Barbara Feder Ostrov, Senior Correspondent for California Healthline, has reported on medicine and health policy for more than 15 years. She covered the medical beat for the San Jose Mercury News for eight years and edited the website of the Center for Health Journalism at the USC Annenberg School of Journalism. She previously worked at The Palm Beach Post and the Miami Herald. Her work also has been published in The Boston Globe, Ms. Magazine, Atlantic.com, PBS NewsHour, NPR, CNN.com and EverydayHealth.com. She has won awards from the Society for Women’s Health Research, the California Newspaper Publishers Association and the Florida Press Club. She is based in San Jose, California.
Barbara Feder Ostrov
Kaiser Health News
From this contributor
How the college admissions cheating scandal hurts students with disabilities
In the wake of this week's college admissions cheating scandal, families and advocates are worried about a backlash that could make it harder for students with legitimate disabilities to get the accommodations the need.

How the college admissions cheating scandal hurts students with disabilities
Study of birth defects, folic acid in foods finds more questions than answers
Fortifying cereal and bread products with folic acid has not led to as dramatic a decline in congenital defects as expected.

Study of birth defects, folic acid in foods finds more questions than answers
Explore more from The Transmitter
Portfolio of SCN2A gene variants, and more
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 9 March.
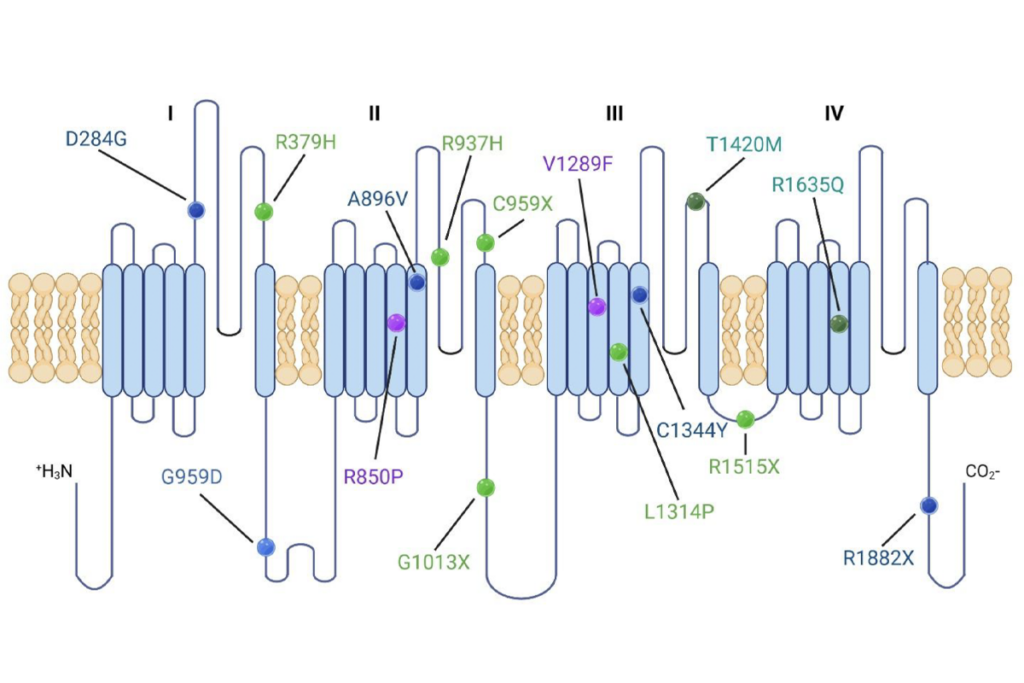
Portfolio of SCN2A gene variants, and more
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 9 March.
Hippocampus builds reputation as ‘general-purpose statistical learning machine’
New cross-species findings may help settle a long-standing debate about whether the hippocampus is required for passive learning.
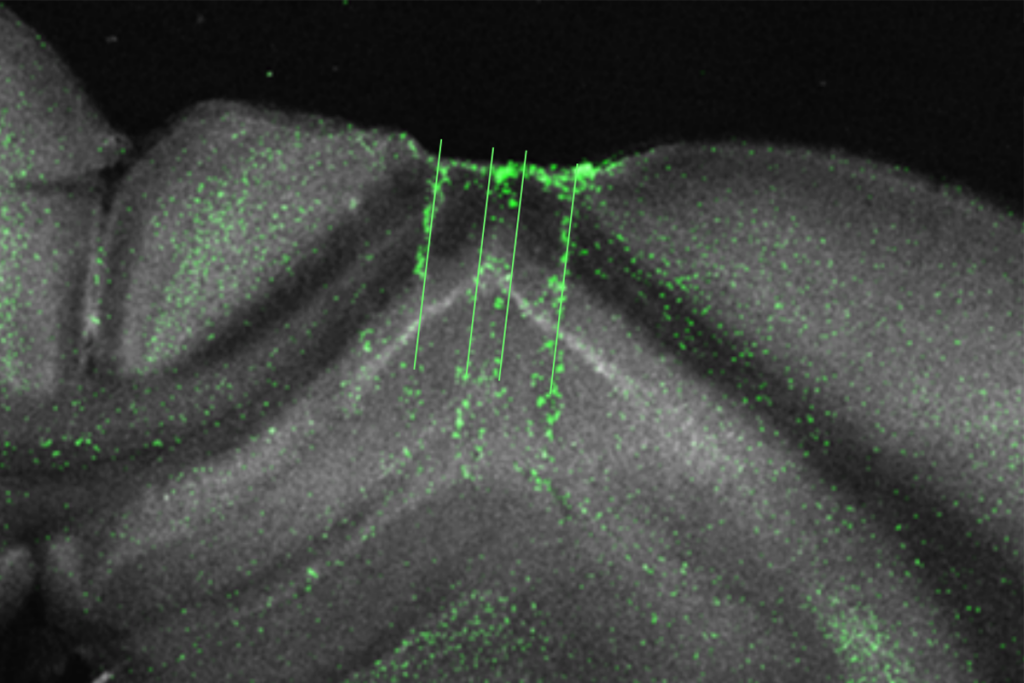
Hippocampus builds reputation as ‘general-purpose statistical learning machine’
New cross-species findings may help settle a long-standing debate about whether the hippocampus is required for passive learning.
‘The Fox, the Shrew, and You: How Brains Evolved,’ an excerpt
In his new book, Rogier Mars provides a detailed account of animal and human brain evolution. In this excerpt from Chapter 1, he starts with the sea squirt—and why it needs the brain it eats after its larval stage.

‘The Fox, the Shrew, and You: How Brains Evolved,’ an excerpt
In his new book, Rogier Mars provides a detailed account of animal and human brain evolution. In this excerpt from Chapter 1, he starts with the sea squirt—and why it needs the brain it eats after its larval stage.