SFN GC 2021
Recent articles
Lost sleep sparks lasting social problems in SHANK3 mice
Sleep disruption early in life has long-lasting consequences for mice missing a copy of the autism-linked gene SHANK3.

Lost sleep sparks lasting social problems in SHANK3 mice
Sleep disruption early in life has long-lasting consequences for mice missing a copy of the autism-linked gene SHANK3.
Organoids show how mutations in top autism gene may lead to brain overgrowth in people
The loss of CHD8, a top autism gene, speeds up the production of certain neurons and leads to overgrowth in spheres of cultured brain cells.
Organoids show how mutations in top autism gene may lead to brain overgrowth in people
The loss of CHD8, a top autism gene, speeds up the production of certain neurons and leads to overgrowth in spheres of cultured brain cells.
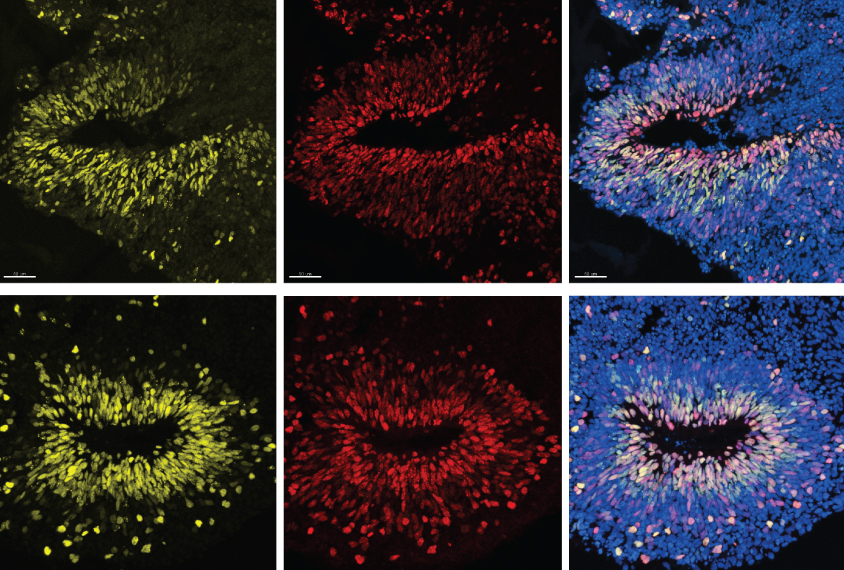
Oxytocin alters brain activity to boost sociability in mice missing autism gene
Infusions of the hormone oxytocin may make mice that model autism more social by normalizing their brain activity patterns.
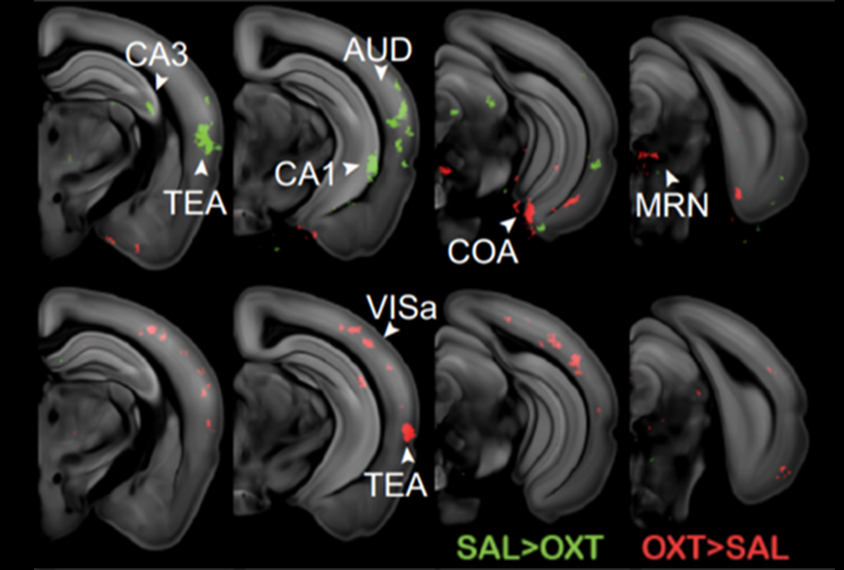
Oxytocin alters brain activity to boost sociability in mice missing autism gene
Infusions of the hormone oxytocin may make mice that model autism more social by normalizing their brain activity patterns.
Community newsletter: All about SfN Global Connectome
We dove into what people on social media thought about the SfN Global Connectome 2021 conference -- and its virtual format.

