Gene networks
Recent articles
Organoid study reveals shared brain pathways across autism-linked variants
The genetic variants initially affect brain development in unique ways, but over time they converge on common molecular pathways.
Organoid study reveals shared brain pathways across autism-linked variants
The genetic variants initially affect brain development in unique ways, but over time they converge on common molecular pathways.
Cell ‘antennae’ link autism, congenital heart disease
Variants in genes tied to both conditions derail the formation of cilia, the tiny hair-like structure found on almost every cell in the body, a new study finds.
Cell ‘antennae’ link autism, congenital heart disease
Variants in genes tied to both conditions derail the formation of cilia, the tiny hair-like structure found on almost every cell in the body, a new study finds.
Sequencing study spotlights tight web of genes tied to autism
The findings, shared in a preprint, help to illuminate how a large and heterogeneous group of genes could be involved in autism.
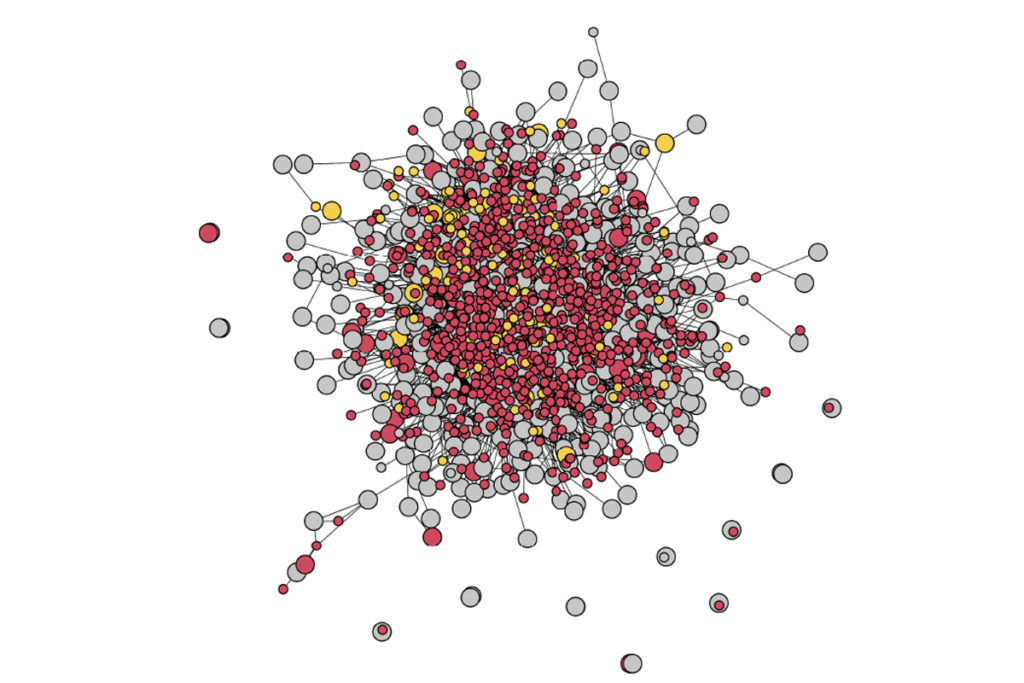
Sequencing study spotlights tight web of genes tied to autism
The findings, shared in a preprint, help to illuminate how a large and heterogeneous group of genes could be involved in autism.
