Sneha Khedkar is a freelance science journalist based out of Bengaluru, India. She writes about health and life sciences. Her work has appeared in Scientific American, Knowable Magazine, New Scientist and The Scientist, among other publications. She completed an M.Sc. in biochemistry at the Maharaja Sayajirao University of Baroda, after which she was a research fellow studying stem cells in the skin. Her website is https://www.snehakhedkar.com/.

Sneha Khedkar
Contributing writer
From this contributor
Egyptian fruit bats’ neural patterns represent different experimenters
The findings underscore the importance of accounting for “experimenter effects” on lab animals.
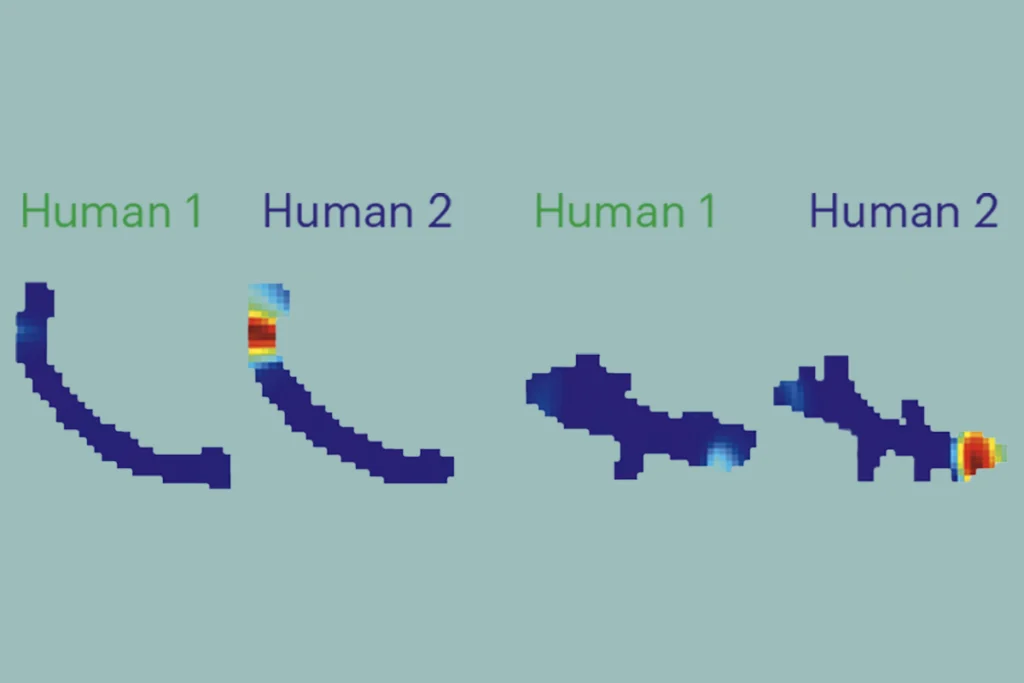
Egyptian fruit bats’ neural patterns represent different experimenters
Explore more from The Transmitter
Portfolio of SCN2A gene variants, and more
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 9 March.
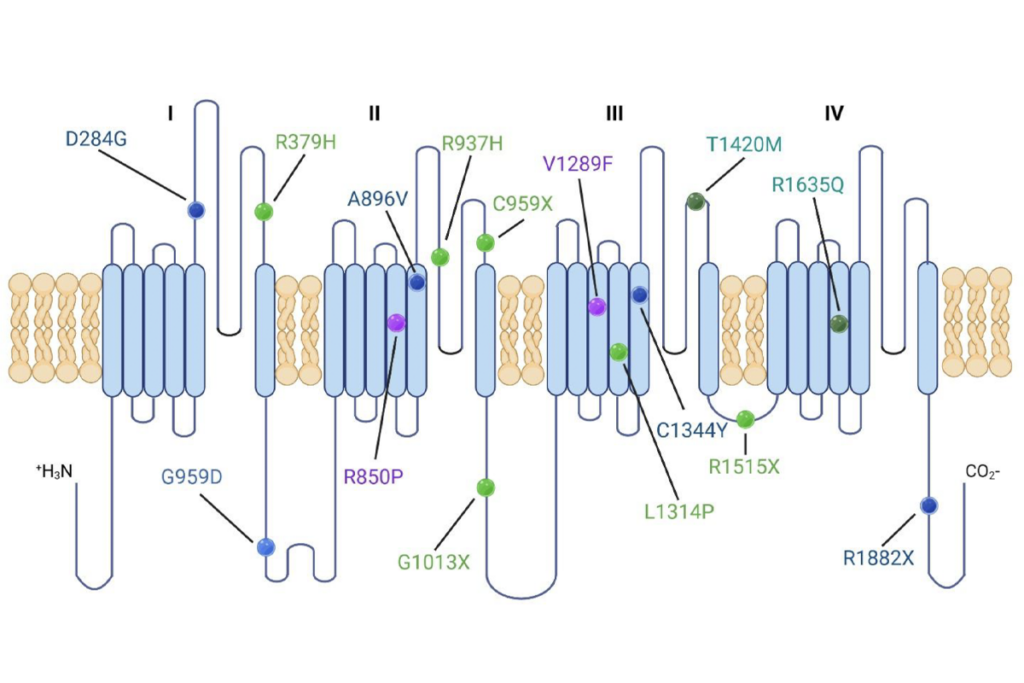
Portfolio of SCN2A gene variants, and more
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 9 March.
