Polina Porotskaya is a former intern at Spectrum and a graduate student in the Science, Health and Environmental Reporting Program at New York University. Polina writes about neuroscience, biology and medicine. She has a B.A. in neuroscience from Columbia University.

Polina Porotskaya
From this contributor
Inside a summer camp for autistic children in Russia
Photographs show how a camp in St. Petersburg this summer helped children on the spectrum and their families find some fun during the pandemic.

Inside a summer camp for autistic children in Russia
Cell stress may sap organoids’ usefulness in autism research
Some cells in brain organoids — 3D clusters of cultured brain cells — fail to develop fully.
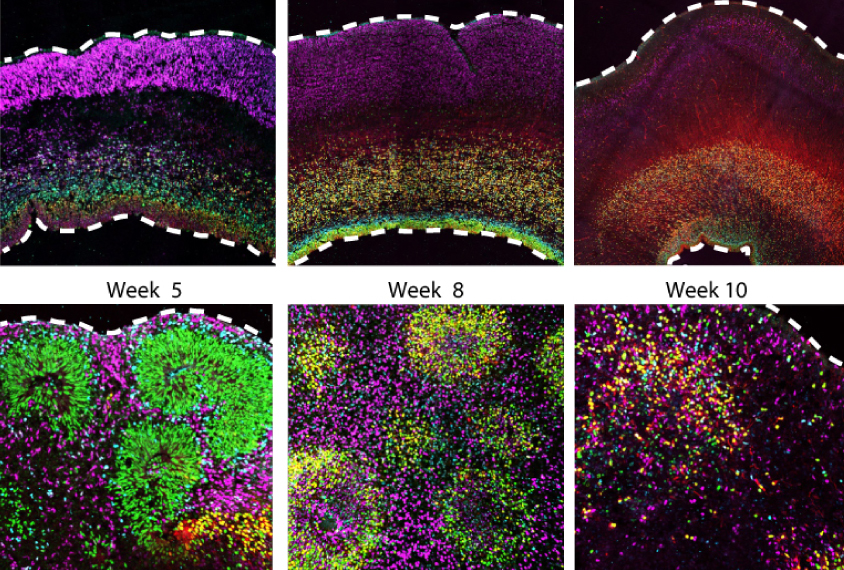
Cell stress may sap organoids’ usefulness in autism research
Diabetes drug delivers multiple benefits for people with fragile X syndrome
Researcher Randi Hagerman is a big proponent of metformin — a diabetes drug that she is testing in people with fragile X syndrome. In fact, Hagerman takes the drug herself as a preventive measure against cancer.

Diabetes drug delivers multiple benefits for people with fragile X syndrome
Mutations in sperm may accrue too slowly to increase autism risk
A new analysis challenges the idea that mutations in the sperm of older fathers lead to higher rates of autism among their children.

Mutations in sperm may accrue too slowly to increase autism risk
New maps of neuronal connections reveal roundworms’ wiring
Two new maps show the entire nervous system of the adult roundworm Caenorhabditis elegans.
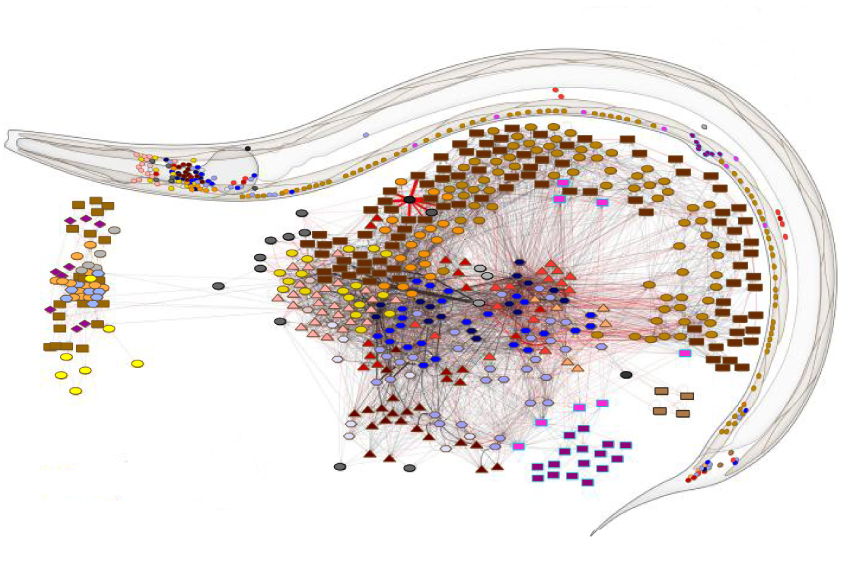
New maps of neuronal connections reveal roundworms’ wiring
Explore more from The Transmitter
Lack of reviewers threatens robustness of neuroscience literature
Simple math suggests that small groups of scientists can significantly bias peer review.

Lack of reviewers threatens robustness of neuroscience literature
Simple math suggests that small groups of scientists can significantly bias peer review.
Dendrites help neuroscientists see the forest for the trees
Dendritic arbors provide just the right scale to study how individual neurons reciprocally interact with their broader circuitry—and are our best bet to bridge cellular and systems neuroscience.

Dendrites help neuroscientists see the forest for the trees
Dendritic arbors provide just the right scale to study how individual neurons reciprocally interact with their broader circuitry—and are our best bet to bridge cellular and systems neuroscience.
Two primate centers drop ‘primate’ from their name
The Washington and Tulane National Biomedical Research Centers—formerly called National Primate Research Centers—say they made the change to better reflect the breadth of research performed at the centers.

Two primate centers drop ‘primate’ from their name
The Washington and Tulane National Biomedical Research Centers—formerly called National Primate Research Centers—say they made the change to better reflect the breadth of research performed at the centers.