Community newsletter: All about SfN Global Connectome
We dove into what people on social media thought about the SfN Global Connectome 2021 conference -- and its virtual format.
Highlights, missed opportunities: SfN by the tweets
Participants video chatted and tweeted their way through the Society for Neuroscience’s three-day virtual conference this week.

Highlights, missed opportunities: SfN by the tweets
Participants video chatted and tweeted their way through the Society for Neuroscience’s three-day virtual conference this week.
Autistic children may have trouble predicting movements
Autistic children may have a harder time catching a ball than non-autistic children do, possibly because they are less able to predict its trajectory.

Autistic children may have trouble predicting movements
Autistic children may have a harder time catching a ball than non-autistic children do, possibly because they are less able to predict its trajectory.
Study hints at microbiome differences in children with autism
Children with autism may have a subtly different set of bacteria in their gut than their non-autistic siblings do.
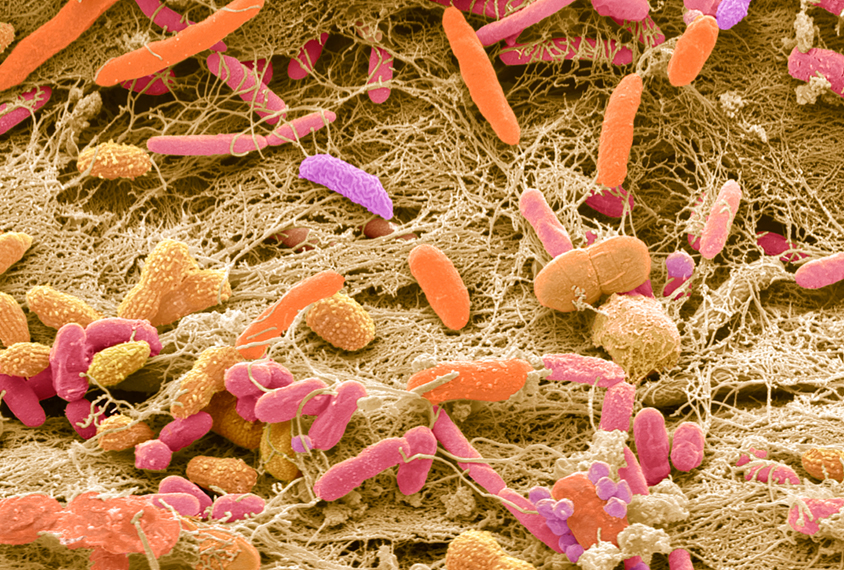
Study hints at microbiome differences in children with autism
Children with autism may have a subtly different set of bacteria in their gut than their non-autistic siblings do.
Autism protein may shape neuronal firing patterns
Cells with excess UBE3A, an autism-linked protein, have atypical firing properties that can be corrected by limiting the protein's levels, according to new research.
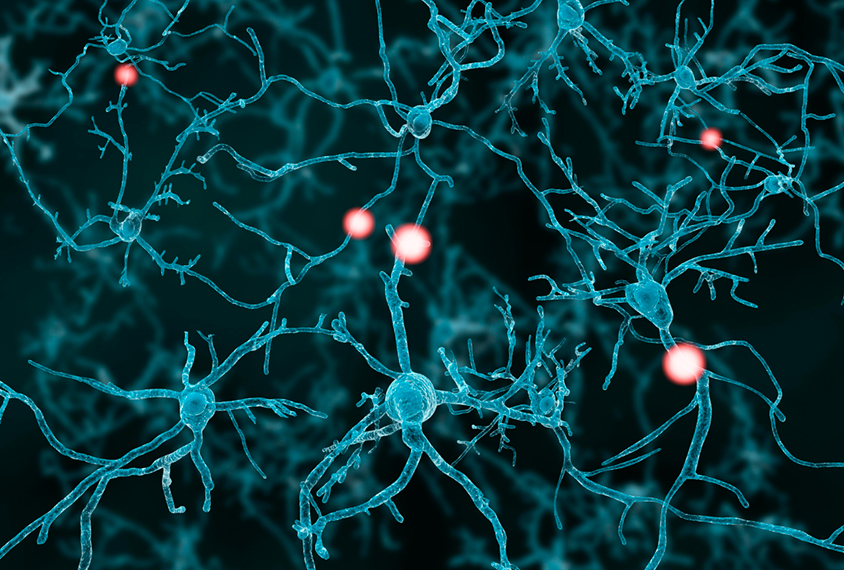
Autism protein may shape neuronal firing patterns
Cells with excess UBE3A, an autism-linked protein, have atypical firing properties that can be corrected by limiting the protein's levels, according to new research.
Inability to attend to cues may cause sensory challenges in fragile X mice
Sensory problems in people with fragile X syndrome may stem from hyperactive neurons, a mouse model study suggests.

