SFN 2018
Recent articles
Distinct brain pathway underlies ecstasy’s social effects
The drug popularly known as ecstasy may boost sociability through brain circuits distinct from that underlying its 'high.'
Distinct brain pathway underlies ecstasy’s social effects
The drug popularly known as ecstasy may boost sociability through brain circuits distinct from that underlying its 'high.'
Brain organoids show realistic neuronal firing rhythms
Brain organoids made from typical human stem cells begin to show synchronized neuronal firing patterns after growing in a dish for at least four months.

Brain organoids show realistic neuronal firing rhythms
Brain organoids made from typical human stem cells begin to show synchronized neuronal firing patterns after growing in a dish for at least four months.
Invisible man? Move over for invisible mouse
A combination of chemical cocktails has created mice that are — yes — virtually invisible. And new imaging technology reveals the mice's underlying nerves and lymphatic system in unprecedented detail.
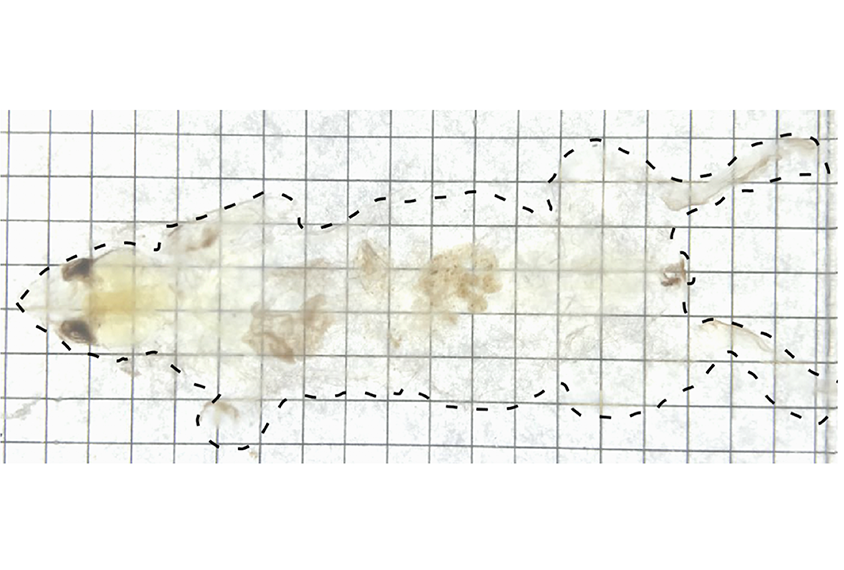
Invisible man? Move over for invisible mouse
A combination of chemical cocktails has created mice that are — yes — virtually invisible. And new imaging technology reveals the mice's underlying nerves and lymphatic system in unprecedented detail.
Takeaways from SfN 2018
After the presentation of more than 14,000 abstracts over five days, the Society for Neuroscience annual meeting in San Diego ended last week.

Takeaways from SfN 2018
After the presentation of more than 14,000 abstracts over five days, the Society for Neuroscience annual meeting in San Diego ended last week.
Monkey motion-capture reveals social behavior in 3-D
A monkey-sized jacket embedded with motion sensors — similar to technology used to animate creatures in movies — is helping researchers develop the common marmoset as a model for studying human social behavior.

Monkey motion-capture reveals social behavior in 3-D
A monkey-sized jacket embedded with motion sensors — similar to technology used to animate creatures in movies — is helping researchers develop the common marmoset as a model for studying human social behavior.
Drug duo delivers brain, behavioral benefits for fragile X syndrome
Administering a cholesterol drug alongside an antibiotic eases atypical behavior and restores the signaling balance in the brains of people with fragile X syndrome.

Drug duo delivers brain, behavioral benefits for fragile X syndrome
Administering a cholesterol drug alongside an antibiotic eases atypical behavior and restores the signaling balance in the brains of people with fragile X syndrome.
Mouse, human ‘co-clinical’ trials could speed autism drug discovery
A team of researchers is trialing a fast approach to autism drug development: simultaneously testing candidates in people and in mice.

Mouse, human ‘co-clinical’ trials could speed autism drug discovery
A team of researchers is trialing a fast approach to autism drug development: simultaneously testing candidates in people and in mice.
Webbing around neurons altered in autism mouse models
Lattice-like structures that surround neurons may be overly abundant — or scarce — in brain regions of three autism mouse models.

