Axons
Recent articles
How developing neurons simplify their search for a synaptic mate
Streamlining the problem from 3D to 1D eases the expedition—a strategy the study investigators deployed to rewire an olfactory circuit in flies.
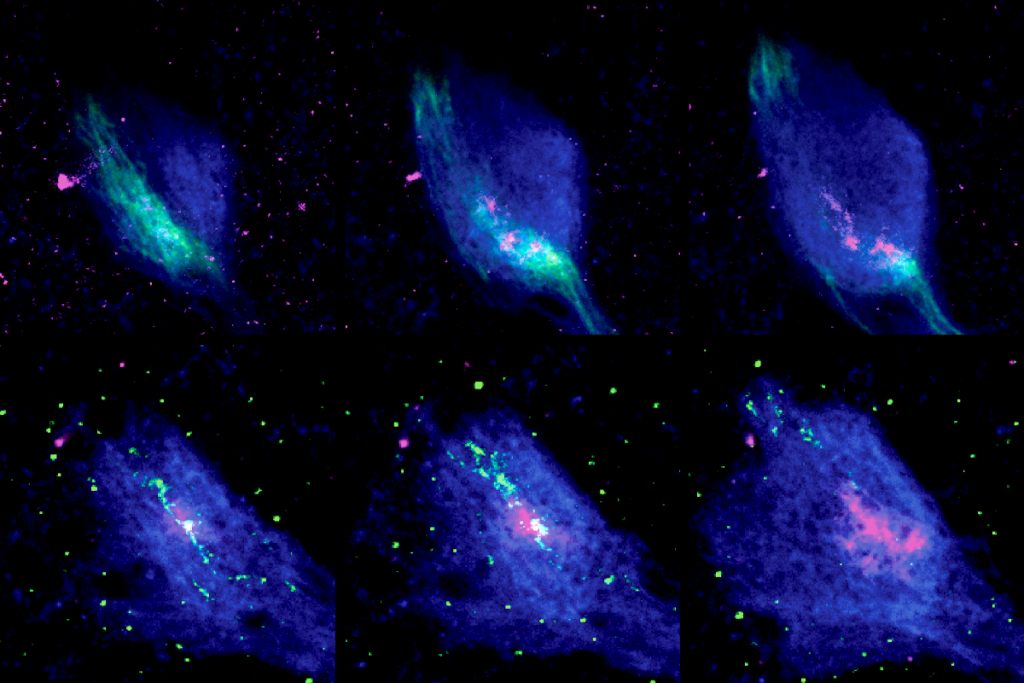

How developing neurons simplify their search for a synaptic mate
Streamlining the problem from 3D to 1D eases the expedition—a strategy the study investigators deployed to rewire an olfactory circuit in flies.
Learning in living mice defies classic synaptic plasticity rule
Donald Hebb’s theory—memorably summarized as “cells that fire together, wire together”—does not explain the shifting hippocampal connections in mice learning to navigate a virtual environment, according to a new study.

Learning in living mice defies classic synaptic plasticity rule
Donald Hebb’s theory—memorably summarized as “cells that fire together, wire together”—does not explain the shifting hippocampal connections in mice learning to navigate a virtual environment, according to a new study.
Inhibitory cells work in concert to orchestrate neuronal activity in mouse brain
A cubic millimeter of brain tissue, meticulously sectioned, stained and scrutinized over the past seven years, reveals in stunning detail the role of inhibitory interneurons in brain structure and function.