Inability to attend to cues may cause sensory challenges in fragile X mice
Sensory problems in people with fragile X syndrome may stem from hyperactive neurons, a mouse model study suggests.
Malfunctioning neurons mute sound processing in mouse model of Rett syndrome
Female mice missing a copy of the autism-linked gene MECP2 in a specific set of inhibitory neurons have a hard time heeding pups’ calls and herding litters.

Malfunctioning neurons mute sound processing in mouse model of Rett syndrome
Female mice missing a copy of the autism-linked gene MECP2 in a specific set of inhibitory neurons have a hard time heeding pups’ calls and herding litters.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Machine learning spots neural progenitors in adult human brains
But the finding has not settled the long-standing debate over the existence and extent of neurogenesis during adulthood, says Yale University neuroscientist Juan Arellano.
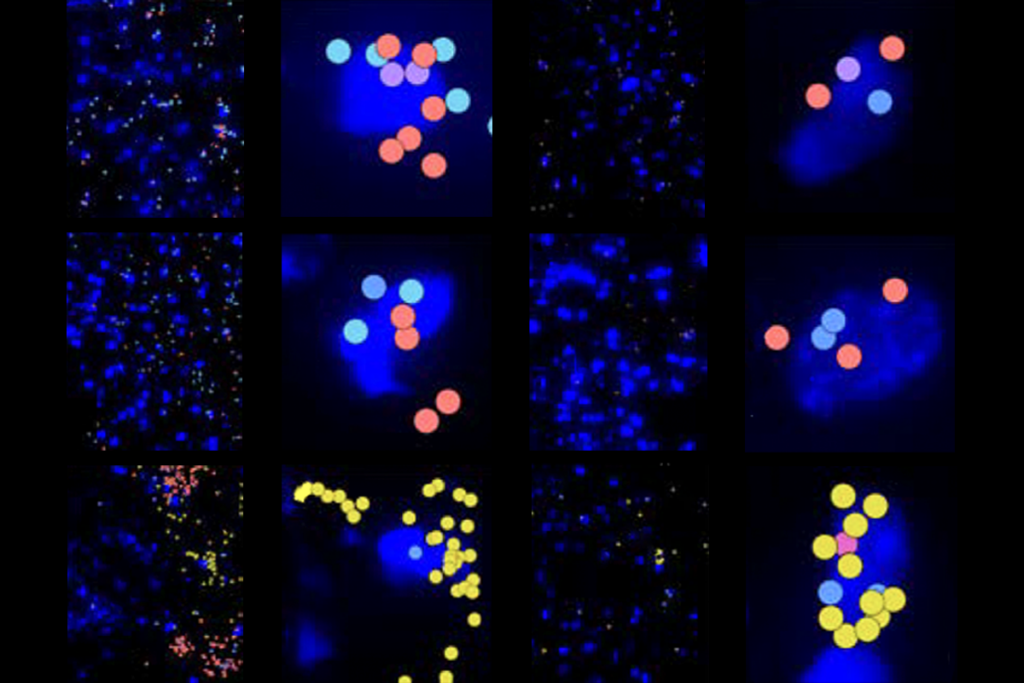
Machine learning spots neural progenitors in adult human brains
But the finding has not settled the long-standing debate over the existence and extent of neurogenesis during adulthood, says Yale University neuroscientist Juan Arellano.
Xiao-Jing Wang outlines the future of theoretical neuroscience
Wang discusses why he decided the time was right for a new theoretical neuroscience textbook and how bifurcation is a key missing concept in neuroscience explanations.
Xiao-Jing Wang outlines the future of theoretical neuroscience
Wang discusses why he decided the time was right for a new theoretical neuroscience textbook and how bifurcation is a key missing concept in neuroscience explanations.
Memory study sparks debate over statistical methods
Critics of a 2024 Nature paper suggest the authors failed to address the risk of false-positive findings. The authors argue more rigorous methods can result in missed leads.
Memory study sparks debate over statistical methods
Critics of a 2024 Nature paper suggest the authors failed to address the risk of false-positive findings. The authors argue more rigorous methods can result in missed leads.