SFN 2019
Recent articles
Loss of insulation on neurons may contribute to autism
Genes involved in the formation of myelin, a fatty substance that sheathes neurons, are altered in autistic people and in several mouse models.
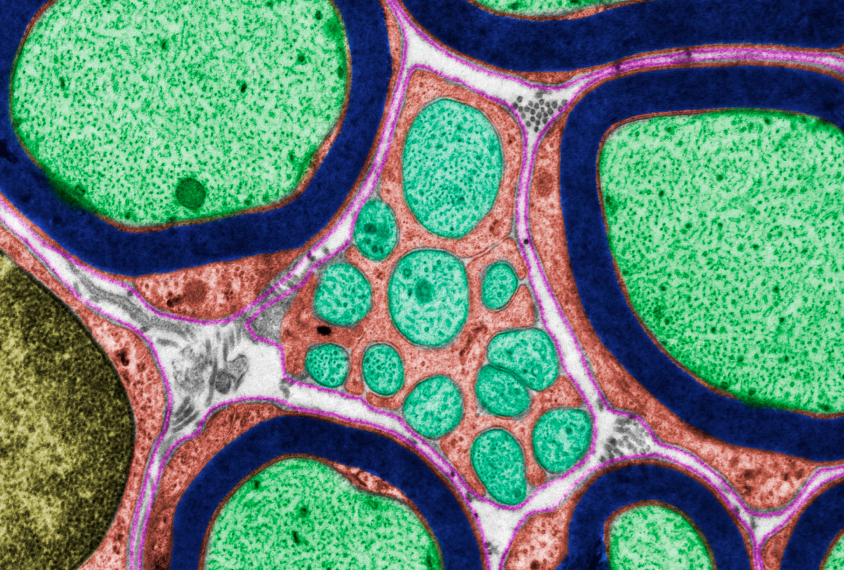
Loss of insulation on neurons may contribute to autism
Genes involved in the formation of myelin, a fatty substance that sheathes neurons, are altered in autistic people and in several mouse models.
In brain imaging studies of autism, location may alter results
A new analysis hints at the source of the rampant inconsistency among brain imaging studies in autism: significant differences among study sites.
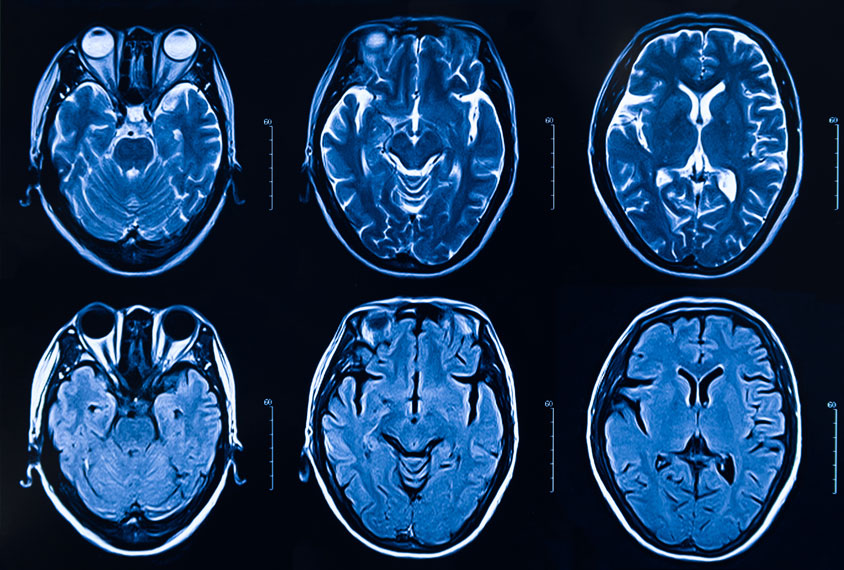
In brain imaging studies of autism, location may alter results
A new analysis hints at the source of the rampant inconsistency among brain imaging studies in autism: significant differences among study sites.
Spheres of brain cells may offer crystal ball for autism’s origins
Researchers have monitored the active genome in brain organoids over the course of nearly two years — and may find clues to autism’s roots.
