Emma Bryce is a freelance journalist and editor based in London. Her work has appeared in publications including The Guardian, WIRED Magazine UK, Audubon Magazine, TED Education, The Atlantic, The New York Times, Slate, and Yale360. She’s written about everything from birds and oil rigs, to wave farms, insect consumption, and egg thieves. On her Guardian blog, World on a Plate, she also covers a range of issues relating to food and the environment. For TED Education, she edits scripts that get turned into animated videos.
Emma Bryce
Freelance writer
From this contributor
Advancing early interventions for autism
Some therapies use play and other activities to reinforce skills that autistic children often find challenging. Trials show these methods can change a child’s trajectory for the better, but the evidence base remains thin.
How the striatum is linked to autism
The repetitive behaviors seen in autism may originate in the striatum, a cluster of neurons involved with initiating and executing movements.
Repetitive behaviors and autism
New thinking about repetitive behaviors suggests they provide stress relief and fun for autistic people; as such, these behaviors deserve careful management.
How autism’s definition has changed over time
Don’t judge this book by its decidedly dull cover: Across its pages, some of the most dramatic changes in the history of autism have played out. This short animation chronicles how a diagnostic manual has defined and redefined autism over the years.
How autism’s definition has changed over time
Explore more from The Transmitter
Astrocytes orchestrate oxytocin’s social effects in mice
The cells amplify oxytocin—and may be responsible for sex differences in social behavior, two preprints find.
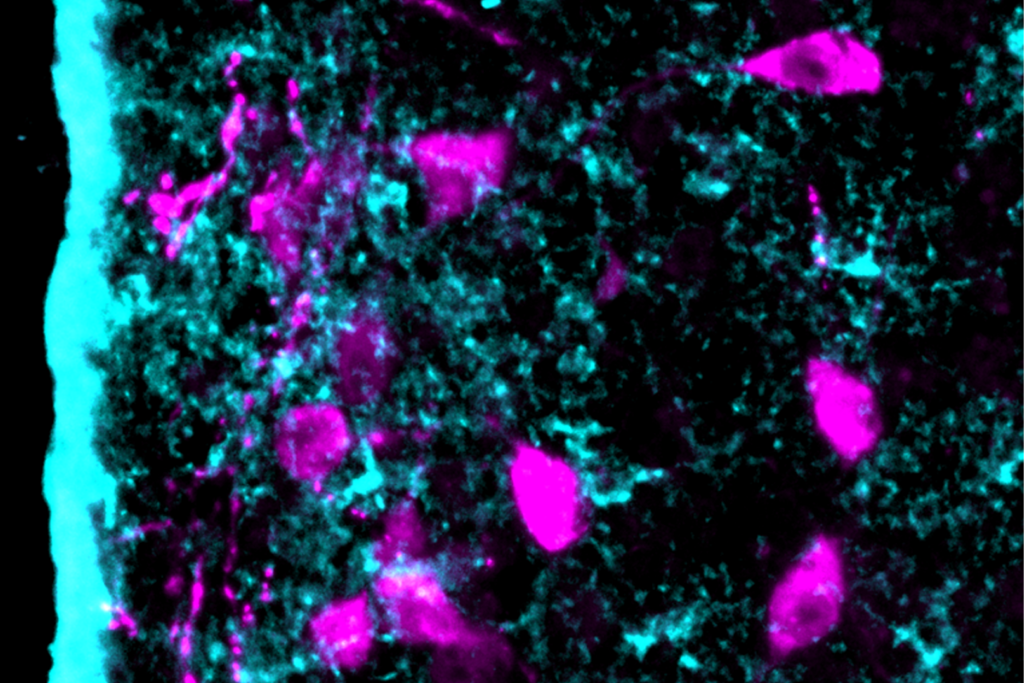
Astrocytes orchestrate oxytocin’s social effects in mice
The cells amplify oxytocin—and may be responsible for sex differences in social behavior, two preprints find.
Neuro’s ark: Spying on the secret sensory world of ticks
Carola Städele, a self-proclaimed “tick magnet,” studies the arachnids’ sensory neurobiology—in other words, how these tiny parasites zero in on their next meal.

Neuro’s ark: Spying on the secret sensory world of ticks
Carola Städele, a self-proclaimed “tick magnet,” studies the arachnids’ sensory neurobiology—in other words, how these tiny parasites zero in on their next meal.
Autism in old age, and more
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 2 March.
Autism in old age, and more
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 2 March.