Maia Szalavitz is the author, most recently, of Unbroken Brain: A Revolutionary New Way of Understanding Addiction, which will be released in paperback in May. She has written about neuroscience and addiction for nearly 30 years for publications ranging from the New York Times and Washington Post to TIME and Scientific American.

Maia Szalavitz
Neuroscience Journalist
Freelance
From this contributor
Autism’s hidden habit
Conventional wisdom holds that people with autism don't get hooked on alcohol or other drugs, but new evidence suggests otherwise.
New tests extend prospects for ‘reading the mind in the eyes’
Researchers have revamped a screen for ‘mind blindness’ — an impaired understanding of others’ intentions and perspectives — which is a key deficit in autism. The revised test may shed light on how autism develops.

New tests extend prospects for ‘reading the mind in the eyes’
‘Resting’ autism brains still hum with activity
Even at rest, the brains of people with autism manage more information than those of their peers, according to a new study that may provide support for the so-called ‘intense world’ theory of autism.

‘Resting’ autism brains still hum with activity
First 1,000 days of life could hold keys to autism
Autism researchers have high hopes for a new project called the First 1,000 Days of Life, which aims to follow 5,000 women and their babies from pregnancy through two years after birth.

First 1,000 days of life could hold keys to autism
Long neglected, severe cases of autism get some attention
A large new project aims to link specialized psychiatric units across the U.S. to investigate the causes and best treatment for autism’s most severe and challenging cases.

Long neglected, severe cases of autism get some attention
Explore more from The Transmitter
Portfolio of SCN2A gene variants, and more
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 9 March.
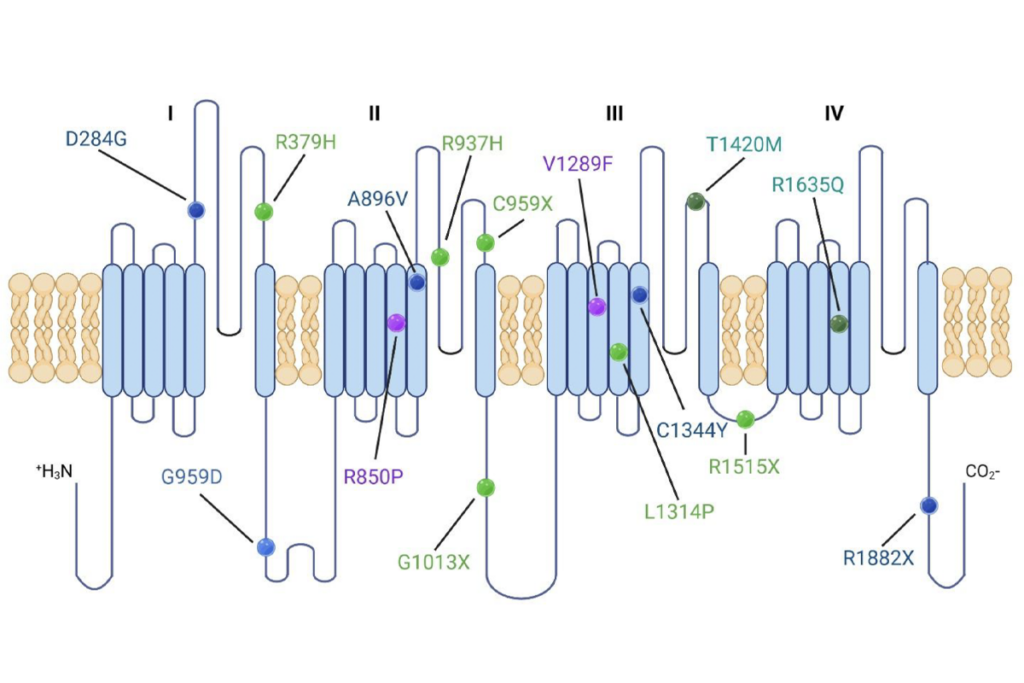
Portfolio of SCN2A gene variants, and more
Here is a roundup of autism-related news and research spotted around the web for the week of 9 March.
Hippocampus builds reputation as ‘general-purpose statistical learning machine’
New cross-species findings may help settle a long-standing debate about whether the hippocampus is required for passive learning.
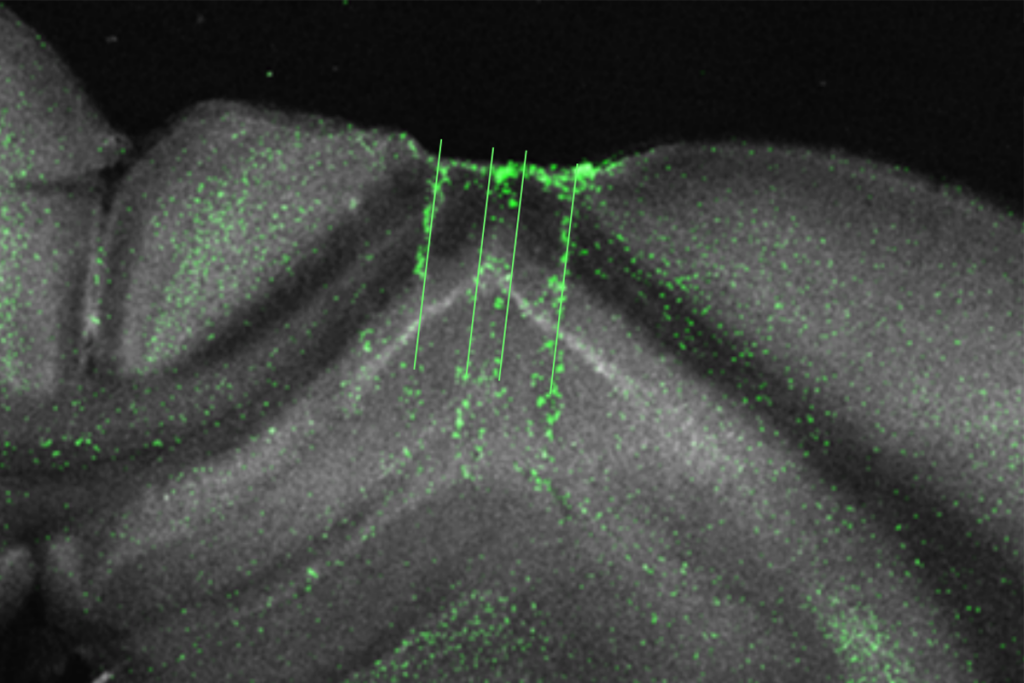
Hippocampus builds reputation as ‘general-purpose statistical learning machine’
New cross-species findings may help settle a long-standing debate about whether the hippocampus is required for passive learning.
‘The Fox, the Shrew, and You: How Brains Evolved,’ an excerpt
In his new book, Rogier Mars provides a detailed account of animal and human brain evolution. In this excerpt from Chapter 1, he starts with the sea squirt—and why it needs the brain it eats after its larval stage.

‘The Fox, the Shrew, and You: How Brains Evolved,’ an excerpt
In his new book, Rogier Mars provides a detailed account of animal and human brain evolution. In this excerpt from Chapter 1, he starts with the sea squirt—and why it needs the brain it eats after its larval stage.
