The brain
Recent articles
Some social issues in DYRK1A model mice stem from faulty inhibitory circuits
Alterations in inhibitory circuits and difficulties in social recognition characterize mice missing one copy of DYRK1A, a gene linked to autism.
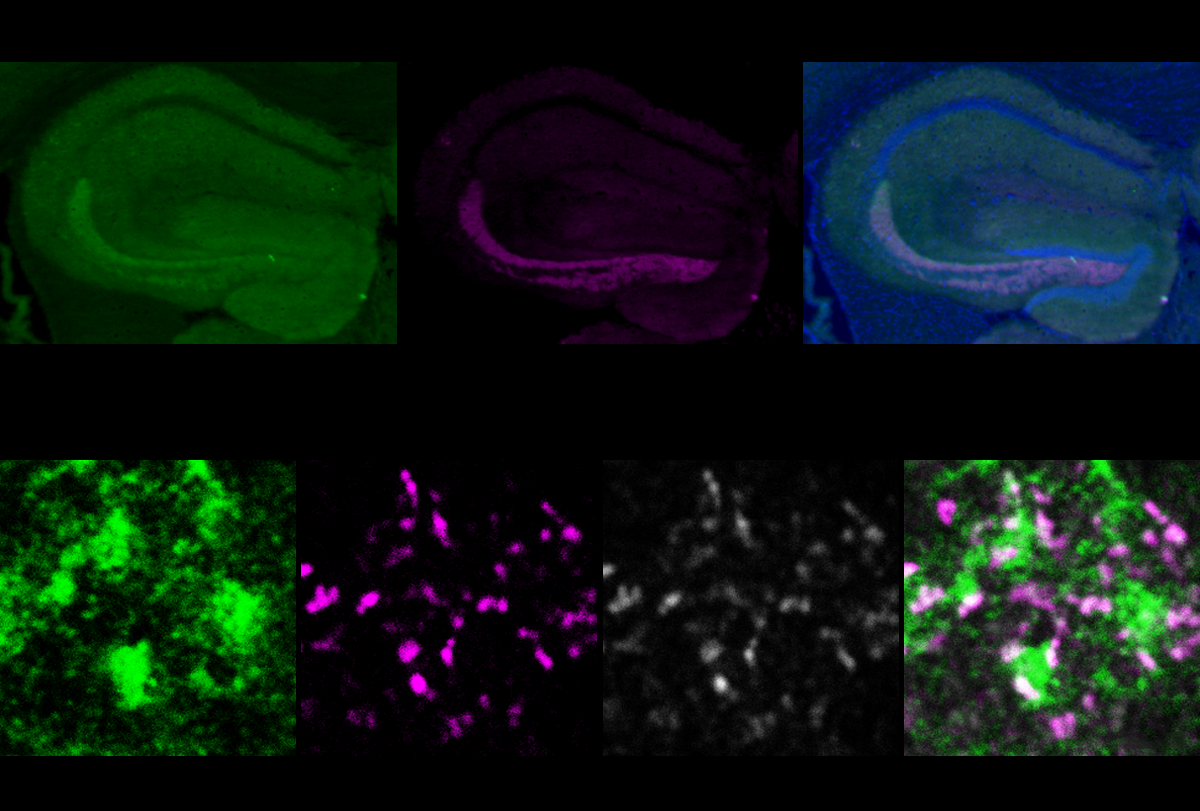
Some social issues in DYRK1A model mice stem from faulty inhibitory circuits
Alterations in inhibitory circuits and difficulties in social recognition characterize mice missing one copy of DYRK1A, a gene linked to autism.
