SFN 2021
Recent articles
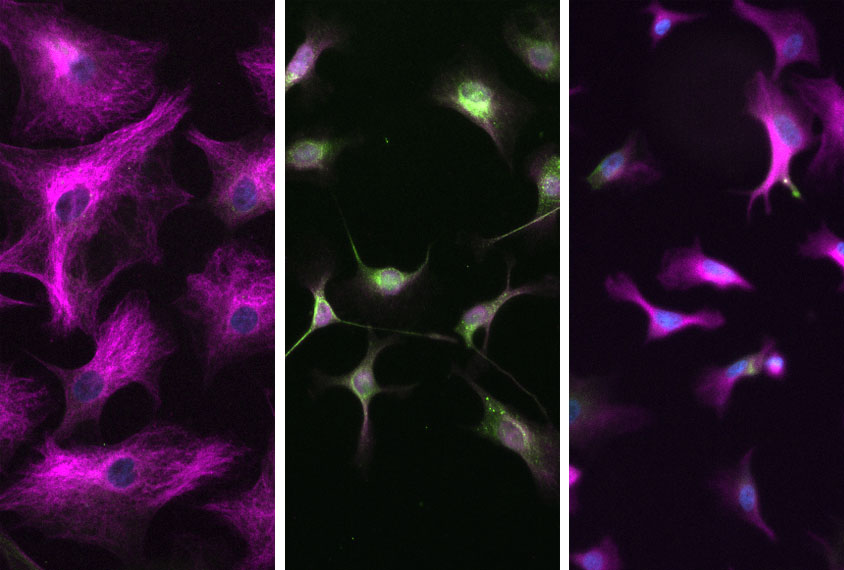
Including immune cells in brain organoids improves model’s accuracy
Cortical organoids that contain non-neuronal brain cells called microglia may reflect human neurodevelopment more faithfully than those that don’t.
Including immune cells in brain organoids improves model’s accuracy
Cortical organoids that contain non-neuronal brain cells called microglia may reflect human neurodevelopment more faithfully than those that don’t.
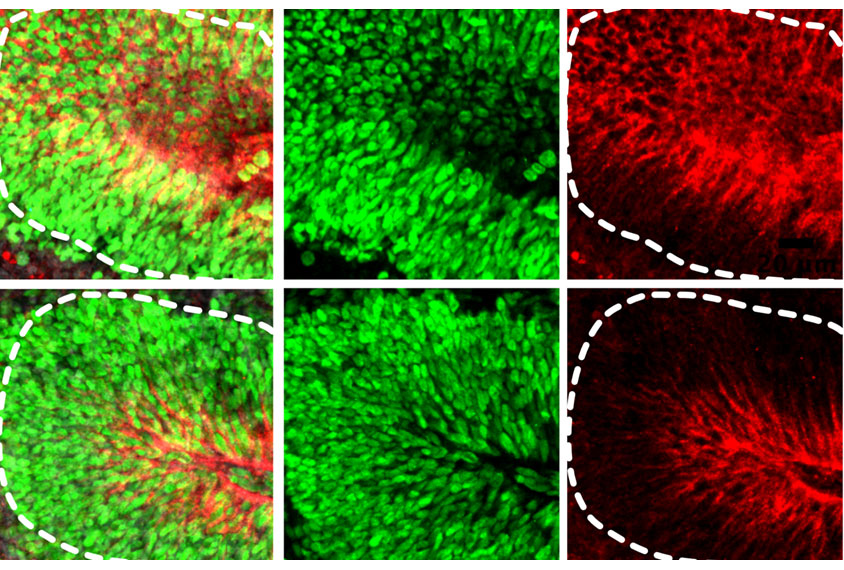
New studies reveal how autism might alter synapse formation, pruning
The work fills in gaps about how synapses change before and after birth — essential knowledge for understanding whether synapse development differs in autism.
