Mustafa Sahin is professor of neurology at Harvard University and director of the Translational Neuroscience Center at Boston Children’s Hospital.
Mustafa Sahin
Professor
Harvard University
From this contributor
Studies of tuberous sclerosis may shed light on biology of autism
Tuberous sclerosis provides a unique opportunity to understand autism because about half of people with that single-gene condition also have autism.

Studies of tuberous sclerosis may shed light on biology of autism
Insights for autism from tuberous sclerosis complex
Studying tuberous sclerosis provides researchers with a unique opportunity to find a common pathway among the various genetic causes of autism, says neurologist Mustafa Sahin.

Insights for autism from tuberous sclerosis complex
Explore more from The Transmitter
PIEZO channels are opening the study of mechanosensation in unexpected places
The force-activated ion channels underlie the senses of touch and proprioception. Now scientists are using them as a tool to explore molecular mechanisms at work in internal organs, including the heart, bladder, uterus and kidney.

PIEZO channels are opening the study of mechanosensation in unexpected places
The force-activated ion channels underlie the senses of touch and proprioception. Now scientists are using them as a tool to explore molecular mechanisms at work in internal organs, including the heart, bladder, uterus and kidney.
Latest iteration of U.S. federal autism committee comes under fire
The new panel “represents a radical departure from all past rosters,” says autism researcher Helen Tager-Flusberg.

Latest iteration of U.S. federal autism committee comes under fire
The new panel “represents a radical departure from all past rosters,” says autism researcher Helen Tager-Flusberg.
‘Tour de force’ study flags fount of interneurons in human brain
The newly discovered cell type might point to the origins of the inhibitory imbalance linked to autism and other conditions.
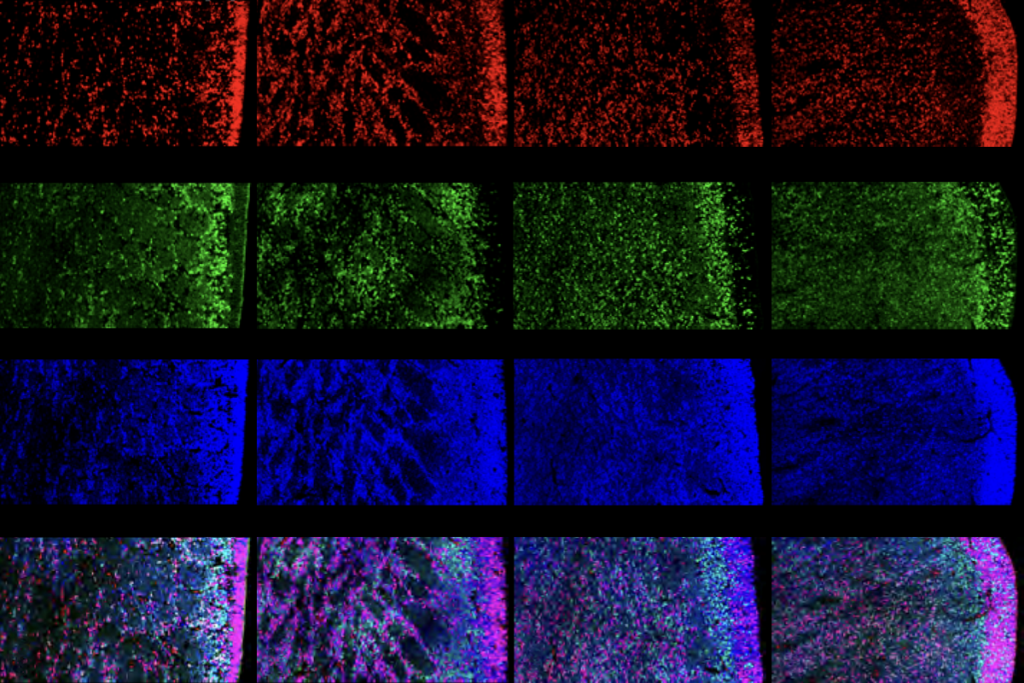
‘Tour de force’ study flags fount of interneurons in human brain
The newly discovered cell type might point to the origins of the inhibitory imbalance linked to autism and other conditions.