Prader-Willi syndrome
Recent articles
Oxytocin lessons from autism-linked syndromes: A chat with Christian Schaaf and Ferdinand Althammer
Oxytocin therapies have failed to consistently benefit autistic people, but their effects in people with two autism-linked conditions may yield new insights, experts argue.
Oxytocin lessons from autism-linked syndromes: A chat with Christian Schaaf and Ferdinand Althammer
Oxytocin therapies have failed to consistently benefit autistic people, but their effects in people with two autism-linked conditions may yield new insights, experts argue.
Dispatches from SfN 2021: Mitochondria, Rett therapy and oxytocin
These short reports from Spectrum journalists highlight some of the autism-related findings that caught our attention at the meeting this past week.
Dispatches from SfN 2021: Mitochondria, Rett therapy and oxytocin
These short reports from Spectrum journalists highlight some of the autism-related findings that caught our attention at the meeting this past week.
The push to screen newborns for rare autism-linked genetic conditions
As treatments for some autism-linked genetic conditions inch closer to the clinic, researchers are talking more urgently about screening all newborns for such conditions.

The push to screen newborns for rare autism-linked genetic conditions
As treatments for some autism-linked genetic conditions inch closer to the clinic, researchers are talking more urgently about screening all newborns for such conditions.
How to safeguard online data collection against fraud
When autism researcher Clare Harrop tried to recruit survey participants over social media, she received hundreds of fraudulent responses. But there are ways researchers can protect themselves from similar experiences.

How to safeguard online data collection against fraud
When autism researcher Clare Harrop tried to recruit survey participants over social media, she received hundreds of fraudulent responses. But there are ways researchers can protect themselves from similar experiences.
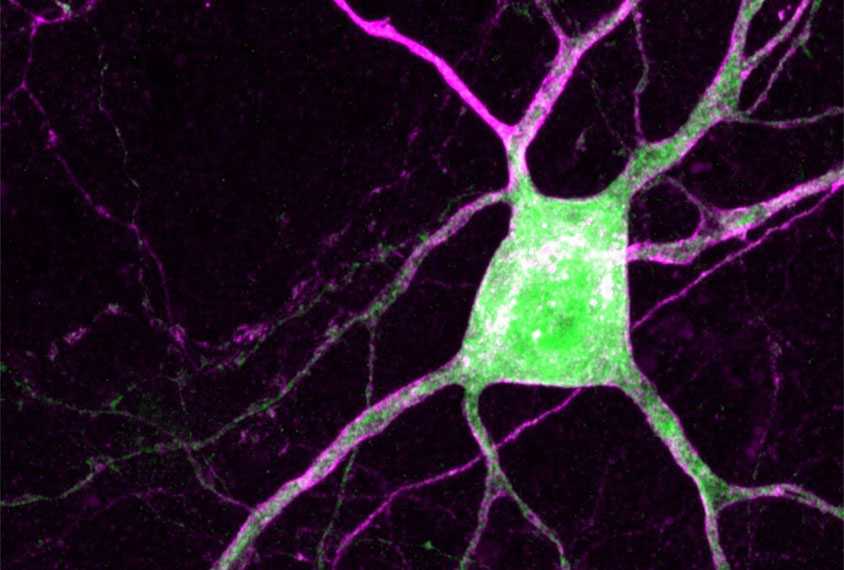
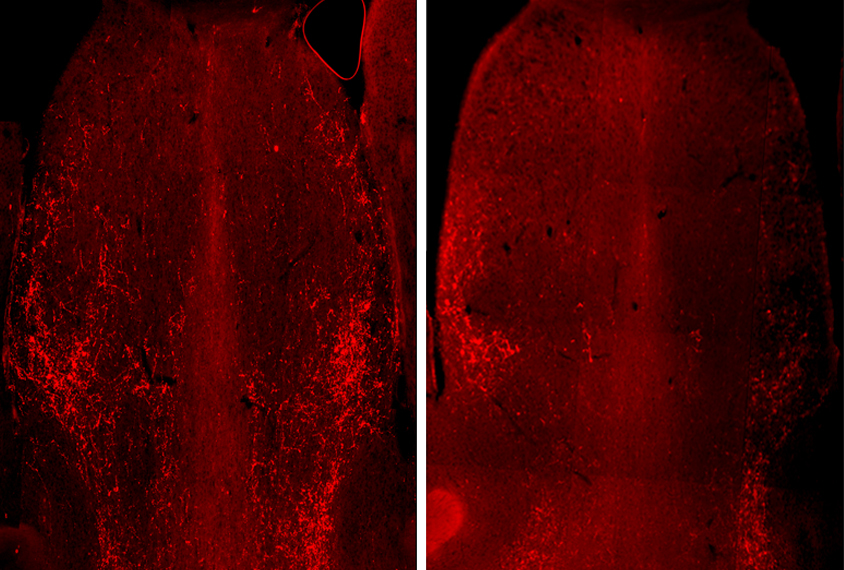
Vasopressin relieves social deficits in an autism mouse model
Mice missing a copy of MAGEL2 have trouble discerning between a familiar mouse and an unfamiliar one; treating them with the social hormone vasopressin reverses this deficit.
Vasopressin relieves social deficits in an autism mouse model
Mice missing a copy of MAGEL2 have trouble discerning between a familiar mouse and an unfamiliar one; treating them with the social hormone vasopressin reverses this deficit.
Brain-body connection may ease autistic people’s social problems
An auditory therapy may improve autistic people's emotional control and help them feel safe enough to engage with the world.

