SYNGAP1 2020
Recent articles
Reactions from the 2020 SYNGAP1 Scientific Conference
Spectrum is covering the 2020 International SYNGAP1 Scientific Conference, which took place virtually because of the coronavirus pandemic. Here we’re highlighting researchers’ reactions to noteworthy presentations.
Reactions from the 2020 SYNGAP1 Scientific Conference
Spectrum is covering the 2020 International SYNGAP1 Scientific Conference, which took place virtually because of the coronavirus pandemic. Here we’re highlighting researchers’ reactions to noteworthy presentations.
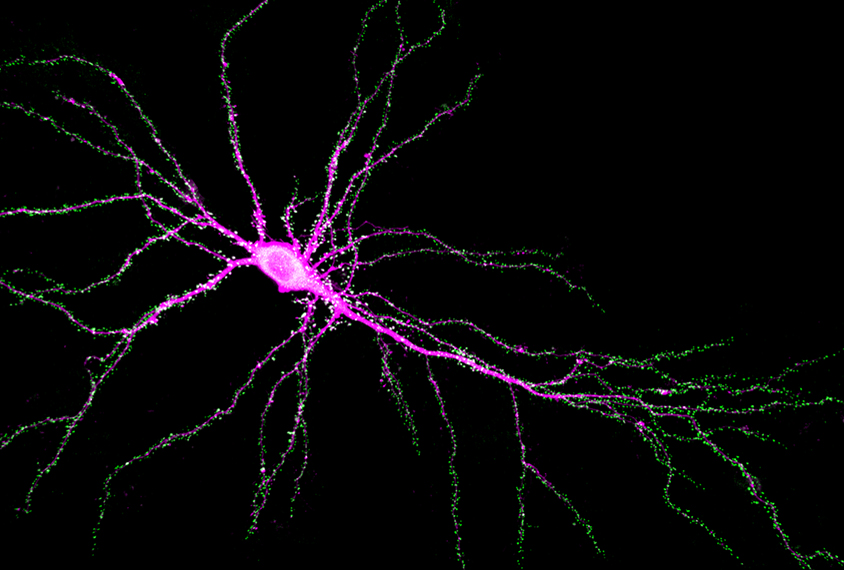
Zebrafish and ‘Smurf cakes’ link autism gene mutation to digestive woes
Mutations in a top autism gene called SYNGAP1 slow the rate at which zebrafish digest food and pass waste, and may also disrupt gut function in people.
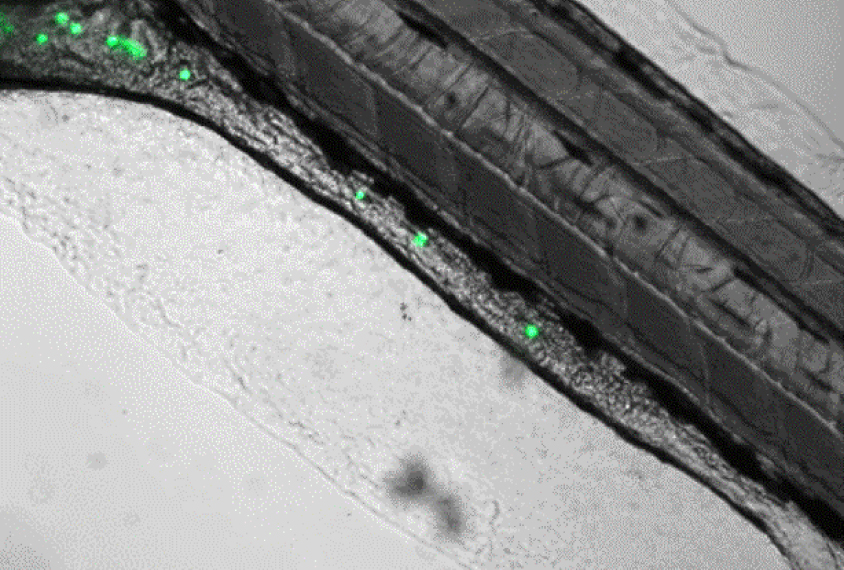
Zebrafish and ‘Smurf cakes’ link autism gene mutation to digestive woes
Mutations in a top autism gene called SYNGAP1 slow the rate at which zebrafish digest food and pass waste, and may also disrupt gut function in people.
Mice reveal roots of sensory issues tied to top autism gene
Mice with mutations in the autism-linked gene SYNGAP1 have trouble sensing touch, which may stem in part from brain-circuit alterations and dulled alertness.
Mice reveal roots of sensory issues tied to top autism gene
Mice with mutations in the autism-linked gene SYNGAP1 have trouble sensing touch, which may stem in part from brain-circuit alterations and dulled alertness.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Revised statistical bar extracts less-common variants from autism genetics studies
Adjusting genetic analyses could help plug autism’s heritability gap, according to a new preprint.

Revised statistical bar extracts less-common variants from autism genetics studies
Adjusting genetic analyses could help plug autism’s heritability gap, according to a new preprint.
Tom Griffiths describes how neural networks, logic and probability theory together explain cognition
In his new book, “The Laws of Thought,” Griffiths shows how these three pillars of study complement one another and together form a solid foundation to eventually explain all of our cognition, from brain to mind.
Tom Griffiths describes how neural networks, logic and probability theory together explain cognition
In his new book, “The Laws of Thought,” Griffiths shows how these three pillars of study complement one another and together form a solid foundation to eventually explain all of our cognition, from brain to mind.
This paper changed my life: Talia Lerner reflects on dopamine neuron diversity and the value of simple experiments
In a 2011 Neuron study, Stephan Lammel and his colleagues showed that dopamine neurons with different projections have different physiological properties. The work inspired Lerner to think about how to challenge widely held assumptions in the field.

This paper changed my life: Talia Lerner reflects on dopamine neuron diversity and the value of simple experiments
In a 2011 Neuron study, Stephan Lammel and his colleagues showed that dopamine neurons with different projections have different physiological properties. The work inspired Lerner to think about how to challenge widely held assumptions in the field.