SFN 2014
Recent articles
Autism gene needed for growth of neurons during gestation
Mutations in one of the strongest autism candidate genes may block the proliferation of neurons during development.
Autism gene needed for growth of neurons during gestation
Mutations in one of the strongest autism candidate genes may block the proliferation of neurons during development.
Enriched environment staves off autism-like behavior in rats
Rats exposed in utero to the epilepsy drug valproic acid, a risk factor for autism, do not develop autism-like behaviors if they are reared in a stimulating environment. Researchers presented the unpublished findings yesterday at the 2014 Society for Neuroscience annual meeting in Washington, D.C.

Enriched environment staves off autism-like behavior in rats
Rats exposed in utero to the epilepsy drug valproic acid, a risk factor for autism, do not develop autism-like behaviors if they are reared in a stimulating environment. Researchers presented the unpublished findings yesterday at the 2014 Society for Neuroscience annual meeting in Washington, D.C.
Who are you going to believe, your body or your lying eyes?
Children with autism tend to rely more on their bodies when learning new motor skills, while controls rely more on their eyes, suggests unpublished research presented Wednesday at the 2014 Society for Neuroscience annual meeting in Washington, D.C.

Who are you going to believe, your body or your lying eyes?
Children with autism tend to rely more on their bodies when learning new motor skills, while controls rely more on their eyes, suggests unpublished research presented Wednesday at the 2014 Society for Neuroscience annual meeting in Washington, D.C.
Feisty mice may reveal autism gene’s link to aggression
Varying the number of copies of a single autism-linked gene modulates social behavior and aggression in mice, according to unpublished results presented yesterday at the 2014 Society for Neuroscience annual meeting in Washington, D.C.

Feisty mice may reveal autism gene’s link to aggression
Varying the number of copies of a single autism-linked gene modulates social behavior and aggression in mice, according to unpublished results presented yesterday at the 2014 Society for Neuroscience annual meeting in Washington, D.C.
Takeaways from SfN 2014
Scientists reflect on the current state of autism research as the 2014 Society for Neuroscience annual meeting in Washington, D.C. comes to a close.

Takeaways from SfN 2014
Scientists reflect on the current state of autism research as the 2014 Society for Neuroscience annual meeting in Washington, D.C. comes to a close.
Different autism subtypes share same genetic signature
A rare form of autism linked to a duplication of the 15q11-13 chromosomal region shares a molecular signature with more common forms of the disorder, suggests unpublished research presented yesterday at the 2014 Society for Neuroscience annual meeting in Washington, D.C.

Different autism subtypes share same genetic signature
A rare form of autism linked to a duplication of the 15q11-13 chromosomal region shares a molecular signature with more common forms of the disorder, suggests unpublished research presented yesterday at the 2014 Society for Neuroscience annual meeting in Washington, D.C.
Monkey missing Rett gene prompts primate research debate
Scientists have created a transgenic monkey modeling Rett syndrome, they announced yesterday at the 2014 Society for Neuroscience annual meeting in Washington, D.C. This model and others sparked a lively discussion about the relative value of animal models in research.

Monkey missing Rett gene prompts primate research debate
Scientists have created a transgenic monkey modeling Rett syndrome, they announced yesterday at the 2014 Society for Neuroscience annual meeting in Washington, D.C. This model and others sparked a lively discussion about the relative value of animal models in research.
In autism, RNA snippets vary little by brain region, age
The expression patterns of microRNAs vary less by brain region and age in people with autism than in controls. Researchers presented the unpublished findings Tuesday at the 2014 Society for Neuroscience annual meeting in Washington, D.C.

In autism, RNA snippets vary little by brain region, age
The expression patterns of microRNAs vary less by brain region and age in people with autism than in controls. Researchers presented the unpublished findings Tuesday at the 2014 Society for Neuroscience annual meeting in Washington, D.C.
Robots come to the rescue in sensory processing studies
Robots that help children with autism become more socially engaged may also increase understanding of sensory processing in the disorder, suggests unpublished research presented today at the 2014 Society for Neuroscience annual meeting in Washington, D.C.