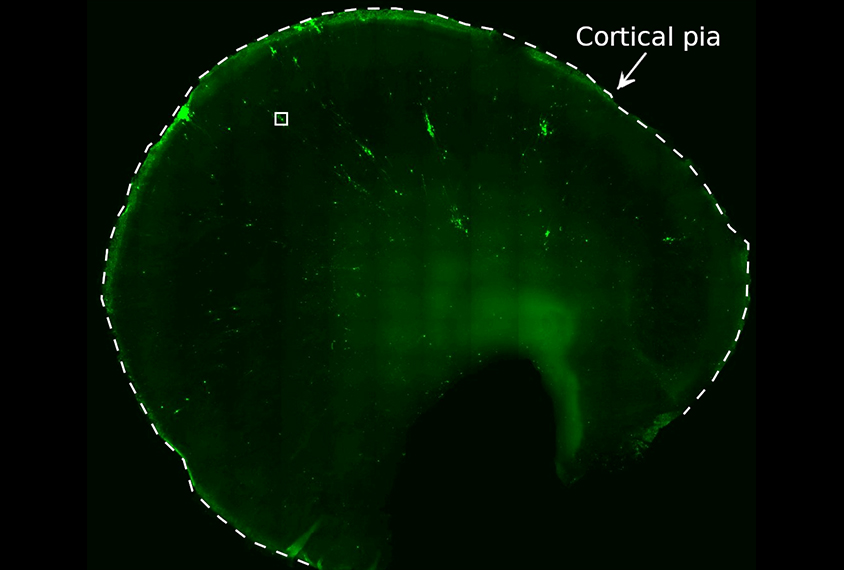
New studies reveal how autism might alter synapse formation, pruning
The work fills in gaps about how synapses change before and after birth — essential knowledge for understanding whether synapse development differs in autism.
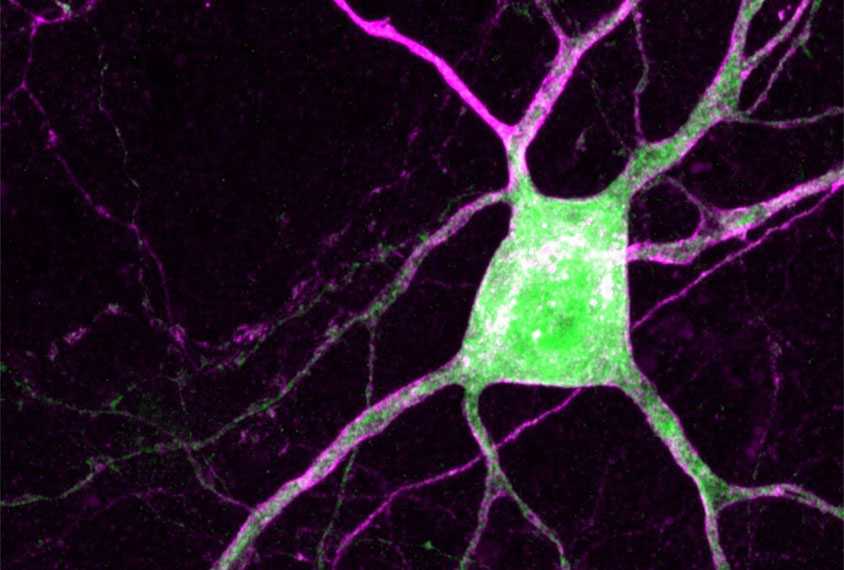
Gene therapy for rare form of autism may treat another
A MECP2 gene therapy for Rett syndrome eases repetitive behaviors, anxiety and hyperactivity in a mouse model of Pitt-Hopkins syndrome.
Gene therapy for rare form of autism may treat another
A MECP2 gene therapy for Rett syndrome eases repetitive behaviors, anxiety and hyperactivity in a mouse model of Pitt-Hopkins syndrome.
Dispatches from SfN 2021: Mitochondria, Rett therapy and oxytocin
These short reports from Spectrum journalists highlight some of the autism-related findings that caught our attention at the meeting this past week.
Dispatches from SfN 2021: Mitochondria, Rett therapy and oxytocin
These short reports from Spectrum journalists highlight some of the autism-related findings that caught our attention at the meeting this past week.