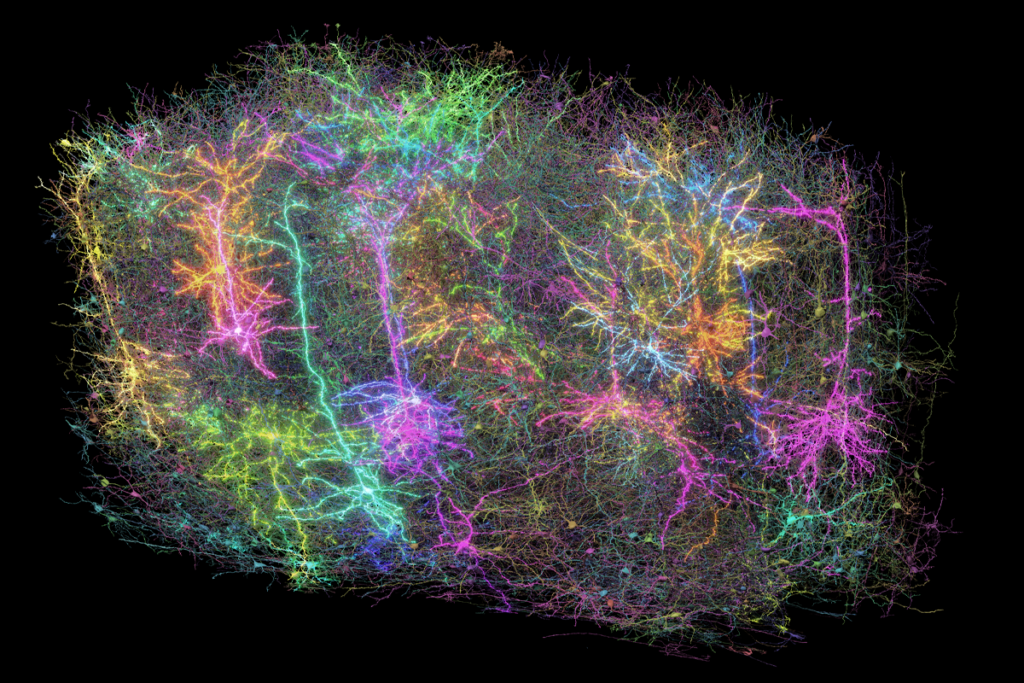
Inhibitory cells work in concert to orchestrate neuronal activity in mouse brain
A cubic millimeter of brain tissue, meticulously sectioned, stained and scrutinized over the past seven years, reveals in stunning detail the role of inhibitory interneurons in brain structure and function.
Some social issues in DYRK1A model mice stem from faulty inhibitory circuits
Alterations in inhibitory circuits and difficulties in social recognition characterize mice missing one copy of DYRK1A, a gene linked to autism.
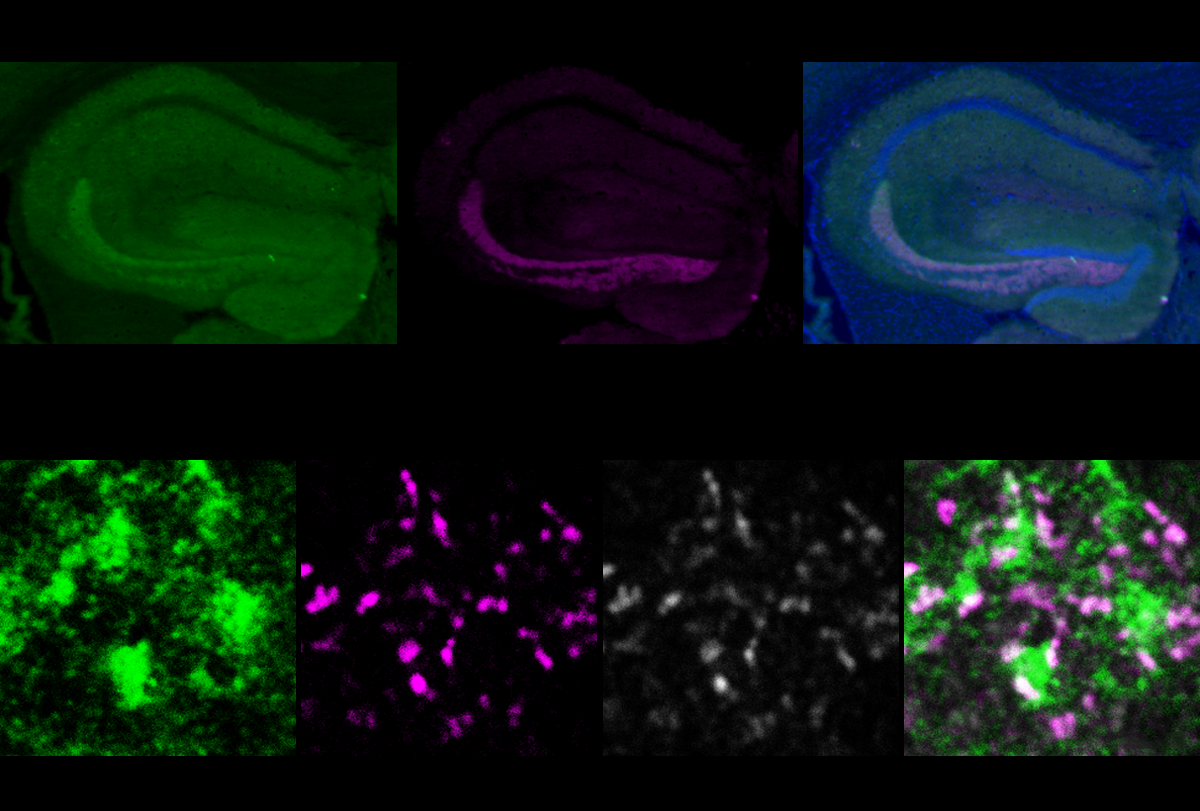
Some social issues in DYRK1A model mice stem from faulty inhibitory circuits
Alterations in inhibitory circuits and difficulties in social recognition characterize mice missing one copy of DYRK1A, a gene linked to autism.