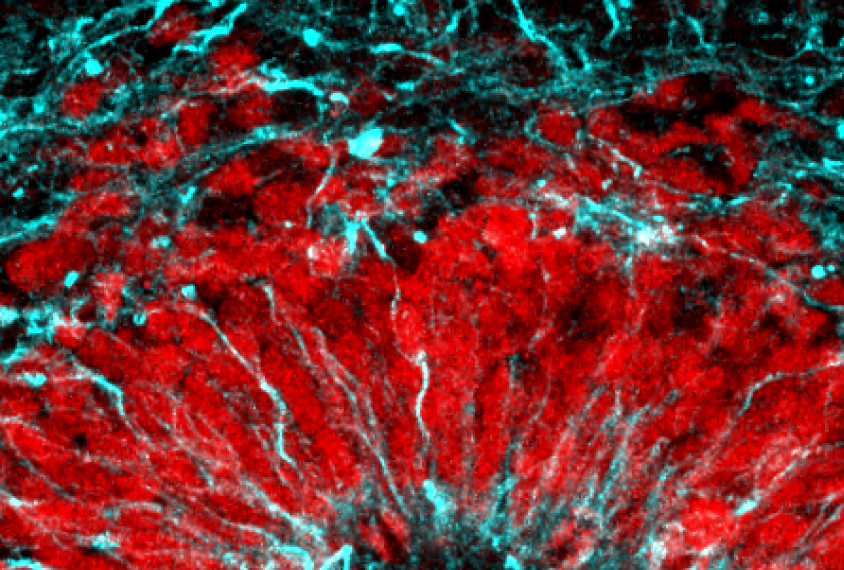
Spheres of brain cells may offer crystal ball for autism’s origins
Researchers have monitored the active genome in brain organoids over the course of nearly two years — and may find clues to autism’s roots.
Fever’s immune effect on brain may ease autism traits
An immune molecule produced during a fever improves sociability in three mouse models of autism.

Fever’s immune effect on brain may ease autism traits
An immune molecule produced during a fever improves sociability in three mouse models of autism.
Takeaways from SfN 2019
Thousands of research presentations, five days: Spectrum looks back at the 2019 Society for Neuroscience annual meeting in Chicago.

Takeaways from SfN 2019
Thousands of research presentations, five days: Spectrum looks back at the 2019 Society for Neuroscience annual meeting in Chicago.
Brain scans from one person build reliable map of brain activity
Mapping brain activity in one person doing multiple tasks creates a more accurate picture of the brain than averaging the brain activity of multiple people doing a single task.
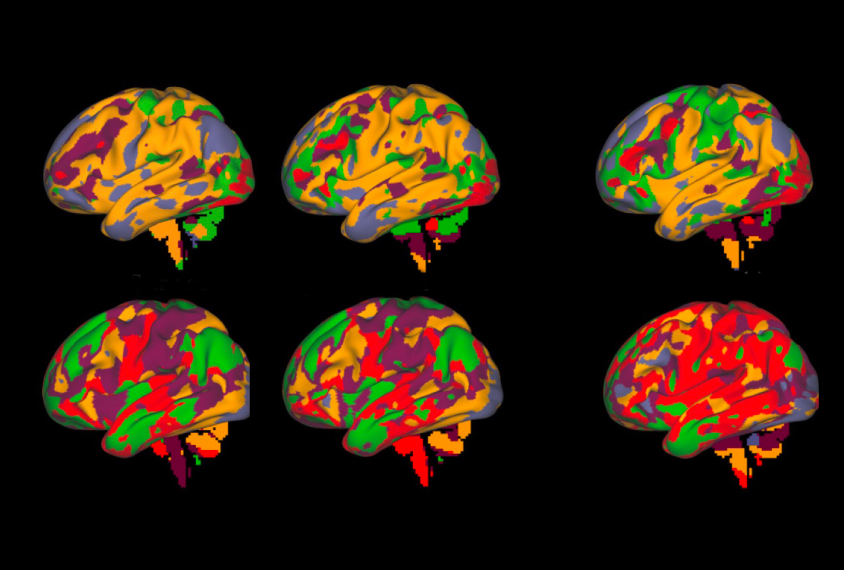
Brain scans from one person build reliable map of brain activity
Mapping brain activity in one person doing multiple tasks creates a more accurate picture of the brain than averaging the brain activity of multiple people doing a single task.
Drug counteracts effects of doubled autism gene
An experimental drug tamps down the expression of a gene duplicated in an autism-related condition and restores typical behavior in mice.