Technical issues force SfN presenters to improvise
Technical issues have plagued the 2021 Society for Neuroscience annual meeting, with presenters unable to log in for their virtual poster sessions and battling auto-captioning quirks.

Technical issues force SfN presenters to improvise
Technical issues have plagued the 2021 Society for Neuroscience annual meeting, with presenters unable to log in for their virtual poster sessions and battling auto-captioning quirks.
Reversing mutations in top autism-linked gene makes adult mice more social
Treatments that counteract the effects of an SCN2A mutation in mice increase the animals’ sociability in adulthood, according to a new unpublished study.
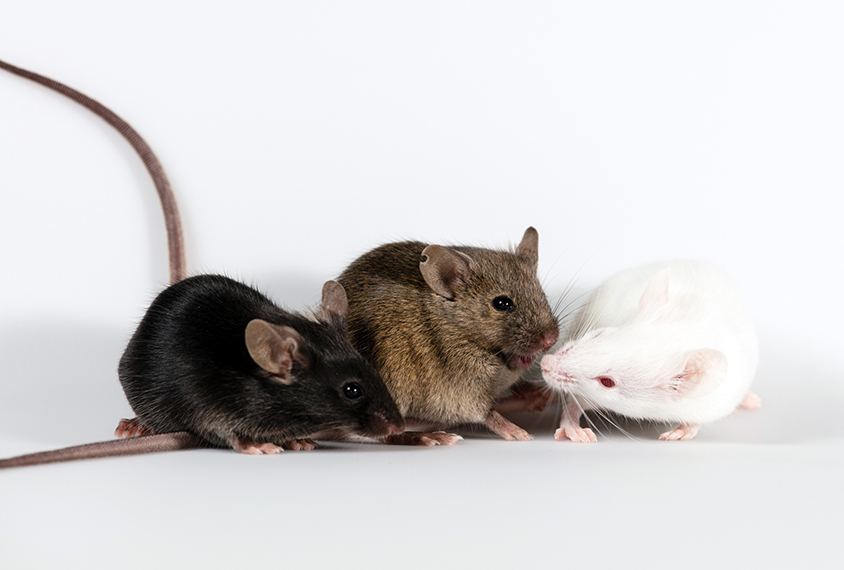

Reversing mutations in top autism-linked gene makes adult mice more social
Treatments that counteract the effects of an SCN2A mutation in mice increase the animals’ sociability in adulthood, according to a new unpublished study.
Despite calls to action, Black scientists remain underrepresented at neuroscience meetings
The percentage of Black researchers presenting at neuroscience conferences has increased by only a meager amount since the Black Lives Matter protests of 2020.
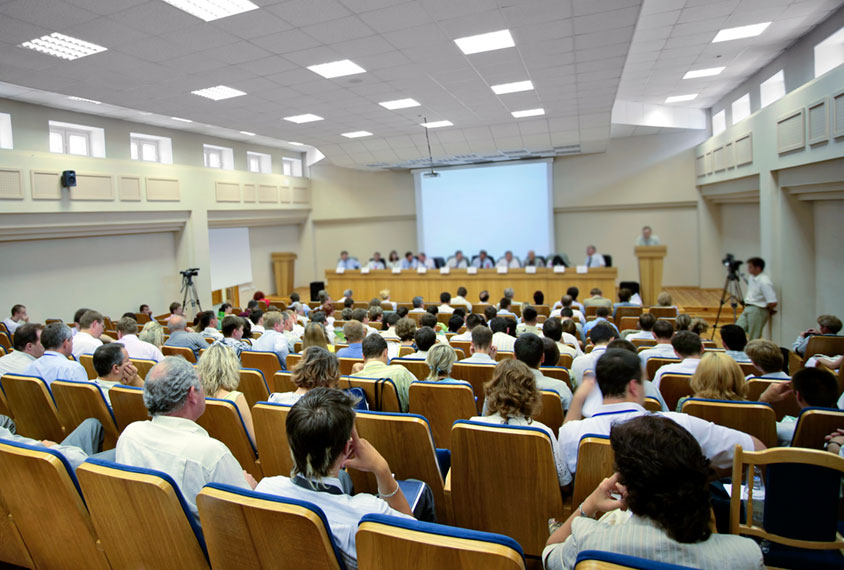

Despite calls to action, Black scientists remain underrepresented at neuroscience meetings
The percentage of Black researchers presenting at neuroscience conferences has increased by only a meager amount since the Black Lives Matter protests of 2020.