Hippocampus builds reputation as ‘general-purpose statistical learning machine’
New cross-species findings may help settle a long-standing debate about whether the hippocampus is required for passive learning.
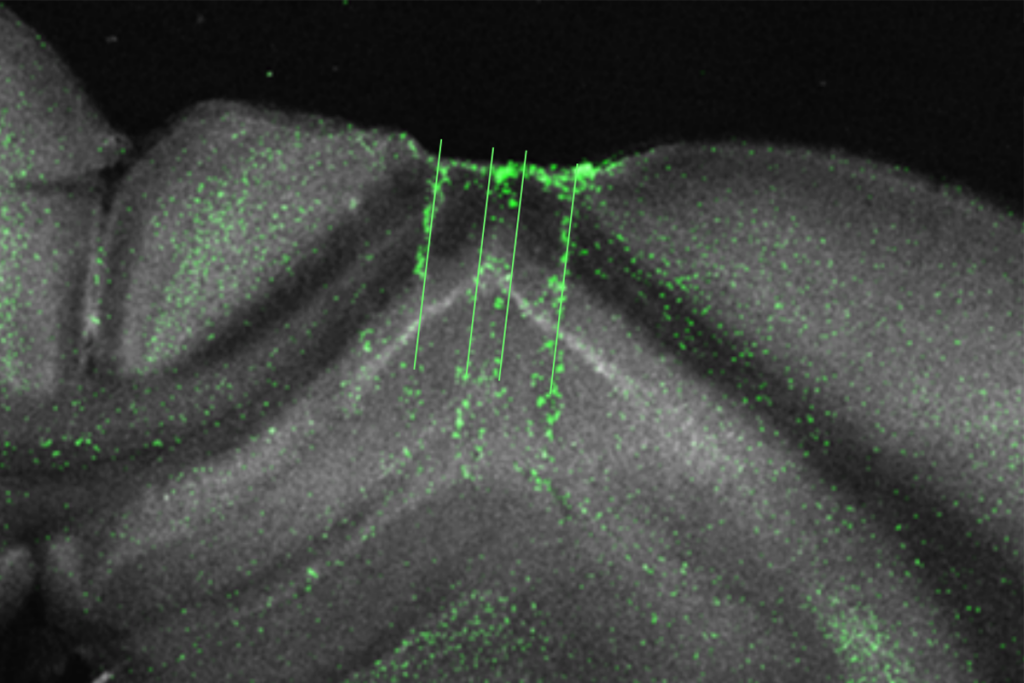
Hippocampus builds reputation as ‘general-purpose statistical learning machine’
New cross-species findings may help settle a long-standing debate about whether the hippocampus is required for passive learning.
‘The Fox, the Shrew, and You: How Brains Evolved,’ an excerpt
In his new book, Rogier Mars provides a detailed account of animal and human brain evolution. In this excerpt from Chapter 1, he starts with the sea squirt—and why it needs the brain it eats after its larval stage.

‘The Fox, the Shrew, and You: How Brains Evolved,’ an excerpt
In his new book, Rogier Mars provides a detailed account of animal and human brain evolution. In this excerpt from Chapter 1, he starts with the sea squirt—and why it needs the brain it eats after its larval stage.