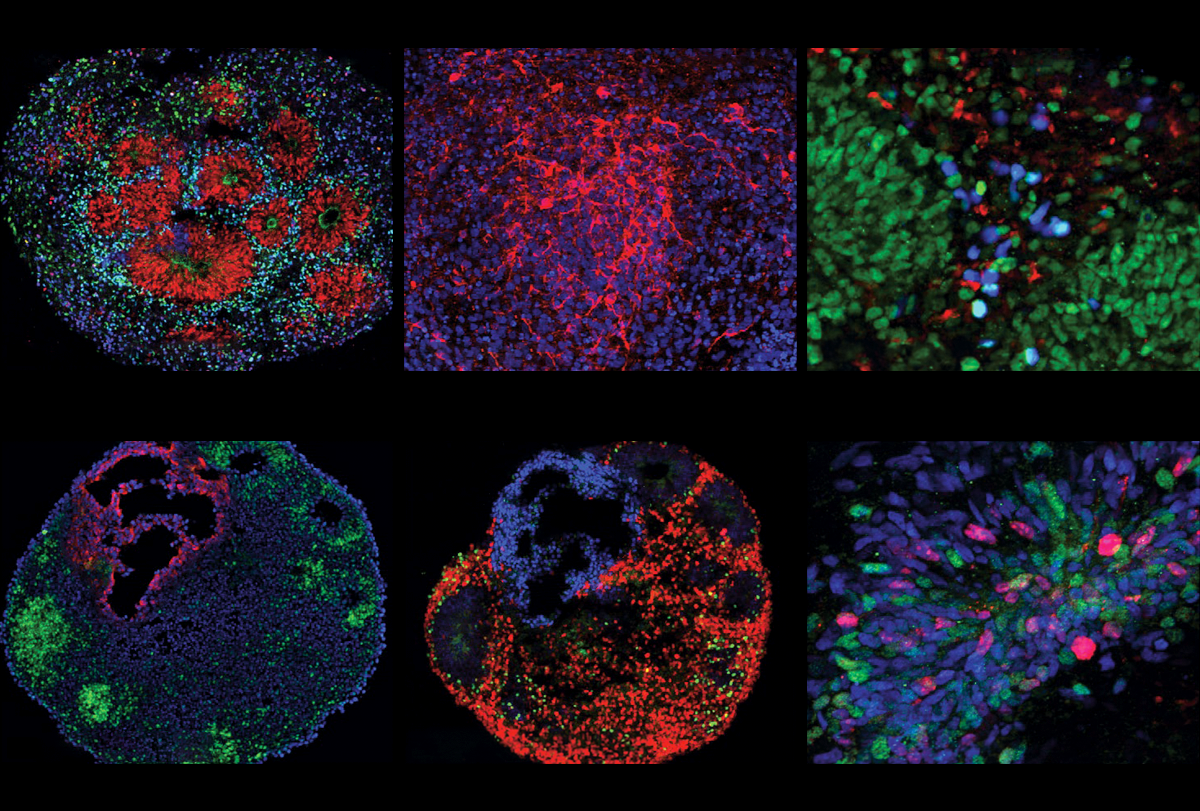
Method pinpoints cell-specific effects of autism-linked mutations
The approach, which combines CRISPR with single-cell analyses of organoids, suggests that intermediate progenitor cells are especially vulnerable to mutations associated with autism.
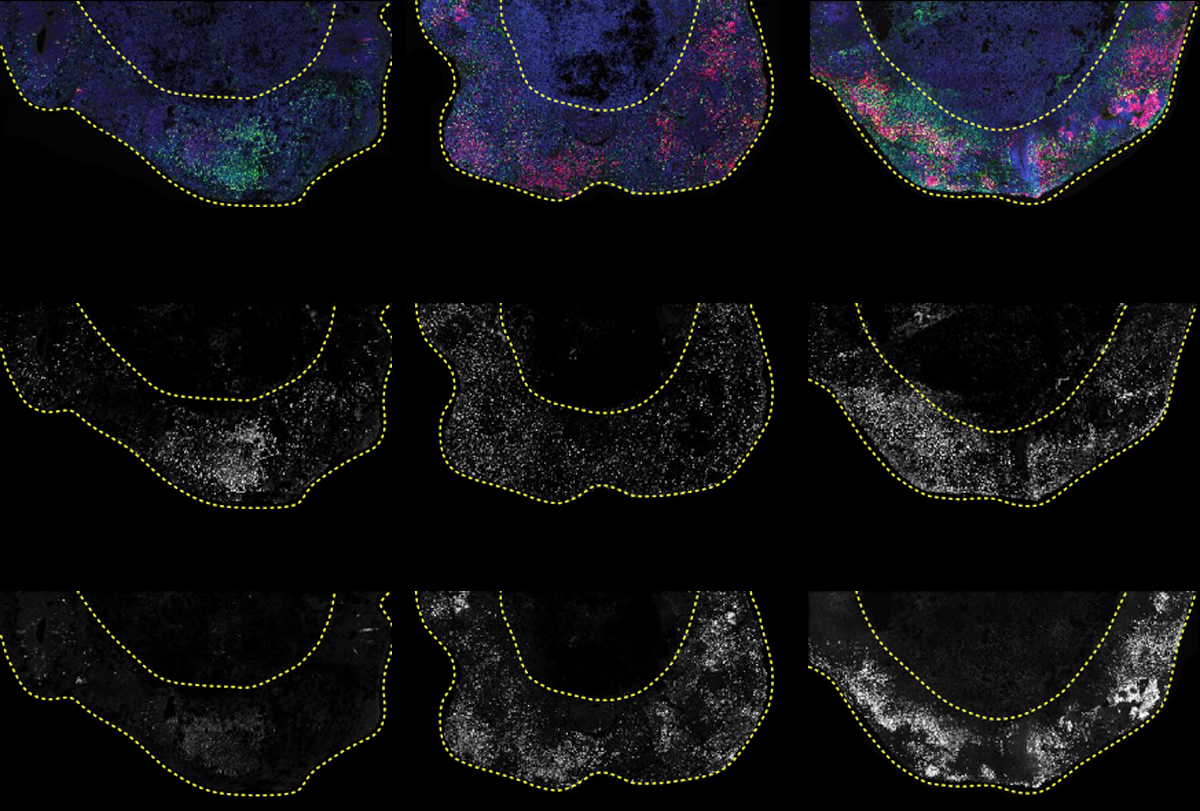
Method pinpoints cell-specific effects of autism-linked mutations
The approach, which combines CRISPR with single-cell analyses of organoids, suggests that intermediate progenitor cells are especially vulnerable to mutations associated with autism.