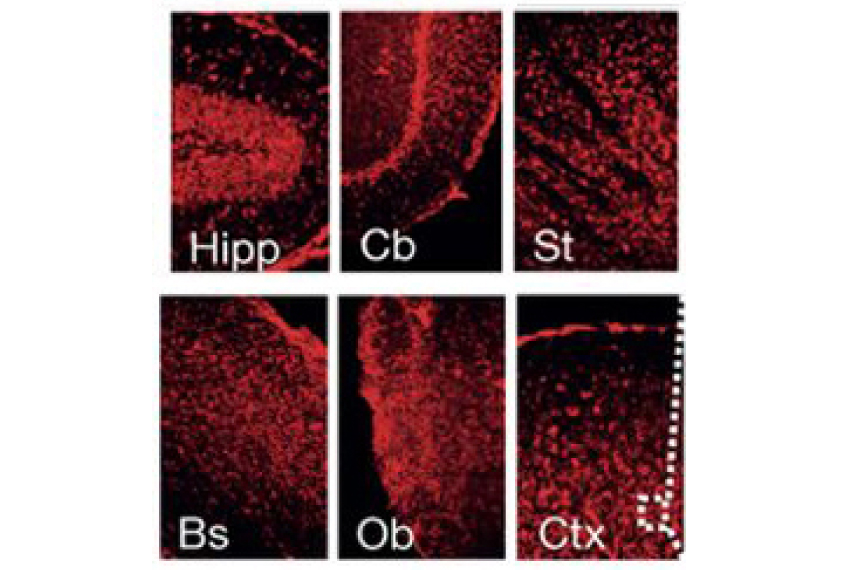
Drug counteracts effects of doubled autism gene
An experimental drug tamps down the expression of a gene duplicated in an autism-related condition and restores typical behavior in mice.
Mass-produced organoids hint at diversity of autism
Researchers have analyzed thousands of brain organoids derived from six autistic people, gaining the potential to rapidly screen drugs.
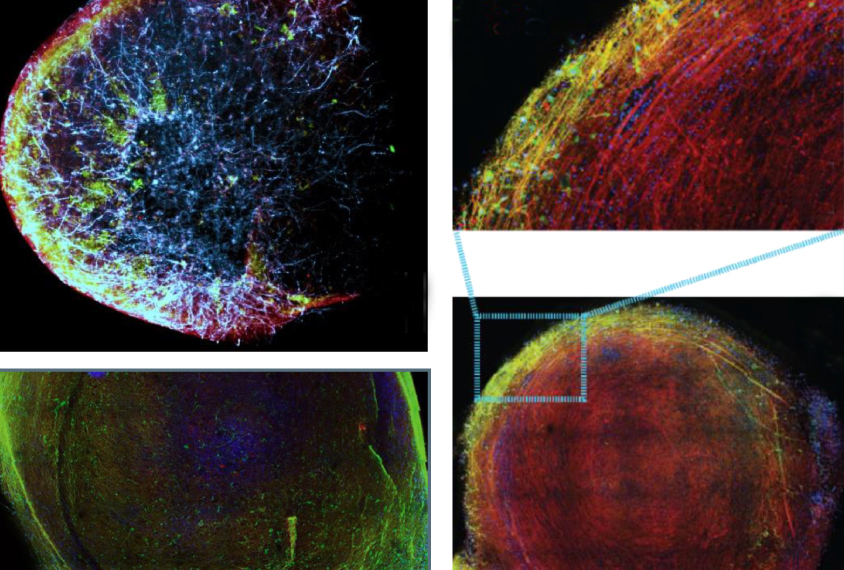
Mass-produced organoids hint at diversity of autism
Researchers have analyzed thousands of brain organoids derived from six autistic people, gaining the potential to rapidly screen drugs.
Leaky mitochondria may play central role in fragile X syndrome
Some traits of fragile X syndrome may be due to problems with mitochondria, the cell’s energy factories.
