SFN 2016
Recent articles
Ecstasy ingredient touted as treatment for anxiety in autism
The active ingredient in the drug popularly known as ecstasy eases social anxiety in people with autism.

Ecstasy ingredient touted as treatment for anxiety in autism
The active ingredient in the drug popularly known as ecstasy eases social anxiety in people with autism.
In autism, brain’s emotion hub begins with too many cells
The amygdala, a brain region that governs emotions, may be enlarged and overly connected in children with autism, but it shrinks as the children grow up.
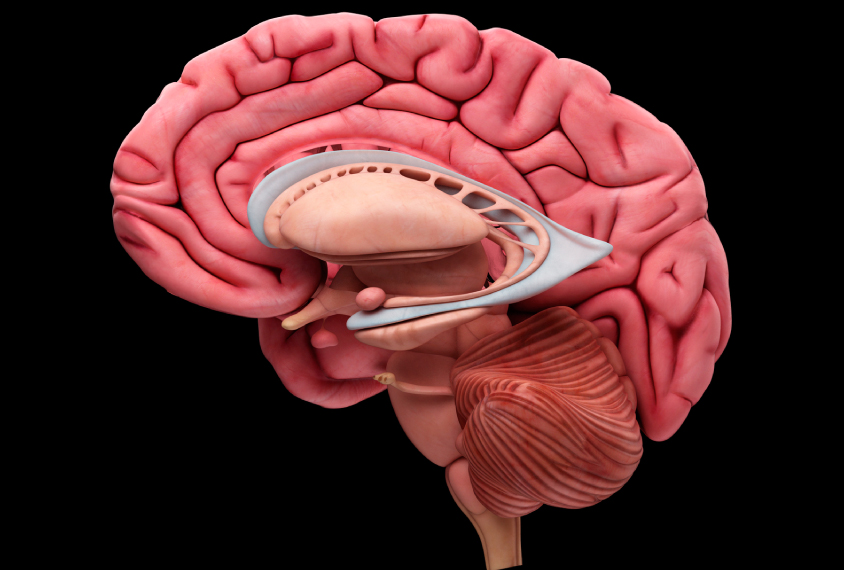
In autism, brain’s emotion hub begins with too many cells
The amygdala, a brain region that governs emotions, may be enlarged and overly connected in children with autism, but it shrinks as the children grow up.
Microglia may have only small appetite for synapses
Microglia come into frequent contact with synapses, the connections between neurons, but they appear to nibble on them rather than engulf and digest them.
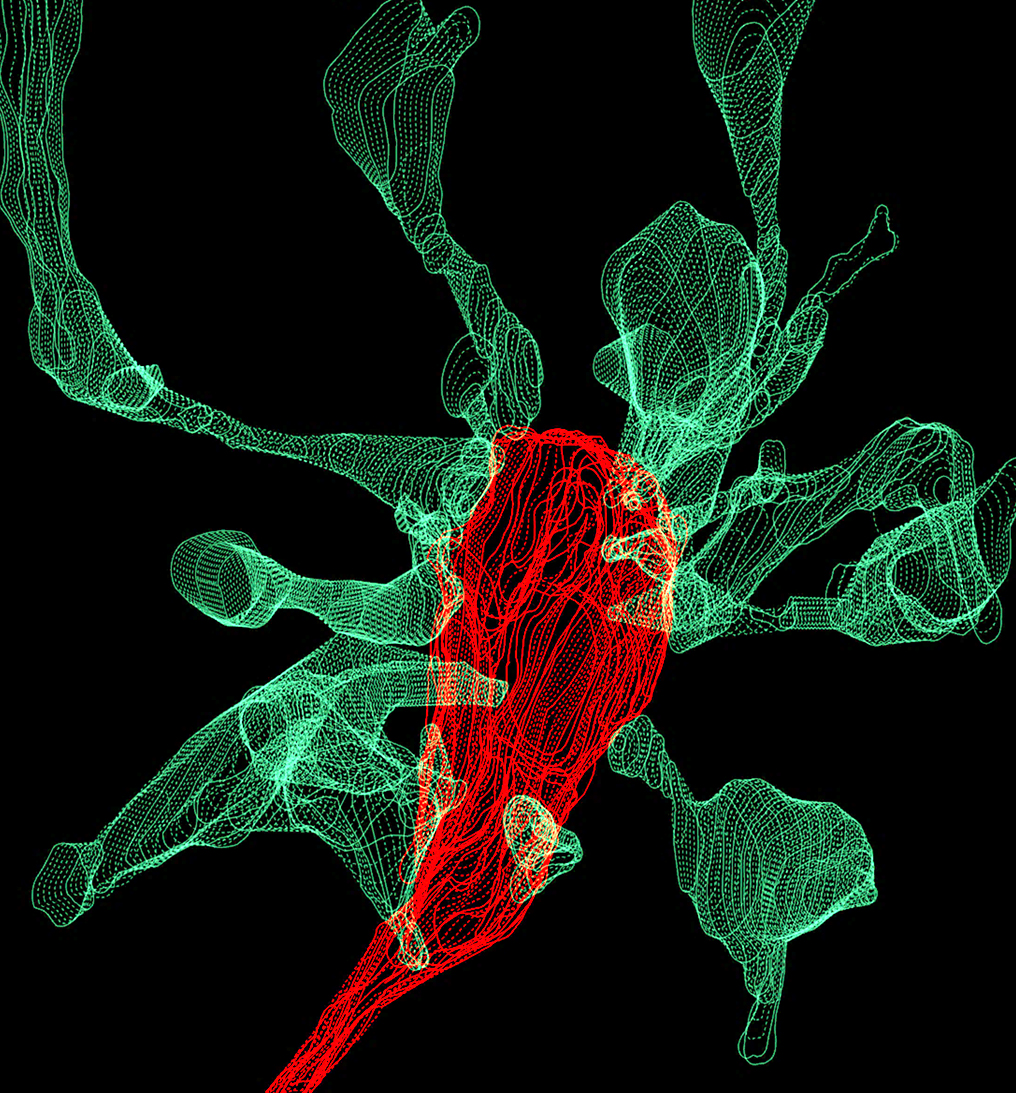
Microglia may have only small appetite for synapses
Microglia come into frequent contact with synapses, the connections between neurons, but they appear to nibble on them rather than engulf and digest them.
Gene on chromosome 16 may be valuable player in autism
Deleting one copy of a gene called MVP impairs the brain's ability to adapt to changes in the environment.

