16p11.2
Recent articles
Autism’s ties to the cell skeleton
Many genes related to the condition play a role in the internal scaffolding of cells, and cytoskeletal disruptions can affect neurodevelopment and behavior.
Autism’s ties to the cell skeleton
Many genes related to the condition play a role in the internal scaffolding of cells, and cytoskeletal disruptions can affect neurodevelopment and behavior.
Multi-lab study hints at benefits of long-tested autism drug
The results lend support for clinical trials of arbaclofen in people with an autism-linked condition, the researchers say.
Multi-lab study hints at benefits of long-tested autism drug
The results lend support for clinical trials of arbaclofen in people with an autism-linked condition, the researchers say.
Going on Trial: Epidiolex for autism; arbaclofen tests; pain monitoring
This month’s issue of Going on Trial takes a sneak peek at some early null results from a small trial of a cannabidiol-based drug for autism, among other recent drug developments.
Going on Trial: Epidiolex for autism; arbaclofen tests; pain monitoring
This month’s issue of Going on Trial takes a sneak peek at some early null results from a small trial of a cannabidiol-based drug for autism, among other recent drug developments.
Trials of arbaclofen for autism yield mixed results
Autistic children taking the drug showed improvements in some behaviors but not in their social skills.

Trials of arbaclofen for autism yield mixed results
Autistic children taking the drug showed improvements in some behaviors but not in their social skills.
Brain signatures of rare variants hint at cardiovascular risk
People whose brains look like those of people who carry autism-linked copy number variants also share markers of heart health.
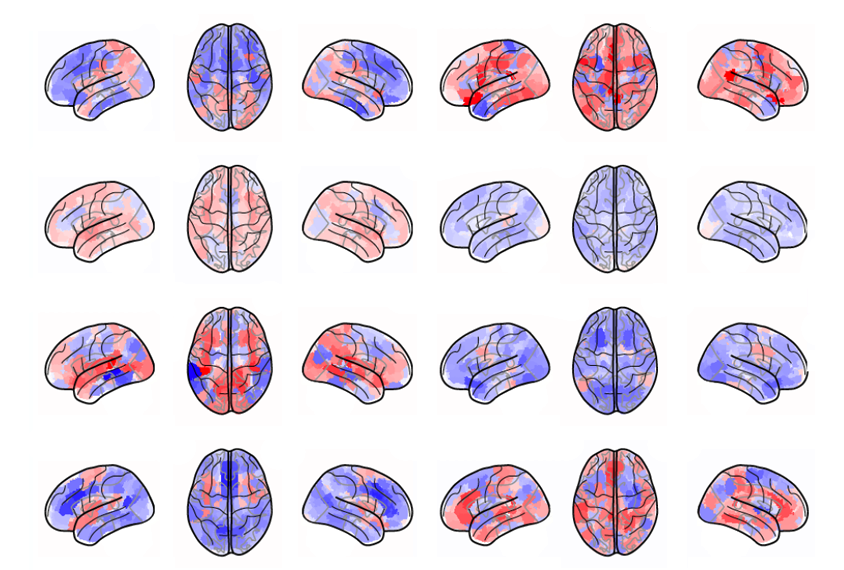
Brain signatures of rare variants hint at cardiovascular risk
People whose brains look like those of people who carry autism-linked copy number variants also share markers of heart health.
Autism and the cell’s antennae
Many autism-linked genes are somehow tied to cilia, the tiny hair-like sensors that stud a cell’s surface. But the question remains whether, and how, cilia differences contribute to the condition.
Autism and the cell’s antennae
Many autism-linked genes are somehow tied to cilia, the tiny hair-like sensors that stud a cell’s surface. But the question remains whether, and how, cilia differences contribute to the condition.
Common and rare autism-linked variants share functional effects
Within the 16p region of the genome, the two types of variants similarly decrease neuronal gene expression — an effect that may reflect their spatial relationship.
Common and rare autism-linked variants share functional effects
Within the 16p region of the genome, the two types of variants similarly decrease neuronal gene expression — an effect that may reflect their spatial relationship.
Excess of ‘don’t eat me’ cell signals may drive brain enlargement in autism
The signal, called CD47, is disrupted in autistic people who have a larger-than-average head.