Robots come to the rescue in sensory processing studies
Robots that help children with autism become more socially engaged may also increase understanding of sensory processing in the disorder, suggests unpublished research presented today at the 2014 Society for Neuroscience annual meeting in Washington, D.C.
In mouse model of Rett, immune cells overly sensitive
Loss of MeCP2, the Rett syndrome gene, depletes immune cells throughout the bodies of mice, researchers reported yesterday at the 2014 Society for Neuroscience annual meeting in Washington, D.C.

In mouse model of Rett, immune cells overly sensitive
Loss of MeCP2, the Rett syndrome gene, depletes immune cells throughout the bodies of mice, researchers reported yesterday at the 2014 Society for Neuroscience annual meeting in Washington, D.C.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Autism in Kenya, organoid research, and more
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 22 December.
Autism in Kenya, organoid research, and more
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 22 December.
‘Unprecedented’ dorsal root ganglion atlas captures 22 types of human sensory neurons
The atlas also offers up molecular and cellular targets for new pain therapies.
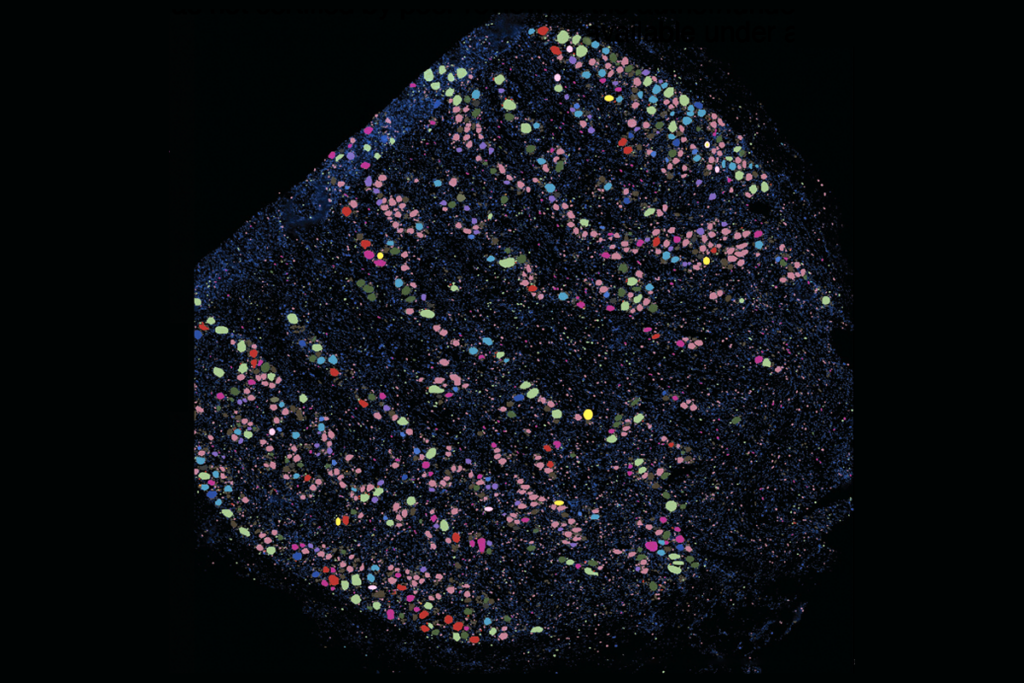
‘Unprecedented’ dorsal root ganglion atlas captures 22 types of human sensory neurons
The atlas also offers up molecular and cellular targets for new pain therapies.
Not playing around: Why neuroscience needs toy models
Amid the rise of billion-parameter models, I argue that toy models, with just a few neurons, remain essential—and may be all neuroscience needs.

Not playing around: Why neuroscience needs toy models
Amid the rise of billion-parameter models, I argue that toy models, with just a few neurons, remain essential—and may be all neuroscience needs.