Gene on chromosome 16 may be valuable player in autism
Deleting one copy of a gene called MVP impairs the brain's ability to adapt to changes in the environment.
Takeaways from SfN 2016
Spectrum’s team reported about 50 stories at the Society for Neuroscience annual meeting in San Diego. One big theme this year: how autism relates to bigger questions in neuroscience.

Takeaways from SfN 2016
Spectrum’s team reported about 50 stories at the Society for Neuroscience annual meeting in San Diego. One big theme this year: how autism relates to bigger questions in neuroscience.
New test scores emotional weight of parent-child connections
Videos of mothers and their infants interacting with each other may contain clues to autism risk.

New test scores emotional weight of parent-child connections
Videos of mothers and their infants interacting with each other may contain clues to autism risk.
Autism treatments may normalize brain volume in adult mice
The effects of autism mutations on brain volume might be reversible, even in a mature brain.
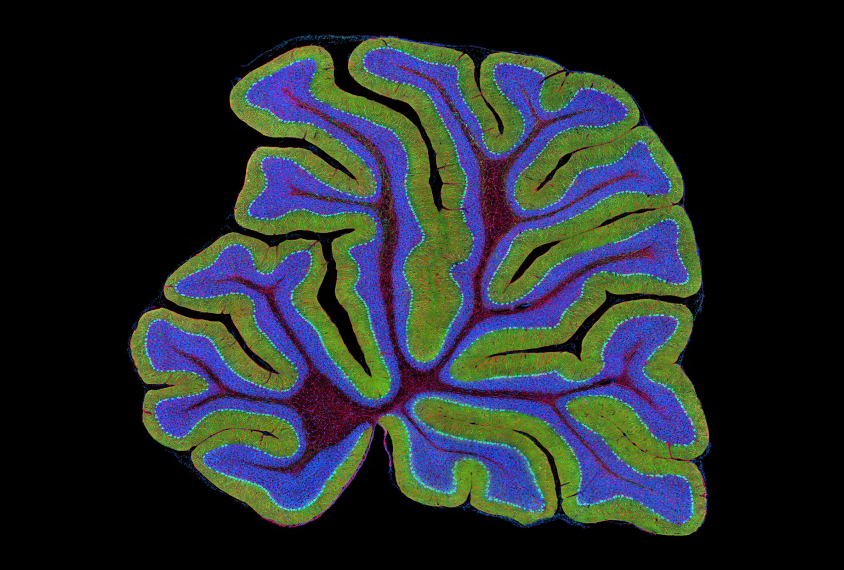
Autism treatments may normalize brain volume in adult mice
The effects of autism mutations on brain volume might be reversible, even in a mature brain.
New mice expose consequences of key autism gene
Mice with an extra copy of the autism risk gene UBE3A have cognitive deficits and anxiety, but do not show any core features of the condition.
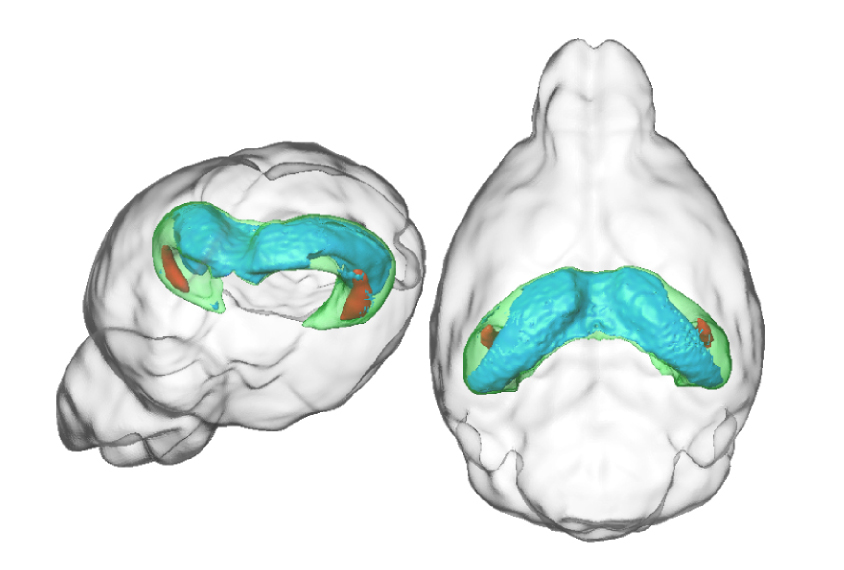
New mice expose consequences of key autism gene
Mice with an extra copy of the autism risk gene UBE3A have cognitive deficits and anxiety, but do not show any core features of the condition.
Genes, immune exposure collude to up autism risk
The interplay between a mouse’s immune system and certain mutations in her pups may increase autism-like features in the pups.
Genes, immune exposure collude to up autism risk
The interplay between a mouse’s immune system and certain mutations in her pups may increase autism-like features in the pups.
New tool takes rapid genetic snapshot of people’s neurons
A new approach quickly captures an individual’s gene expression pattern at the level of a single neuron.