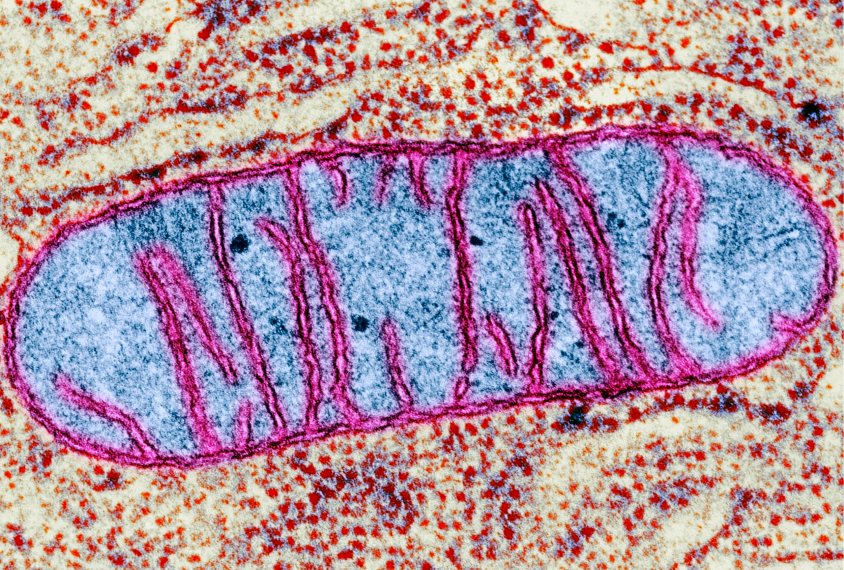
Leaky mitochondria may play central role in fragile X syndrome
Some traits of fragile X syndrome may be due to problems with mitochondria, the cell’s energy factories.
Rat model mimics communication problems in Angelman syndrome
Rats missing UBE3A, the gene mutated in people with Angelman syndrome, squeak frequently but tend not to be responsive to the play and squeaks of other rats.
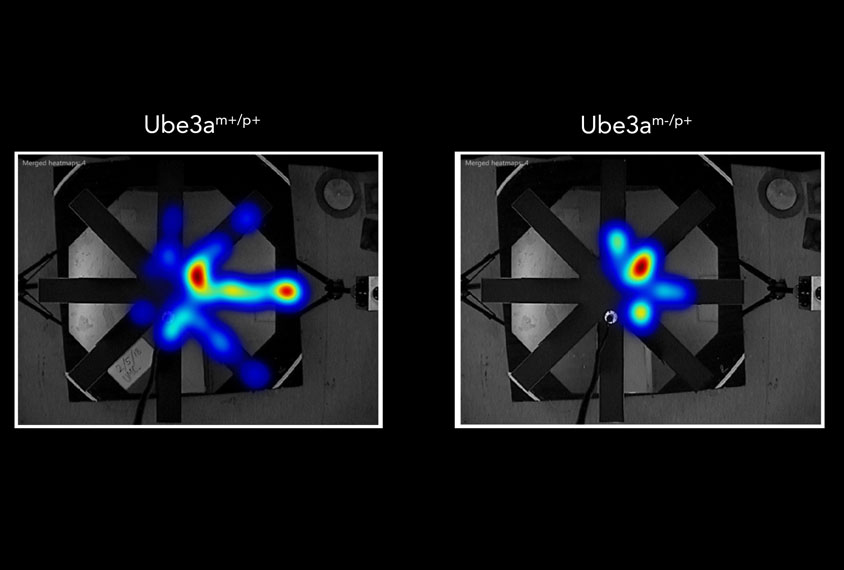
Rat model mimics communication problems in Angelman syndrome
Rats missing UBE3A, the gene mutated in people with Angelman syndrome, squeak frequently but tend not to be responsive to the play and squeaks of other rats.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Remembering Annette Dolphin, who helped explain gabapentin’s effects
The "intuitive" neuropharmacologist pushed against the status quo.

Remembering Annette Dolphin, who helped explain gabapentin’s effects
The "intuitive" neuropharmacologist pushed against the status quo.
Revised statistical bar extracts less-common variants from autism genetics studies
Adjusting genetic analyses could help plug autism’s heritability gap, according to a new preprint.

Revised statistical bar extracts less-common variants from autism genetics studies
Adjusting genetic analyses could help plug autism’s heritability gap, according to a new preprint.
Tom Griffiths describes how neural networks, logic and probability theory together explain cognition
In his new book, “The Laws of Thought,” Griffiths shows how these three pillars of study complement one another and together form a solid foundation to eventually explain all of our cognition, from brain to mind.
Tom Griffiths describes how neural networks, logic and probability theory together explain cognition
In his new book, “The Laws of Thought,” Griffiths shows how these three pillars of study complement one another and together form a solid foundation to eventually explain all of our cognition, from brain to mind.