Katie Moisse is contributing editor and former news editor at The Transmitter. She teaches science communication at McMaster University in Hamilton, Ontario, Canada. She has a Ph.D. in neuropathology from the University of Western Ontario and an M.S. in journalism from Columbia University.

Katie Moisse
Contributing editor
The Transmitter
From this contributor
Frameshift: Raphe Bernier followed his heart out of academia, then made his way back again
After a clinical research career, an interlude at Apple and four months in early retirement, Raphe Bernier found joy in teaching.

Frameshift: Raphe Bernier followed his heart out of academia, then made his way back again
Frameshift: At a biotech firm, Ubadah Sabbagh embraces the expansive world outside academia
As chief of staff at Arcadia, Ubadah Sabbagh gets to do science while also pushing the boundaries of how science gets done.
Frameshift: At a biotech firm, Ubadah Sabbagh embraces the expansive world outside academia
Frameshift: Shari Wiseman reflects on her pivot from science to publishing
As chief editor of Nature Neuroscience, Wiseman applies critical-thinking skills she learned in the lab to manage the journal’s day-to-day operations.

Frameshift: Shari Wiseman reflects on her pivot from science to publishing
The spectrum goes multidimensional in search of autism subtypes
Grouping people with autism based on shared features, genetics and co-occurring conditions may improve clinical trial outcomes, researchers say.
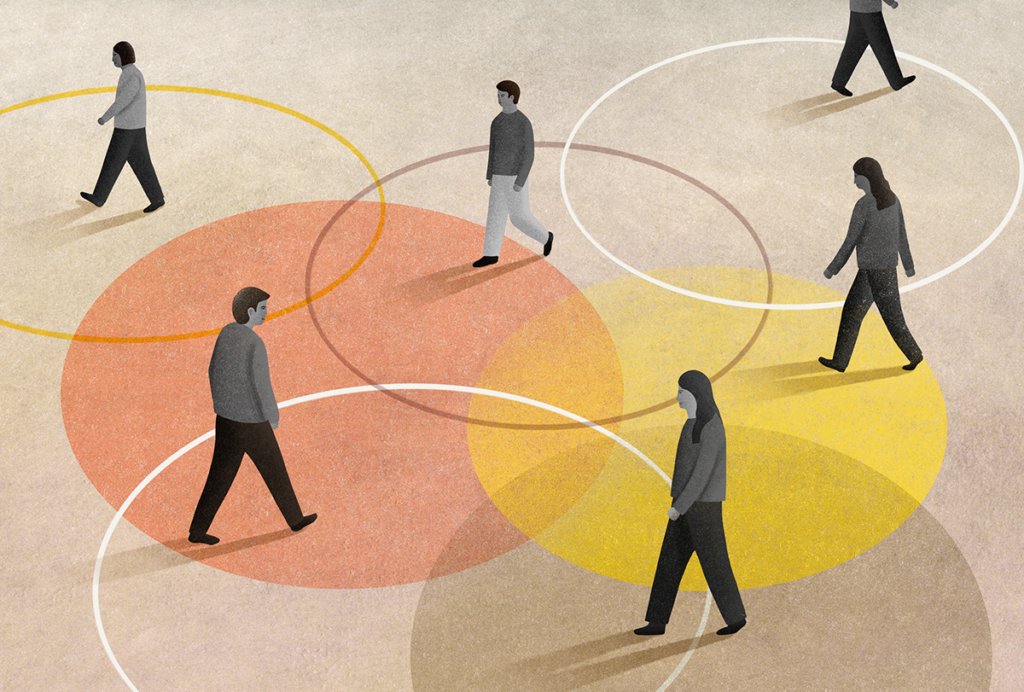

The spectrum goes multidimensional in search of autism subtypes
Memory study sparks debate over statistical methods
Critics of a 2024 Nature paper suggest the authors failed to address the risk of false-positive findings. The authors argue more rigorous methods can result in missed leads.
Memory study sparks debate over statistical methods
Explore more from The Transmitter
Remembering Annette Dolphin, who helped explain gabapentin’s effects
The "intuitive" neuropharmacologist pushed against the status quo.

Remembering Annette Dolphin, who helped explain gabapentin’s effects
The "intuitive" neuropharmacologist pushed against the status quo.
Revised statistical bar extracts less-common variants from autism genetics studies
Adjusting genetic analyses could help plug autism’s heritability gap, according to a new preprint.

Revised statistical bar extracts less-common variants from autism genetics studies
Adjusting genetic analyses could help plug autism’s heritability gap, according to a new preprint.
Tom Griffiths describes how neural networks, logic and probability theory together explain cognition
In his new book, “The Laws of Thought,” Griffiths shows how these three pillars of study complement one another and together form a solid foundation to eventually explain all of our cognition, from brain to mind.
Tom Griffiths describes how neural networks, logic and probability theory together explain cognition
In his new book, “The Laws of Thought,” Griffiths shows how these three pillars of study complement one another and together form a solid foundation to eventually explain all of our cognition, from brain to mind.