New tool takes rapid genetic snapshot of people’s neurons
A new approach quickly captures an individual’s gene expression pattern at the level of a single neuron.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Worms help untangle brain structure/function mystery
The synaptic connectome of most animals bears little resemblance to functional brain maps, but it can still predict neuronal activity, according to two preprints that tackle the puzzle in C. elegans.

Worms help untangle brain structure/function mystery
The synaptic connectome of most animals bears little resemblance to functional brain maps, but it can still predict neuronal activity, according to two preprints that tackle the puzzle in C. elegans.
Microglia nurture young interneurons
The immune cells secrete a growth factor that “sets the supply of GABAergic interneurons in the developing brain.”
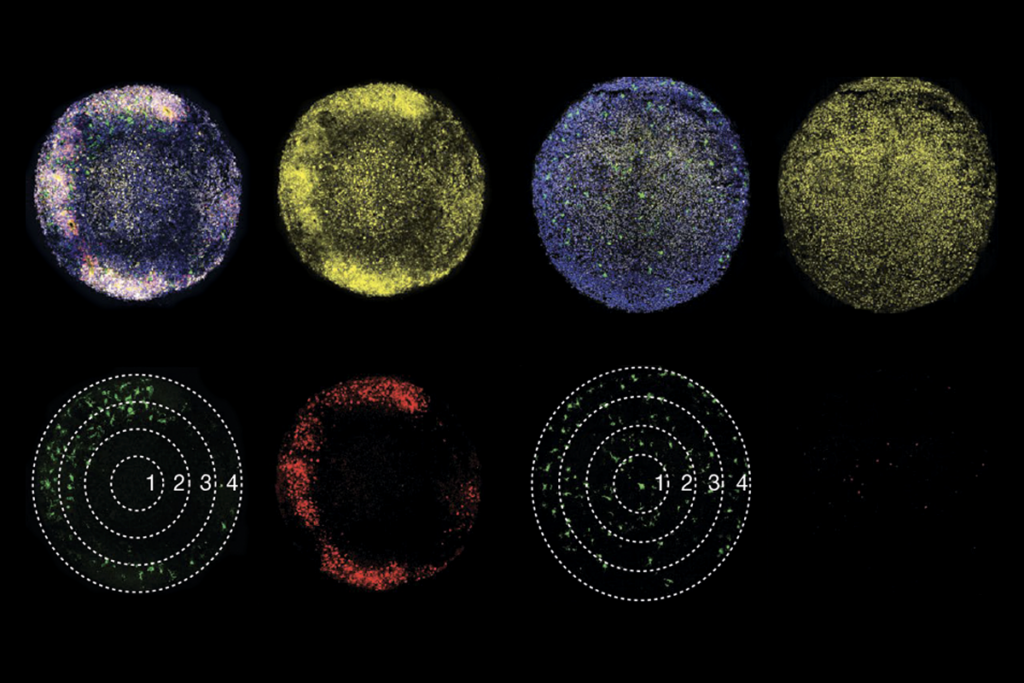
Microglia nurture young interneurons
The immune cells secrete a growth factor that “sets the supply of GABAergic interneurons in the developing brain.”
Xaq Pitkow shares his principles for studying cognition in our imperfect brains and bodies
Pitkow discusses how evolution's messy constraints shape optimal brain algorithms, from Bayesian inference to ecological affordances.
Xaq Pitkow shares his principles for studying cognition in our imperfect brains and bodies
Pitkow discusses how evolution's messy constraints shape optimal brain algorithms, from Bayesian inference to ecological affordances.