatrist is committed to supporting autistic people at every age.
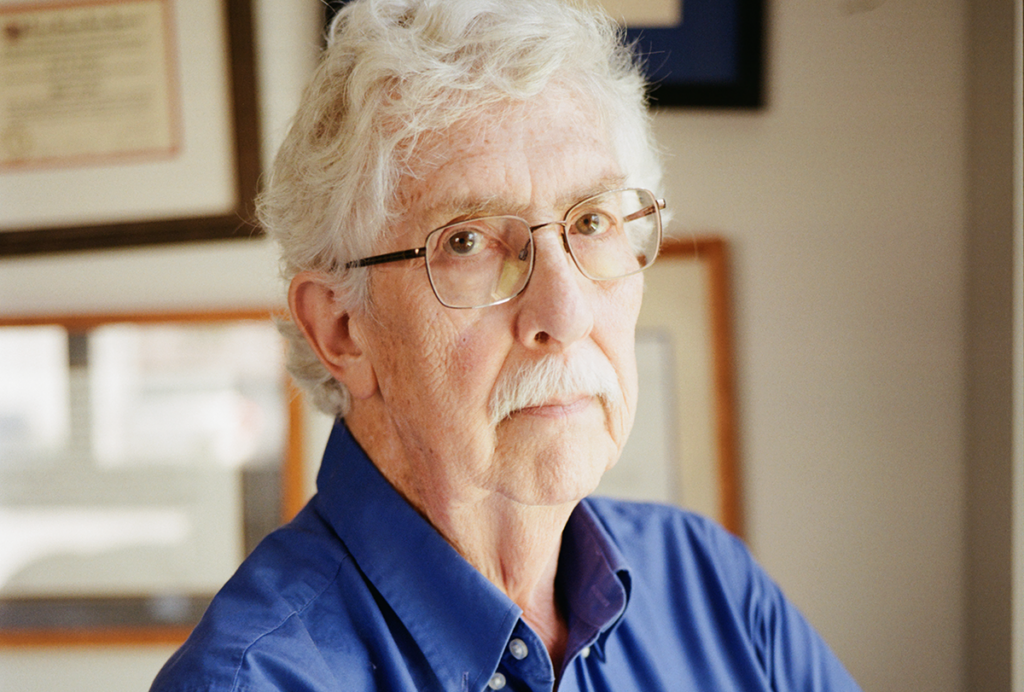

How pragmatism and passion drive Fred Volkmar—even after retirement
Whether looking back at his career highlights or forward to his latest projects, the psychiatrist is committed to supporting autistic people at every age.
The brain’s quiet conductor: How hidden cells fine-tune arousal
New research published today suggests that the pericoeruleus acts as a kind of micromanager of arousal, selectively inhibiting different subgroups of locus coeruleus neurons depending on the behavioral context.
The brain’s quiet conductor: How hidden cells fine-tune arousal
New research published today suggests that the pericoeruleus acts as a kind of micromanager of arousal, selectively inhibiting different subgroups of locus coeruleus neurons depending on the behavioral context.