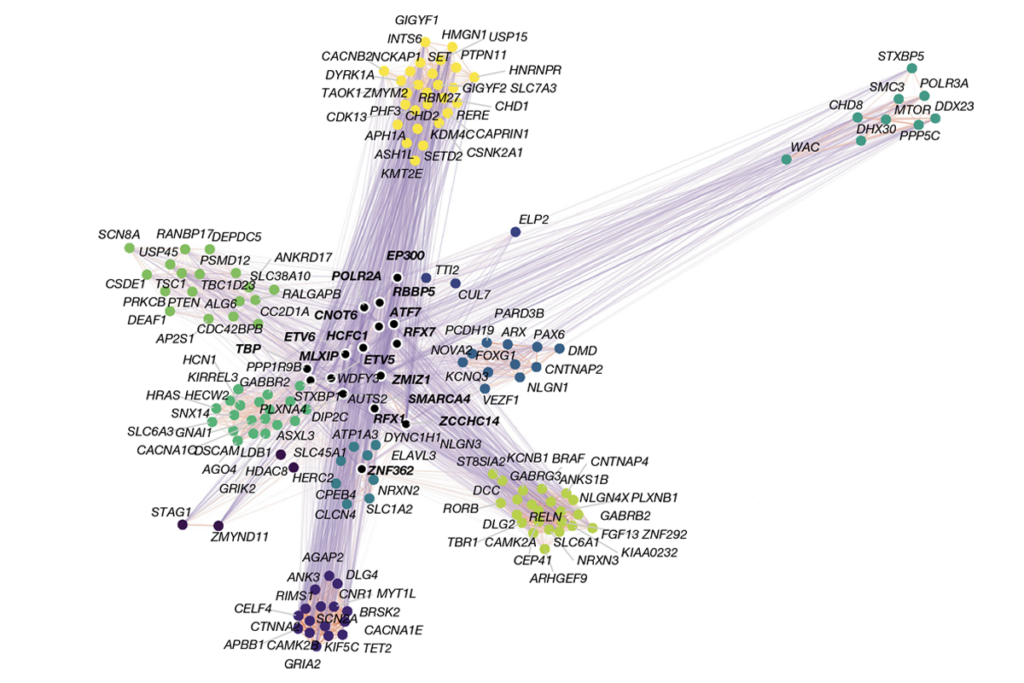
Newfound gene network controls long-range connections between emotional, cognitive brain areas
The finding could help unravel gene regulatory networks and explain how genetic and environmental factors interact in neurodevelopmental conditions.
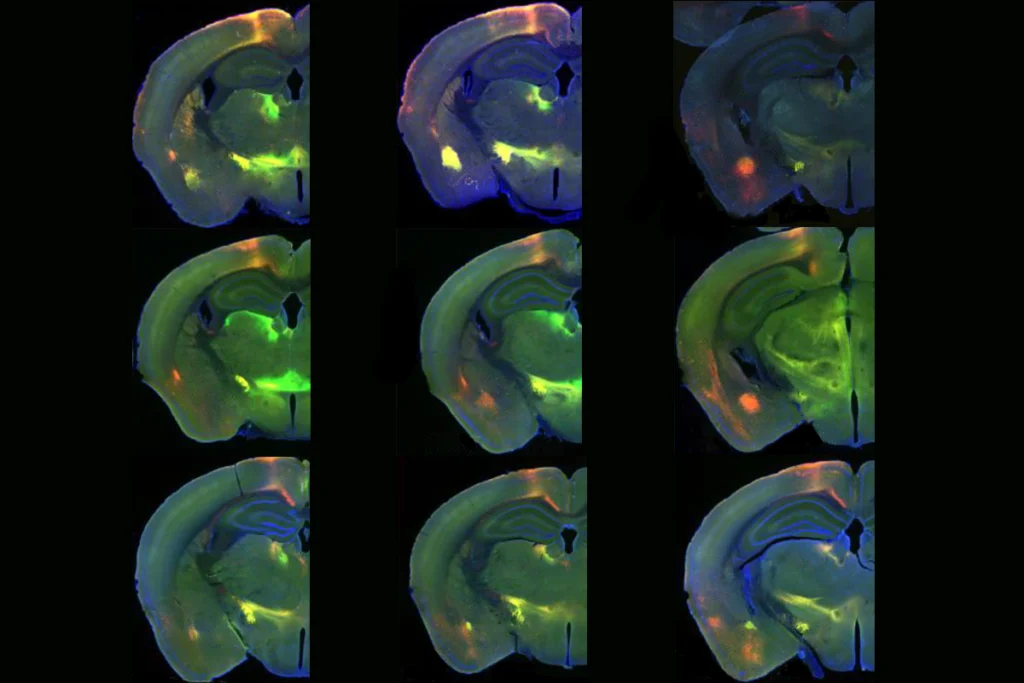
Newfound gene network controls long-range connections between emotional, cognitive brain areas
The finding could help unravel gene regulatory networks and explain how genetic and environmental factors interact in neurodevelopmental conditions.