Webbing around neurons altered in autism mouse models
Lattice-like structures that surround neurons may be overly abundant — or scarce — in brain regions of three autism mouse models.
Study tracks social brain development in African infants
An inexpensive, noninvasive method can track social brain development in infants in low-resource countries.
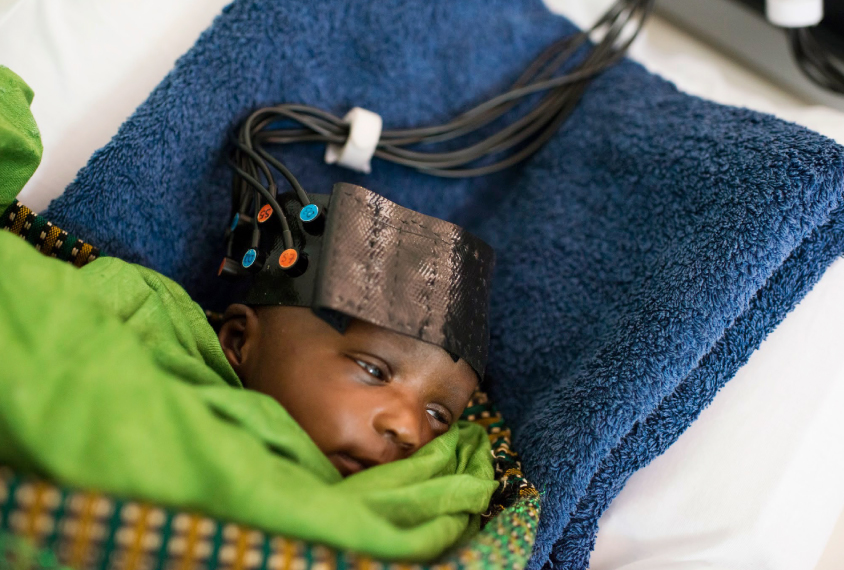
Study tracks social brain development in African infants
An inexpensive, noninvasive method can track social brain development in infants in low-resource countries.
Gene expression ‘barcode’ maps cells in brain tissue
A new technique transforms the previous broad-brush picture of a brain region into a pointillist masterpiece of neuronal subpopulations associated with specific activities.
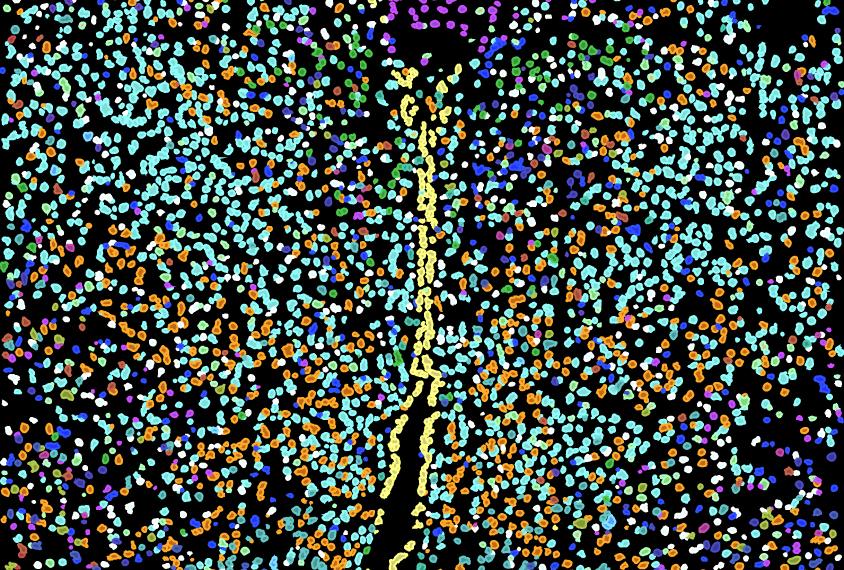
Gene expression ‘barcode’ maps cells in brain tissue
A new technique transforms the previous broad-brush picture of a brain region into a pointillist masterpiece of neuronal subpopulations associated with specific activities.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Securing the academic pipeline amid uncertain U.S. funding climate
Finding creative ways to keep early-career researchers in academia—for example, through part-time roles—can help the field weather the storm.

Securing the academic pipeline amid uncertain U.S. funding climate
Finding creative ways to keep early-career researchers in academia—for example, through part-time roles—can help the field weather the storm.
Let’s teach neuroscientists how to be thoughtful and fair reviewers
Blanco-Suárez revamped the traditional journal club by developing a course in which students peer review preprints alongside the published papers that evolved from them.

Let’s teach neuroscientists how to be thoughtful and fair reviewers
Blanco-Suárez revamped the traditional journal club by developing a course in which students peer review preprints alongside the published papers that evolved from them.
New autism committee positions itself as science-backed alternative to government group
The Independent Autism Coordinating Committee plans to meet at the same time as the U.S. federal Interagency Autism Coordinating Committee later this month—and offer its own research agenda.

New autism committee positions itself as science-backed alternative to government group
The Independent Autism Coordinating Committee plans to meet at the same time as the U.S. federal Interagency Autism Coordinating Committee later this month—and offer its own research agenda.