UBE3A’s link to synaptic pruning bolstered by fly study
Increasing or reducing the levels of the UBE3A gene, which is associated with autism and autism-related syndromes, results in altered patterns of synaptic pruning — a process that snips away brain cell connections.
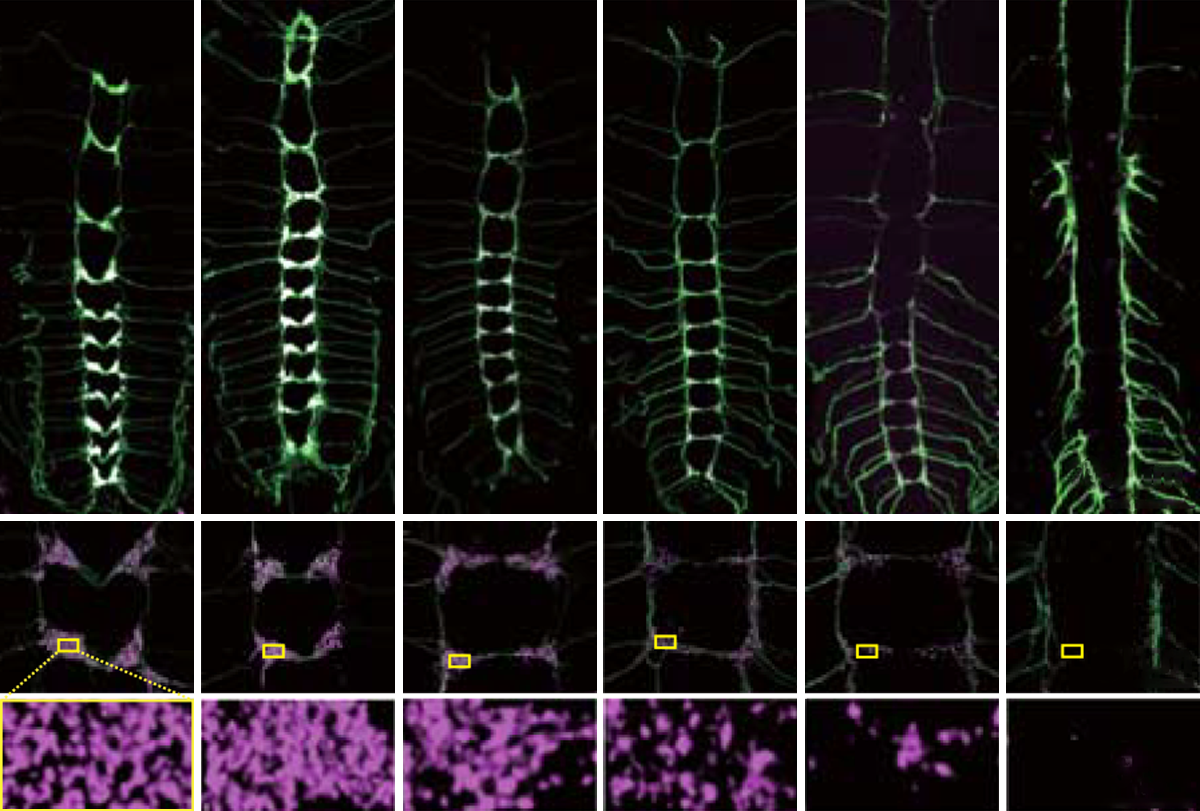
UBE3A’s link to synaptic pruning bolstered by fly study
Increasing or reducing the levels of the UBE3A gene, which is associated with autism and autism-related syndromes, results in altered patterns of synaptic pruning — a process that snips away brain cell connections.