Auto-antibodies shape brain development in myriad ways
Animal models of autism rooted in exposure to maternal antibodies hint at different mechanisms.
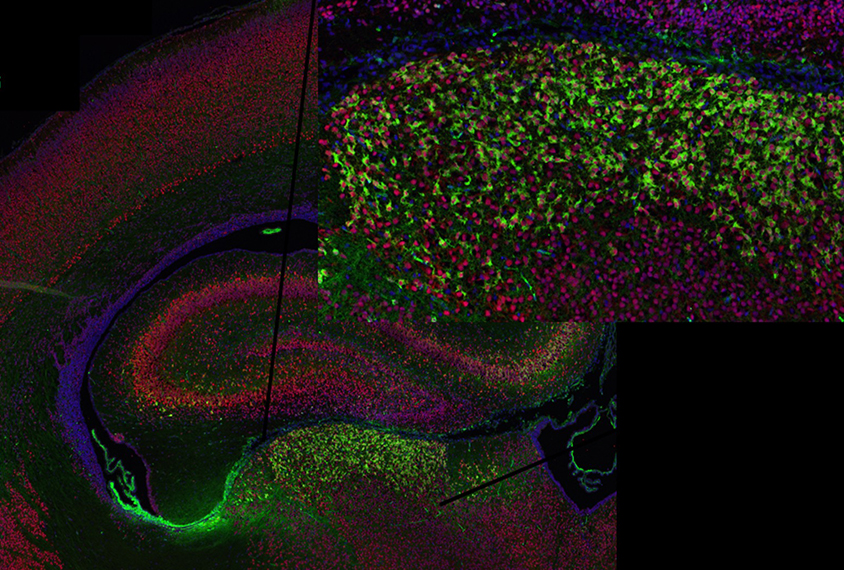
Auto-antibodies shape brain development in myriad ways
Animal models of autism rooted in exposure to maternal antibodies hint at different mechanisms.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Early trajectory of Alzheimer’s tracked in single-cell brain atlases
Inflammation in glia and the loss of certain inhibitory cells may kick off a disease cascade decades before diagnosis.
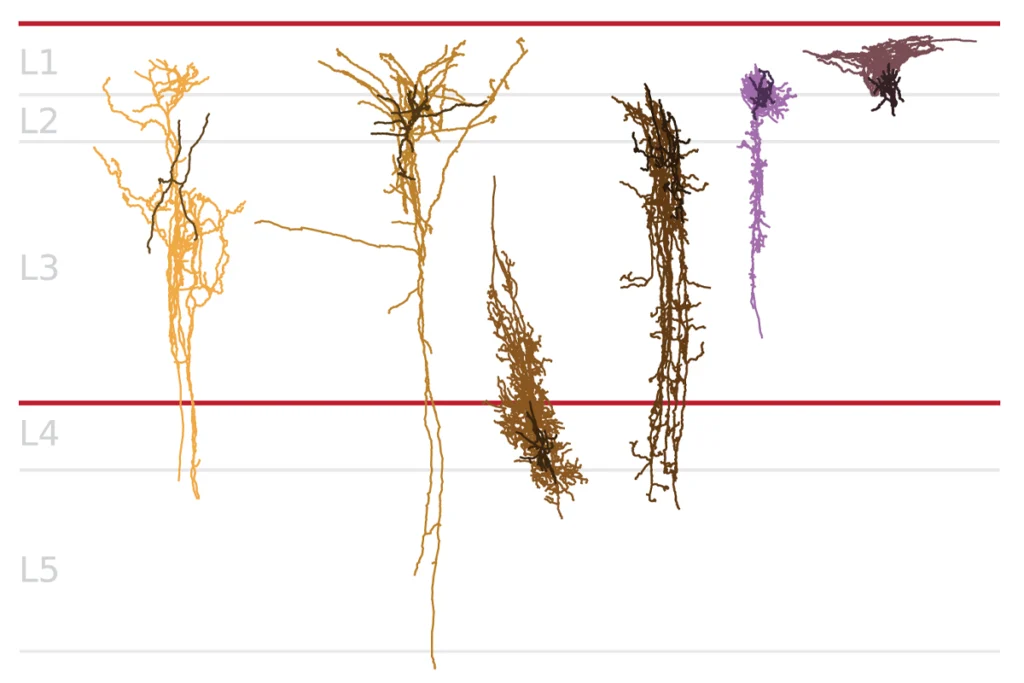

Early trajectory of Alzheimer’s tracked in single-cell brain atlases
Inflammation in glia and the loss of certain inhibitory cells may kick off a disease cascade decades before diagnosis.
