Earl K. Miller is Picower Professor of Neuroscience at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, with faculty roles in the Picower Institute for Learning and Memory and the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences. His lab focuses on neural mechanisms of cognition, especially working memory, attention and executive control, using both experimental and computational methods. He holds a B.A. from Kent State University and an M.A. and Ph.D. from Princeton University. In 2020, he received an honorary Doctor of Science degree from Kent State University.

Earl K. Miller
Professor of neuroscience
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Selected articles
- “An integrative theory of prefrontal cortex function” | Annual Review of Neuroscience
- “Top-down versus bottom-up control of attention in the prefrontal and posterior parietal cortices” | Science
- “The importance of mixed selectivity in complex cognitive tasks” | Nature
- “Gamma and beta bursts during working memory readout suggest roles in its volitional control” | Nature Communications
Explore more from The Transmitter
Portfolio of SCN2A gene variants, and more
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 9 March.
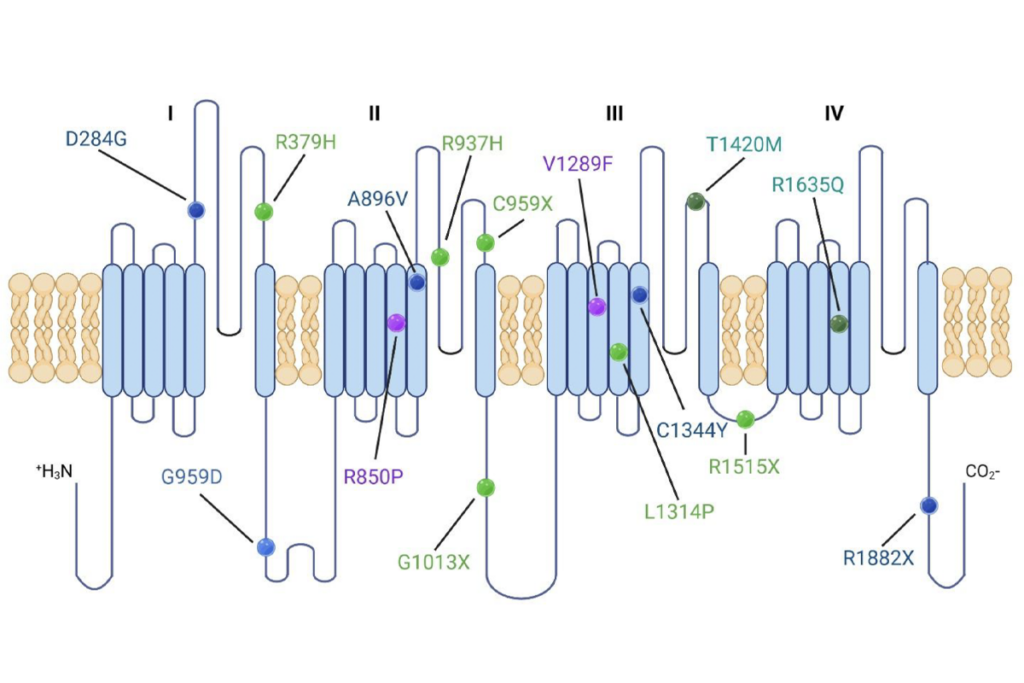
Portfolio of SCN2A gene variants, and more
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 9 March.
Hippocampus builds reputation as ‘general-purpose statistical learning machine’
New cross-species findings may help settle a long-standing debate about whether the hippocampus is required for passive learning.
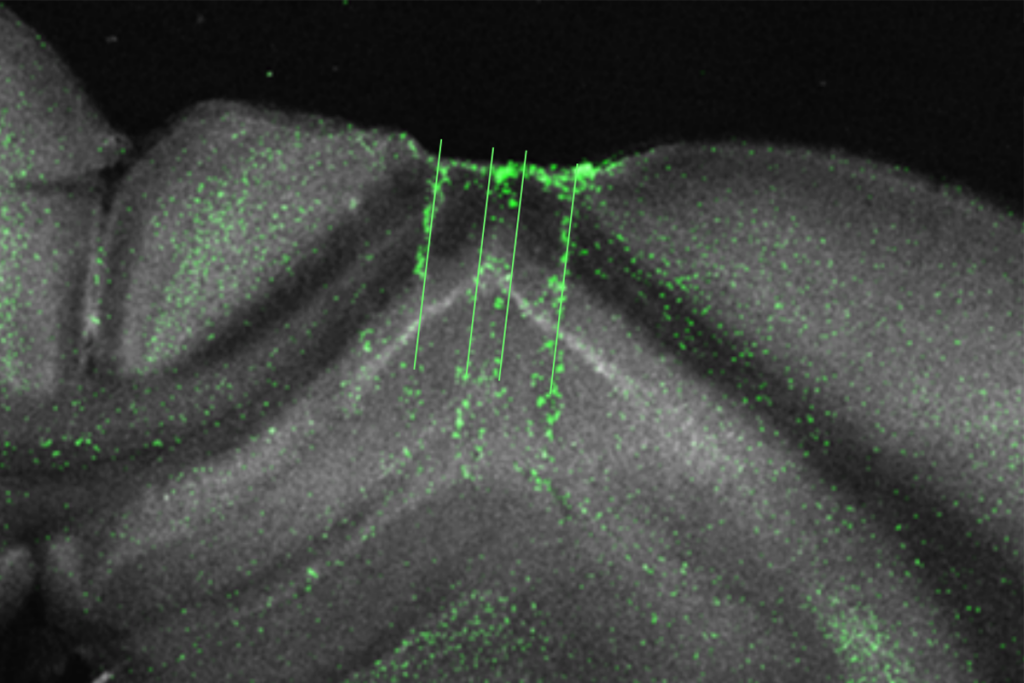
Hippocampus builds reputation as ‘general-purpose statistical learning machine’
New cross-species findings may help settle a long-standing debate about whether the hippocampus is required for passive learning.
‘The Fox, the Shrew, and You: How Brains Evolved,’ an excerpt
In his new book, Rogier Mars provides a detailed account of animal and human brain evolution. In this excerpt from Chapter 1, he starts with the sea squirt—and why it needs the brain it eats after its larval stage.

‘The Fox, the Shrew, and You: How Brains Evolved,’ an excerpt
In his new book, Rogier Mars provides a detailed account of animal and human brain evolution. In this excerpt from Chapter 1, he starts with the sea squirt—and why it needs the brain it eats after its larval stage.