Head size parts autism into two major subtypes
An imbalance in the number of excitatory neurons in early brain development may account for the difference.
Head size parts autism into two major subtypes
An imbalance in the number of excitatory neurons in early brain development may account for the difference.
Magnetic stimulation for autism: Q&A with Xujun Duan
A new individualized approach to transcranial magnetic stimulation may one day be an effective treatment for social and communication difficulties, if the results from Duan’s small preliminary trial pan out.
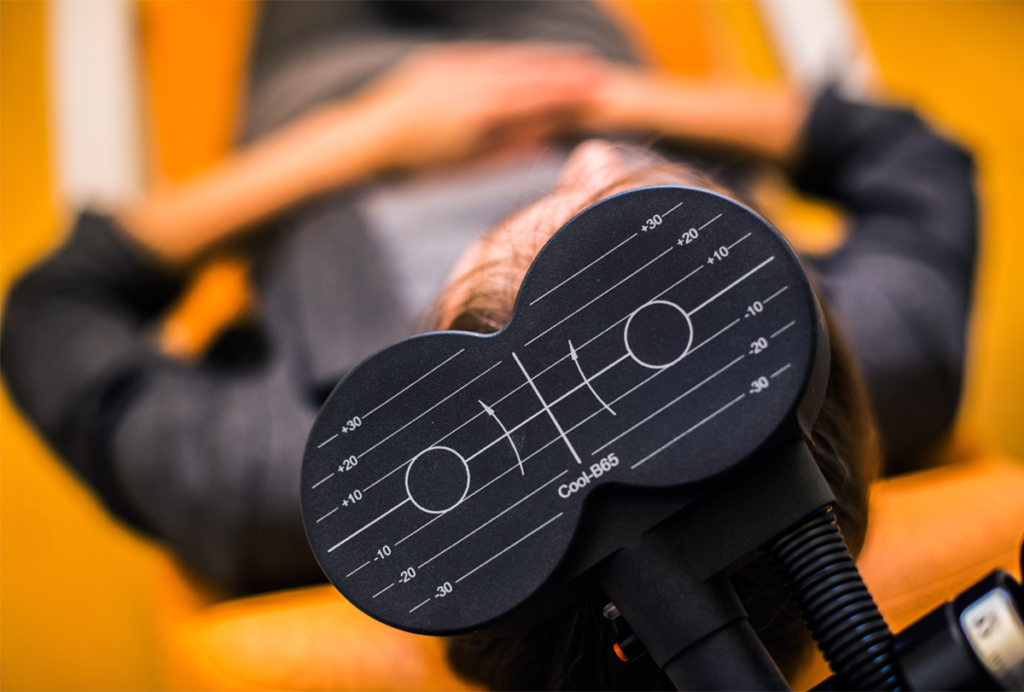

Magnetic stimulation for autism: Q&A with Xujun Duan
A new individualized approach to transcranial magnetic stimulation may one day be an effective treatment for social and communication difficulties, if the results from Duan’s small preliminary trial pan out.
Skewed signaling in striatum may spawn repetitive behaviors
Synaptic changes in the brain region could drive a core trait of fragile X syndrome, a new mouse study suggests.
Skewed signaling in striatum may spawn repetitive behaviors
Synaptic changes in the brain region could drive a core trait of fragile X syndrome, a new mouse study suggests.
Is excess brain fluid an early marker of autism?
Brain scans of hundreds of infants suggest that up to 80 percent of those with autism have unusual amounts of cerebrospinal fluid. Researchers are studying how this might contribute to the condition.
Is excess brain fluid an early marker of autism?
Brain scans of hundreds of infants suggest that up to 80 percent of those with autism have unusual amounts of cerebrospinal fluid. Researchers are studying how this might contribute to the condition.