Okur-Chung neurodevelopmental syndrome; excess CSF; autistic girls
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 21 October.
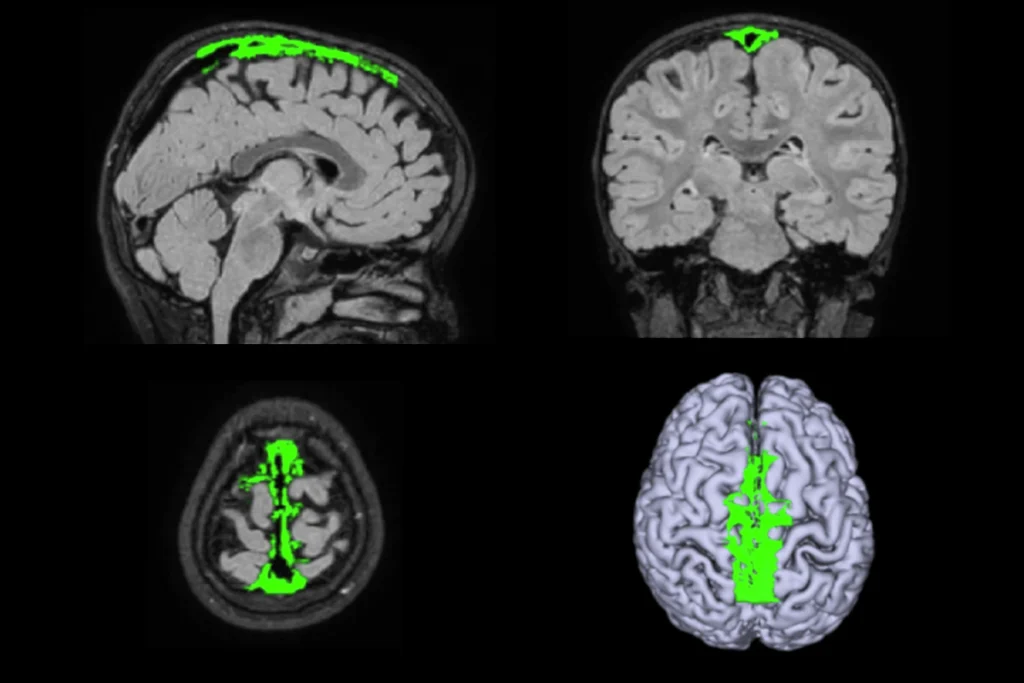
Okur-Chung neurodevelopmental syndrome; excess CSF; autistic girls
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 21 October.
Brains, biases and amyloid beta: Why the female brain deserves a closer look in Alzheimer’s research
New results suggest the disease progresses differently in women, but we need more basic science to unpack the mechanisms involved.

Brains, biases and amyloid beta: Why the female brain deserves a closer look in Alzheimer’s research
New results suggest the disease progresses differently in women, but we need more basic science to unpack the mechanisms involved.