Brain-body connection may ease autistic people’s social problems
An auditory therapy may improve autistic people's emotional control and help them feel safe enough to engage with the world.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Early trajectory of Alzheimer’s tracked in single-cell brain atlases
Inflammation in glia and the loss of certain inhibitory cells may kick off a disease cascade decades before diagnosis.
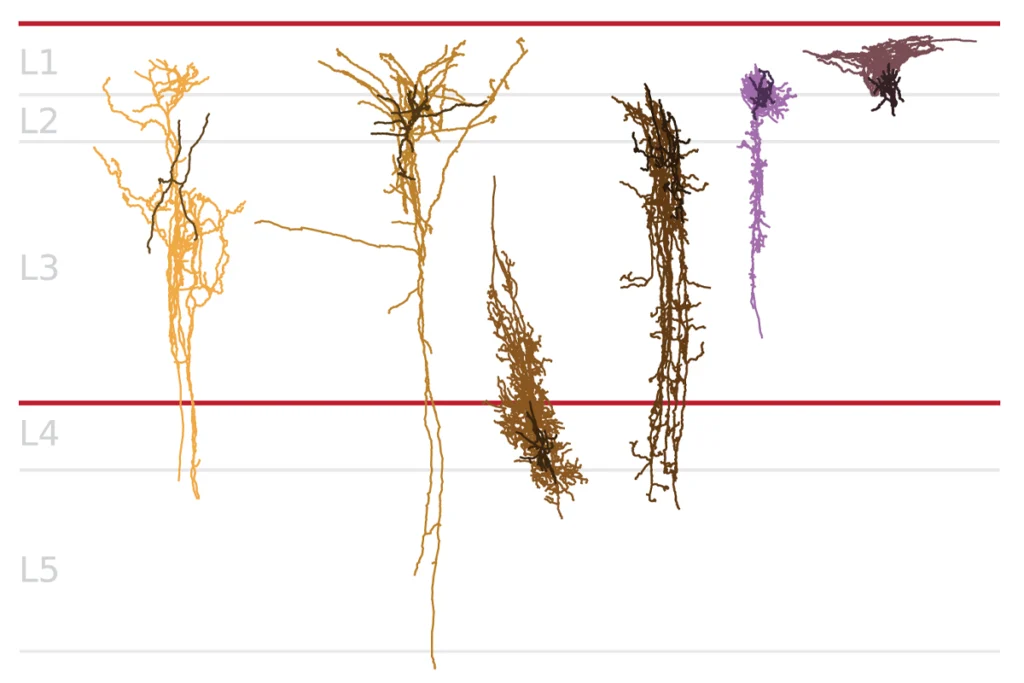

Early trajectory of Alzheimer’s tracked in single-cell brain atlases
Inflammation in glia and the loss of certain inhibitory cells may kick off a disease cascade decades before diagnosis.
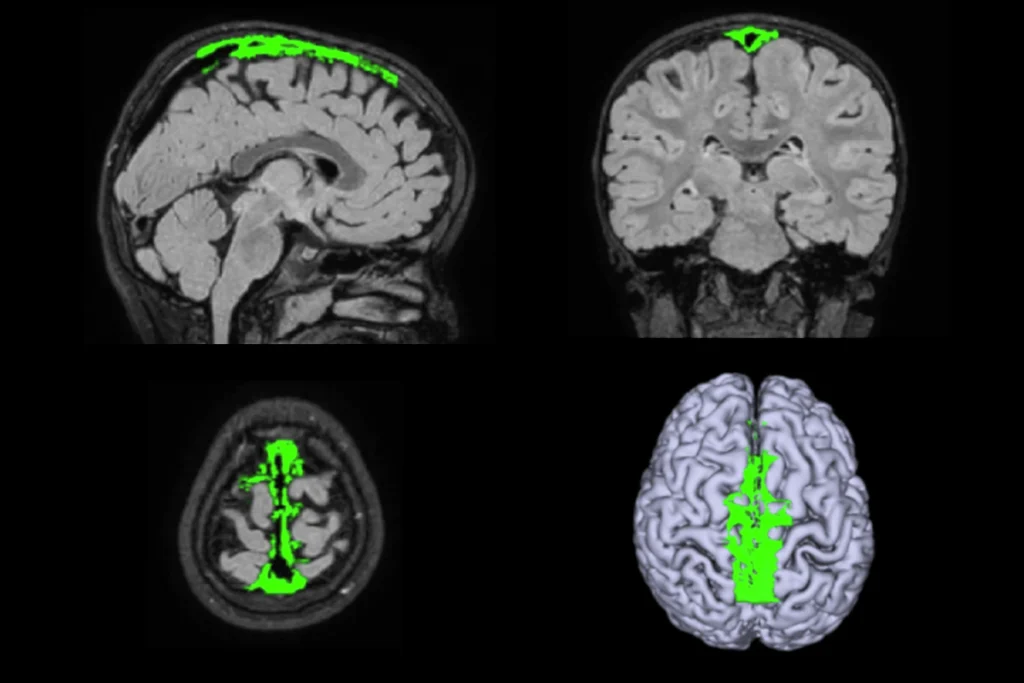
Okur-Chung neurodevelopmental syndrome; excess CSF; autistic girls
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 21 October.
Okur-Chung neurodevelopmental syndrome; excess CSF; autistic girls
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 21 October.
Brains, biases and amyloid beta: Why the female brain deserves a closer look in Alzheimer’s research
New results suggest the disease progresses differently in women, but we need more basic science to unpack the mechanisms involved.

Brains, biases and amyloid beta: Why the female brain deserves a closer look in Alzheimer’s research
New results suggest the disease progresses differently in women, but we need more basic science to unpack the mechanisms involved.