New labels: We’re closely following coverage tied to last week’s White House press conference about autism, in which U.S. federal administration officials announced plans to add warnings for pregnant people on acetaminophen (Tylenol) labels and to approve the supplement leucovorin for autism treatment. STAT reported on the “unreliable” testimony the Trump administration cited in asserting a link between Tylenol use during pregnancy and autism. (A 2024 sibling study found no such link.) Endpoints News covered a highly unusual move by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration—requesting that leucovorin’s maker, GSK (formerly known as GlaxoSmithKline), add cerebral folate deficiency, which can cause autism-like traits, as an indication to its label without supplying supporting evidence for the change. Meanwhile, KFF Health News shared the dismay and frustrations of autism experts in academia, government and nonprofit organizations, as did The Transmitter. See also coverage in Nature and Science.
More autism research we spotted:
- “GRIN2B-mutant mice exhibit heightened remote fear via suppressed extinction and chronic amygdalar synaptic and neuronal dysfunction” Science Advances
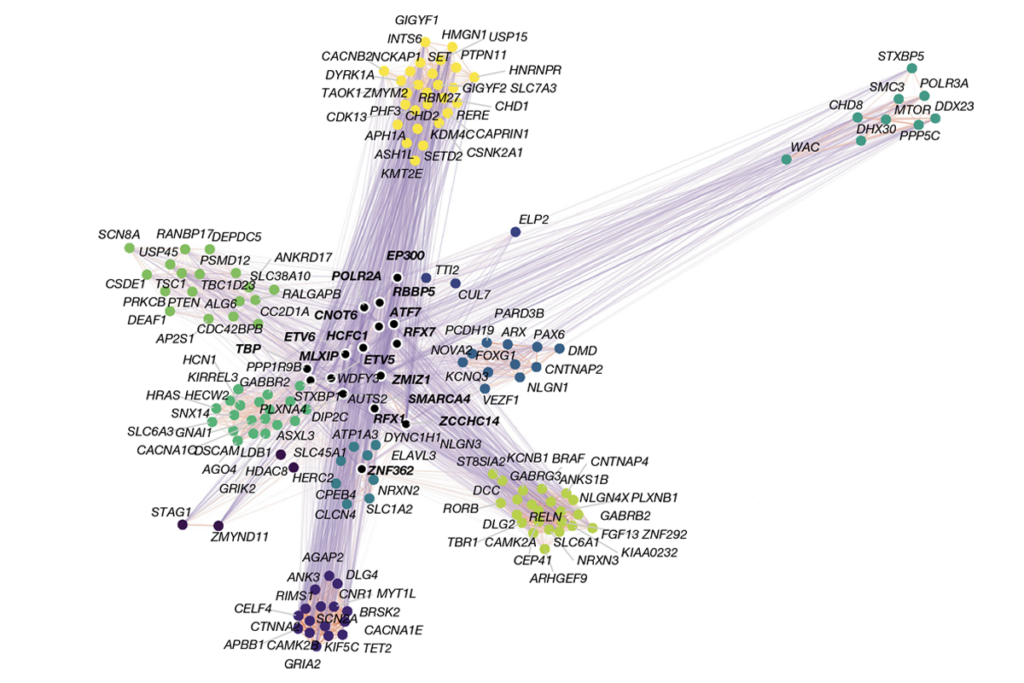
- “Cell-type-specific dysregulation of gene expression due to CHD8 haploinsufficiency during mouse cortical development” Cell Genomics
- “Neural mechanisms contributing to increased acoustic startle reactivity in CNTNAP2 knock-out rats” Neuroscience
See also: “Sensory troubles may yield key clues to autism’s origins” - “Association of umbilical cord blood serotonin levels with neurodevelopmental outcomes” Developmental Neuroscience
See also: “Serotonin’s link to autism, explained” - “Impaired thalamic burst firing in fragile X syndrome” Cell Reports