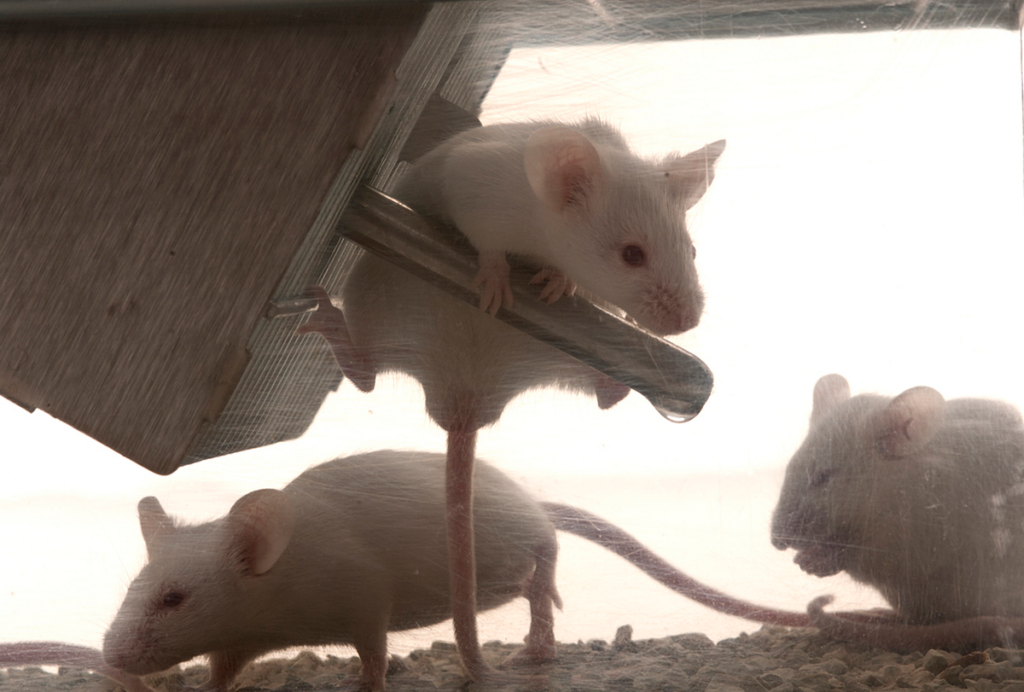
New test taps nose pokes as a proxy for social motivation in mice
Over one hour, a particularly motivated mouse poked its nose 350 times into a hole in the test chamber in the hopes of meeting a playmate.
New test taps nose pokes as a proxy for social motivation in mice
Over one hour, a particularly motivated mouse poked its nose 350 times into a hole in the test chamber in the hopes of meeting a playmate.
Abundant motor proteins disrupt cries in FOXP2 mice
Knocking down the gene that codes for the proteins normalizes the vocalizations.
Abundant motor proteins disrupt cries in FOXP2 mice
Knocking down the gene that codes for the proteins normalizes the vocalizations.
Change of heart and mind: Autism’s ties to cardiac defects
Children with congenital heart disease have an increased likelihood of autism. Why?
Change of heart and mind: Autism’s ties to cardiac defects
Children with congenital heart disease have an increased likelihood of autism. Why?
Explore more from The Transmitter
Cracking the neural code for emotional states
Rather than act as a simple switchboard for innate behaviors, the hypothalamus encodes an animal's internal state, which influences behavior.

Cracking the neural code for emotional states
Rather than act as a simple switchboard for innate behaviors, the hypothalamus encodes an animal's internal state, which influences behavior.
Alex Maier argues that a scientific explanation of consciousness requires grounding in formalized mathematics
When it comes to discovering laws of nature for consciousness similar to those in physics, Maier argues that integrated information theory is the only game in town.
Alex Maier argues that a scientific explanation of consciousness requires grounding in formalized mathematics
When it comes to discovering laws of nature for consciousness similar to those in physics, Maier argues that integrated information theory is the only game in town.
Neuro’s ark: How goats can model neurodegeneration
Since debunking an urban legend that headbutting animals don’t damage their brain, Nicole Ackermans has been investigating how the behavior correlates with neurodegeneration.

Neuro’s ark: How goats can model neurodegeneration
Since debunking an urban legend that headbutting animals don’t damage their brain, Nicole Ackermans has been investigating how the behavior correlates with neurodegeneration.