Brain patterning in utero may be implicated in autism, other conditions
Genes tied to several conditions are expressed in regions that control neural stem cell fate within the first few months post-conception.
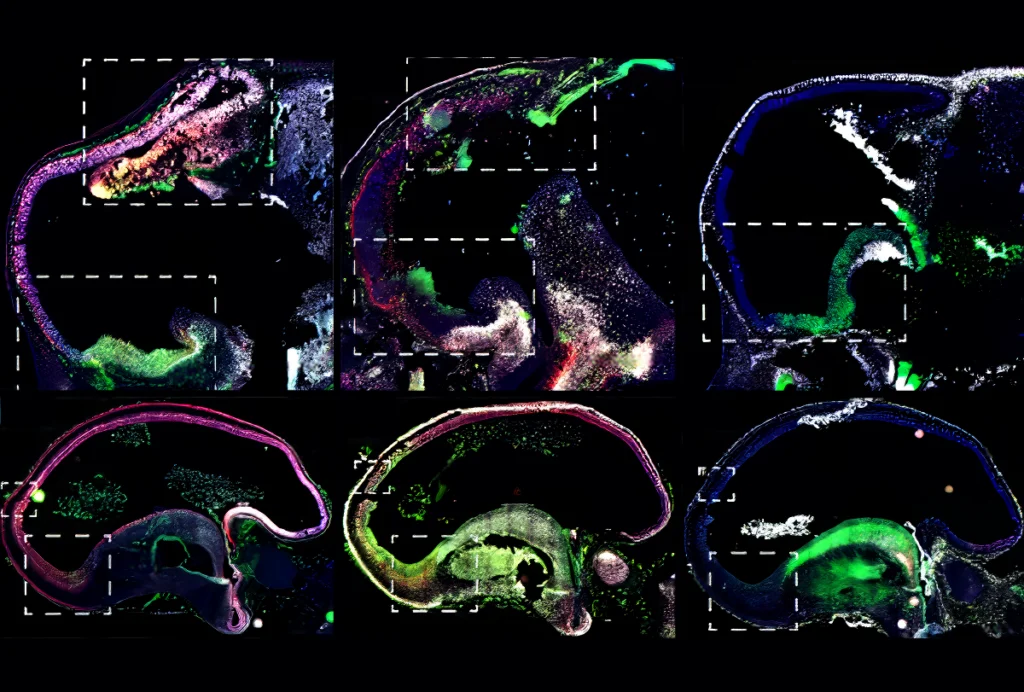
Brain patterning in utero may be implicated in autism, other conditions
Genes tied to several conditions are expressed in regions that control neural stem cell fate within the first few months post-conception.
Autism-linked proteins mingle with other molecules in overlapping networks
A massive new set of interaction maps illuminates especially high convergence in protein networks related to autism and shows how mutations could disrupt those networks.
Autism-linked proteins mingle with other molecules in overlapping networks
A massive new set of interaction maps illuminates especially high convergence in protein networks related to autism and shows how mutations could disrupt those networks.
Change of heart and mind: Autism’s ties to cardiac defects
Children with congenital heart disease have an increased likelihood of autism. Why?
Change of heart and mind: Autism’s ties to cardiac defects
Children with congenital heart disease have an increased likelihood of autism. Why?
Fishing for protein partners nets clues to autism
Connections between 13 autism-linked proteins and their binding partners in excitatory neurons implicate a new molecular pathway.