UBE3A’s link to synaptic pruning bolstered by fly study
Increasing or reducing the levels of the UBE3A gene, which is associated with autism and autism-related syndromes, results in altered patterns of synaptic pruning — a process that snips away brain cell connections.
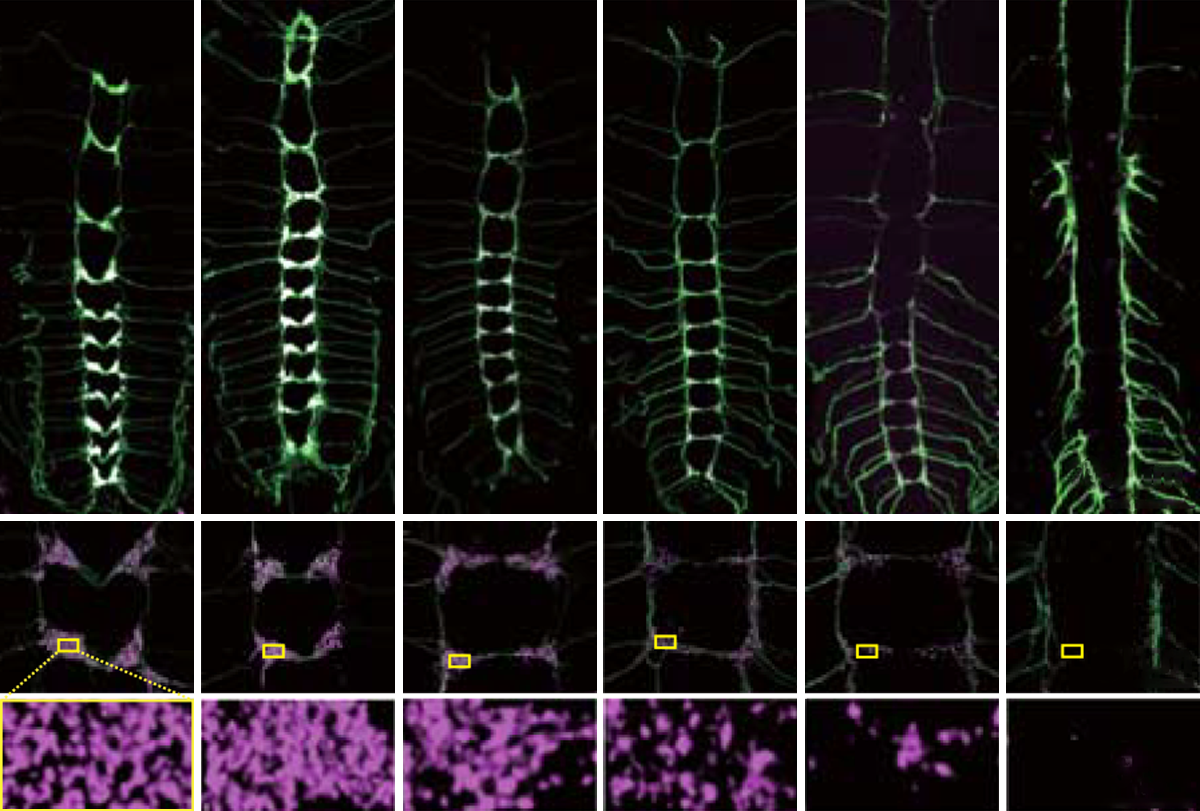
UBE3A’s link to synaptic pruning bolstered by fly study
Increasing or reducing the levels of the UBE3A gene, which is associated with autism and autism-related syndromes, results in altered patterns of synaptic pruning — a process that snips away brain cell connections.
