Benjamin Philpot
Professor of neuroscience
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
From this contributor
Angelman syndrome: Bellwether for genetic therapy in autism
It is not a matter of whether there will be clinical trials of genetic therapy for Angelman syndrome, but when.
Angelman syndrome: Bellwether for genetic therapy in autism
Insights for autism from Angelman syndrome
Deletions or duplications of the UBE3A gene lead to both Angelman syndrome and some cases of autism, respectively. Studying the effects of altered gene dosage in this region will provide insights into brain defects and suggest targets for therapies for both disorders, says expert Benjamin Philpot.

Insights for autism from Angelman syndrome
Explore more from The Transmitter
Michael Shadlen explains how theory of mind ushers nonconscious thoughts into consciousness
All of our thoughts, mostly nonconscious, are interrogations of the world, Shadlen says. The opportunity to report our answers to ourselves or others brings a thought into conscious awareness.
Michael Shadlen explains how theory of mind ushers nonconscious thoughts into consciousness
All of our thoughts, mostly nonconscious, are interrogations of the world, Shadlen says. The opportunity to report our answers to ourselves or others brings a thought into conscious awareness.
‘Peer review is our strength’: Q&A with Walter Koroshetz, former NINDS director
In his first week off the job, the former National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke director urges U.S. scientists to remain optimistic about the future of neuroscience research, even if the executive branch “may not value what we do.”

‘Peer review is our strength’: Q&A with Walter Koroshetz, former NINDS director
In his first week off the job, the former National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke director urges U.S. scientists to remain optimistic about the future of neuroscience research, even if the executive branch “may not value what we do.”
Viral remnant in chimpanzees silences brain gene humans still use
The retroviral insert appears to inadvertently switch off a gene involved in brain development.
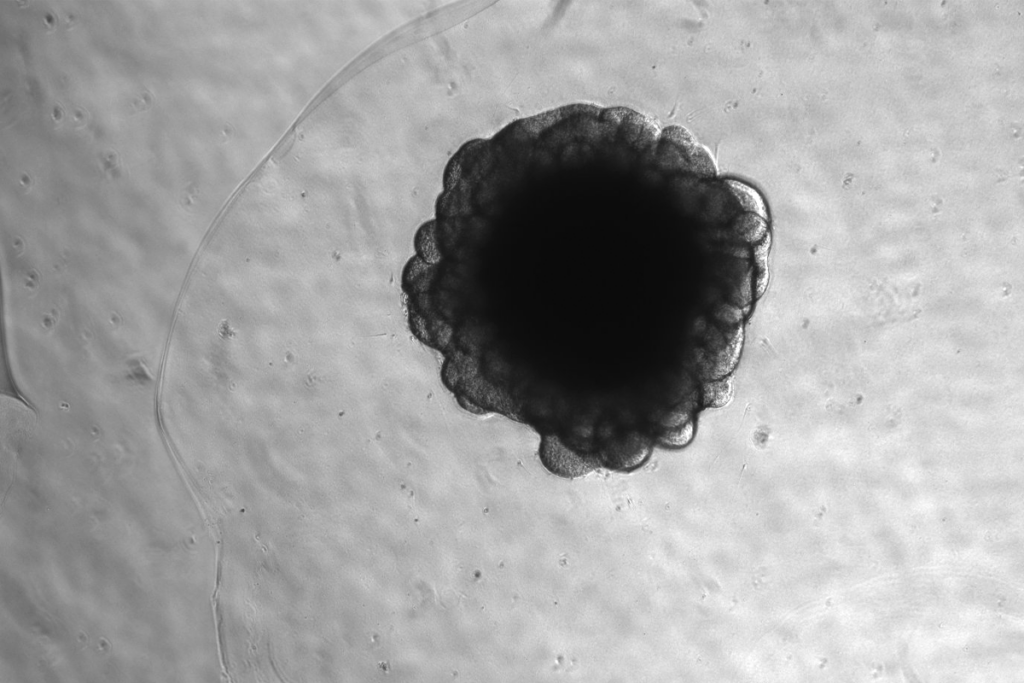
Viral remnant in chimpanzees silences brain gene humans still use
The retroviral insert appears to inadvertently switch off a gene involved in brain development.