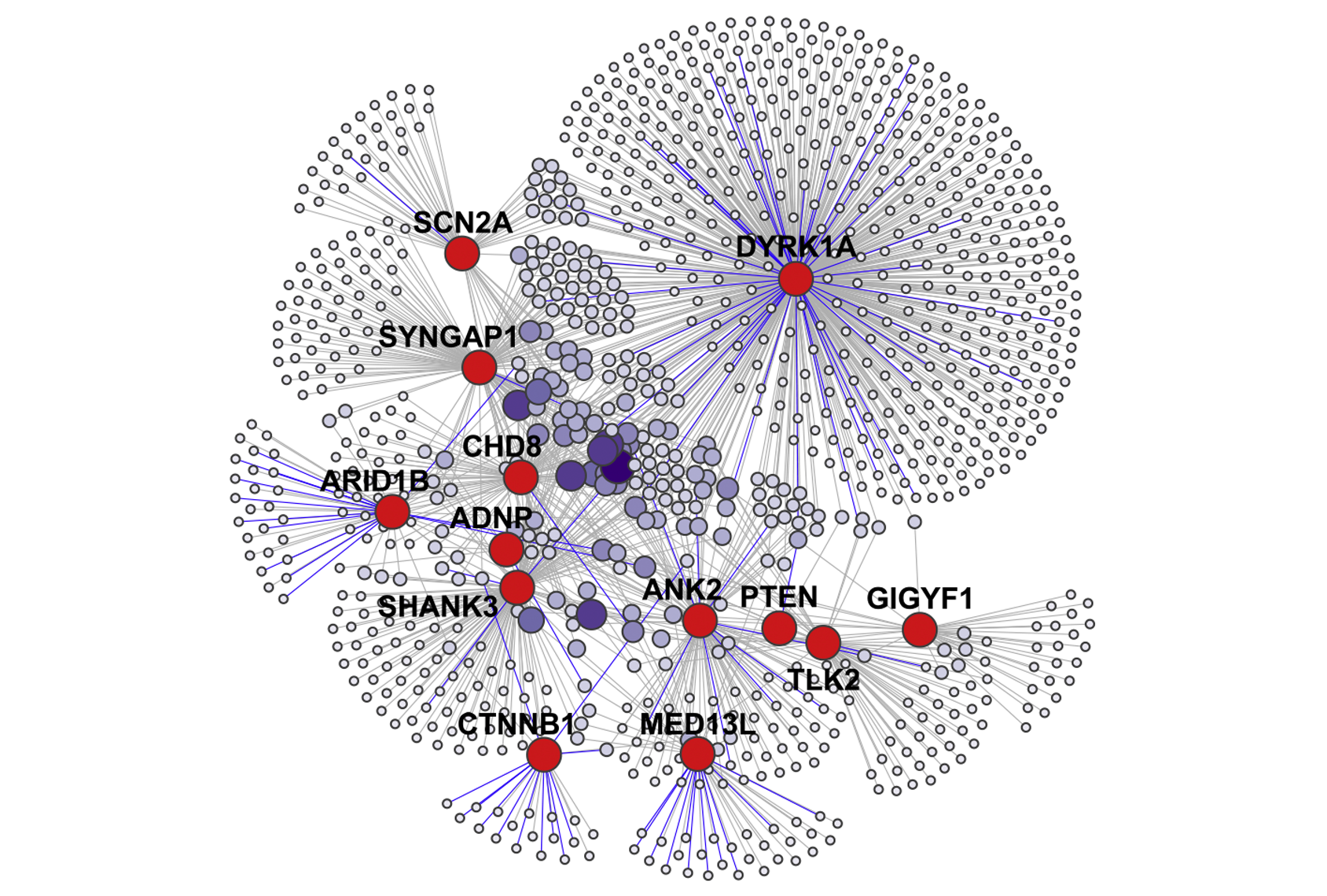
Fishing for protein partners nets clues to autism
Connections between 13 autism-linked proteins and their binding partners in excitatory neurons implicate a new molecular pathway.