Excess of ‘don’t eat me’ cell signals may drive brain enlargement in autism
The signal, called CD47, is disrupted in autistic people who have a larger-than-average head.
Gene in autism hotspot regulates neuronal migration
Restoring the gene, TAOK2, in mice missing an autism-linked region of chromosome 16 normalizes neuronal movement during development.
Gene in autism hotspot regulates neuronal migration
Restoring the gene, TAOK2, in mice missing an autism-linked region of chromosome 16 normalizes neuronal movement during development.
Autism’s genetic heterogeneity evident in brain connectivity patterns
The results highlight the importance of subgrouping study participants based on their underlying genetics, the researchers say.

Autism’s genetic heterogeneity evident in brain connectivity patterns
The results highlight the importance of subgrouping study participants based on their underlying genetics, the researchers say.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Okur-Chung neurodevelopmental syndrome; excess CSF; autistic girls
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 21 October.
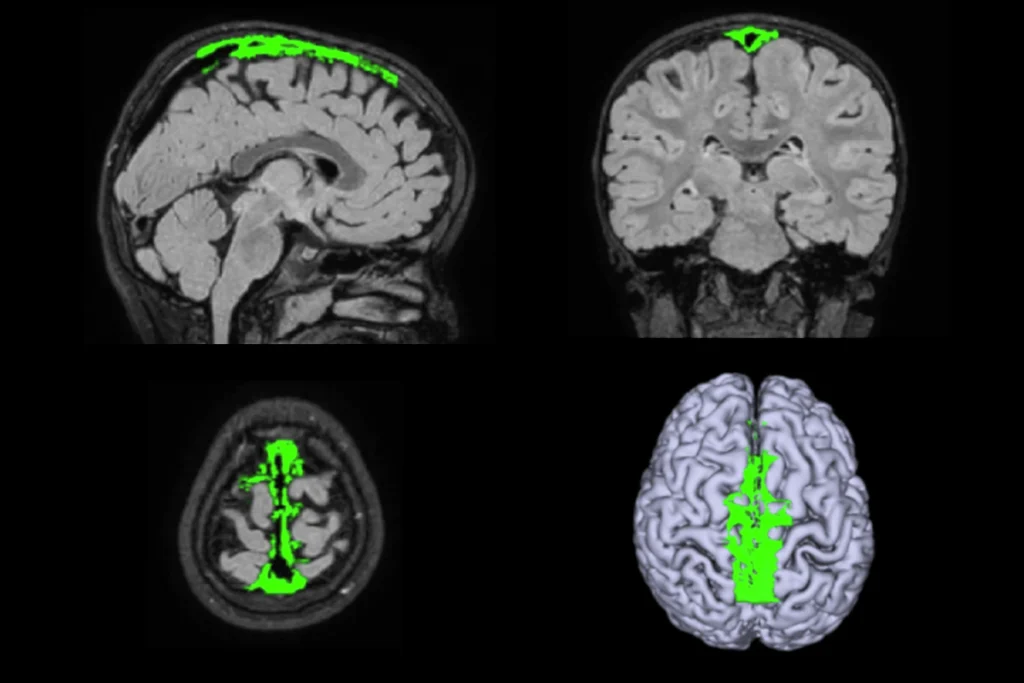
Okur-Chung neurodevelopmental syndrome; excess CSF; autistic girls
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 21 October.
Brains, biases and amyloid beta: Why the female brain deserves a closer look in Alzheimer’s research
New results suggest the disease progresses differently in women, but we need more basic science to unpack the mechanisms involved.

Brains, biases and amyloid beta: Why the female brain deserves a closer look in Alzheimer’s research
New results suggest the disease progresses differently in women, but we need more basic science to unpack the mechanisms involved.
Are brains and AI converging?—an excerpt from ‘ChatGPT and the Future of AI: The Deep Language Revolution’
In his new book, to be published next week, computational neuroscience pioneer Terrence Sejnowski tackles debates about AI’s capacity to mirror cognitive processes.
Are brains and AI converging?—an excerpt from ‘ChatGPT and the Future of AI: The Deep Language Revolution’
In his new book, to be published next week, computational neuroscience pioneer Terrence Sejnowski tackles debates about AI’s capacity to mirror cognitive processes.