Repurposed electronics lens spies neurons across entire mouse brain
When combined with tissue-inflation methods, the microscope can image axons without the need for tissue slicing, the researchers say.
Repurposed electronics lens spies neurons across entire mouse brain
When combined with tissue-inflation methods, the microscope can image axons without the need for tissue slicing, the researchers say.
Autism’s ties to the cell skeleton
Many genes related to the condition play a role in the internal scaffolding of cells, and cytoskeletal disruptions can affect neurodevelopment and behavior.
Autism’s ties to the cell skeleton
Many genes related to the condition play a role in the internal scaffolding of cells, and cytoskeletal disruptions can affect neurodevelopment and behavior.
Nerve regeneration paper retracted over faked data
The paper marks the second retraction for one of the co-authors.
Nerve regeneration paper retracted over faked data
The paper marks the second retraction for one of the co-authors.
Wiring map reveals how larval fruit fly brain converts sensory signals to movement
The map diagrams more than half a million neuronal connections in the first complete connectome of Drosophila and holds clues about which brain architectures best support learning.
Wiring map reveals how larval fruit fly brain converts sensory signals to movement
The map diagrams more than half a million neuronal connections in the first complete connectome of Drosophila and holds clues about which brain architectures best support learning.
Protein networks identified in autism-linked genetic deletion
The OTUD7A gene, which may account for some traits in people missing a segment of chromosome 15, appears to interact with several known autism-linked genes.
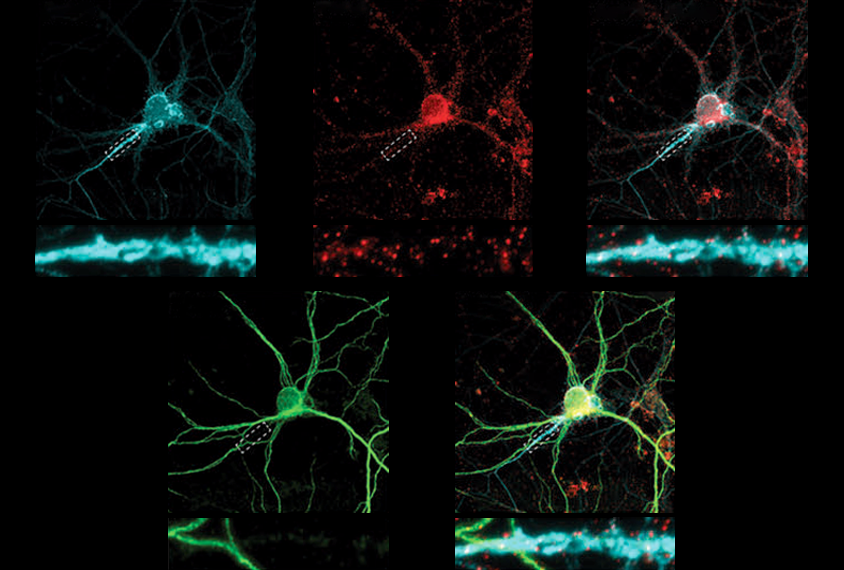
Protein networks identified in autism-linked genetic deletion
The OTUD7A gene, which may account for some traits in people missing a segment of chromosome 15, appears to interact with several known autism-linked genes.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Securing the academic pipeline amid uncertain U.S. funding climate
Finding creative ways to keep early-career researchers in academia—for example, through part-time roles—can help the field weather the storm.

Securing the academic pipeline amid uncertain U.S. funding climate
Finding creative ways to keep early-career researchers in academia—for example, through part-time roles—can help the field weather the storm.
Let’s teach neuroscientists how to be thoughtful and fair reviewers
Blanco-Suárez revamped the traditional journal club by developing a course in which students peer review preprints alongside the published papers that evolved from them.

Let’s teach neuroscientists how to be thoughtful and fair reviewers
Blanco-Suárez revamped the traditional journal club by developing a course in which students peer review preprints alongside the published papers that evolved from them.
New autism committee positions itself as science-backed alternative to government group
The Independent Autism Coordinating Committee plans to meet at the same time as the U.S. federal Interagency Autism Coordinating Committee later this month—and offer its own research agenda.

New autism committee positions itself as science-backed alternative to government group
The Independent Autism Coordinating Committee plans to meet at the same time as the U.S. federal Interagency Autism Coordinating Committee later this month—and offer its own research agenda.