Multi-omics study captures CNTNAP2’s far-ranging effects
The in-depth approach shows mutations in the autism-linked gene disrupt neuronal growth and communication, as well as mitochondrial gene expression.
Multi-omics study captures CNTNAP2’s far-ranging effects
The in-depth approach shows mutations in the autism-linked gene disrupt neuronal growth and communication, as well as mitochondrial gene expression.
Two top autism-linked proteins connect to build cell ‘skeleton’
ADNP and SHANK3 proteins may bind together and alter a neuron’s internal scaffold, hinting at a mechanism that, when disrupted, may underlie several forms of autism.
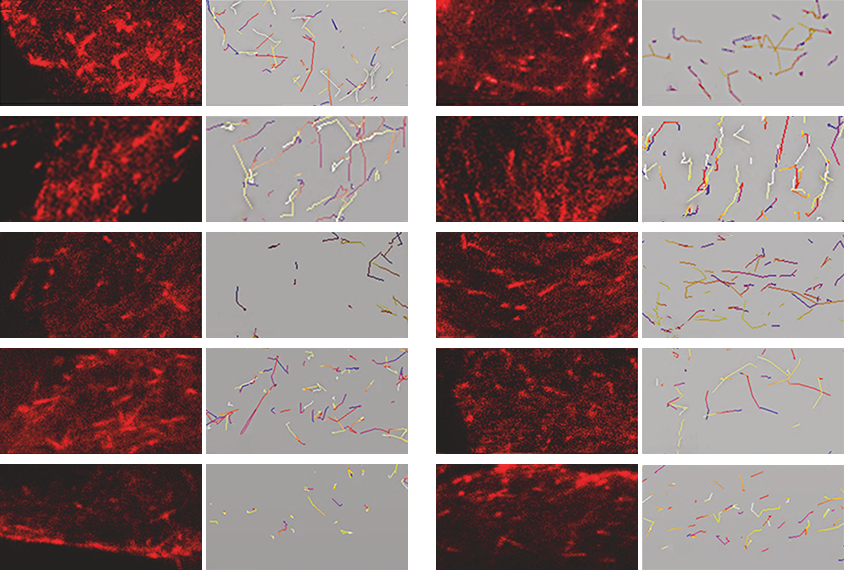
Two top autism-linked proteins connect to build cell ‘skeleton’
ADNP and SHANK3 proteins may bind together and alter a neuron’s internal scaffold, hinting at a mechanism that, when disrupted, may underlie several forms of autism.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Revised statistical bar extracts less-common variants from autism genetics studies
Adjusting genetic analyses could help plug autism’s heritability gap, according to a new preprint.

Revised statistical bar extracts less-common variants from autism genetics studies
Adjusting genetic analyses could help plug autism’s heritability gap, according to a new preprint.
Tom Griffiths describes how neural networks, logic and probability theory together explain cognition
In his new book, “The Laws of Thought,” Griffiths shows how these three pillars of study complement one another and together form a solid foundation to eventually explain all of our cognition, from brain to mind.
Tom Griffiths describes how neural networks, logic and probability theory together explain cognition
In his new book, “The Laws of Thought,” Griffiths shows how these three pillars of study complement one another and together form a solid foundation to eventually explain all of our cognition, from brain to mind.
This paper changed my life: Talia Lerner reflects on dopamine neuron diversity and the value of simple experiments
In a 2011 Neuron study, Stephan Lammel and his colleagues showed that dopamine neurons with different projections have different physiological properties. The work inspired Lerner to think about how to challenge widely held assumptions in the field.

This paper changed my life: Talia Lerner reflects on dopamine neuron diversity and the value of simple experiments
In a 2011 Neuron study, Stephan Lammel and his colleagues showed that dopamine neurons with different projections have different physiological properties. The work inspired Lerner to think about how to challenge widely held assumptions in the field.