Rachel Nuwer is a freelance science journalist who contributes to outlets such as the New York Times, Scientific American and New Scientist. She writes news articles for Spectrum. She lives in Brooklyn.
Rachel Nuwer
Contributing Writer
Spectrum
From this contributor
Lisa Croen: Autism’s first dedicated epidemiologist
Inspired by watching her autistic nephew grow up, Croen has also been an advocate for bolstering research and services for autistic adults.

Lisa Croen: Autism’s first dedicated epidemiologist
Finding strengths in autism
Autism comprises a set of difficulties, but growing evidence suggests that certain abilities also define the condition.
Meet the autistic scientists redefining autism research
Growing ranks of researchers on the spectrum are overcoming barriers — from neurotypical bias to sensory sensitivities — to shape autism science.

Meet the autistic scientists redefining autism research
Growing old with autism
For many autistic adults, the golden years are tarnished by poor health, poverty and, in some cases, homelessness. Their plight reveals huge gaps in care.
Mouse study links gene to some autism symptoms
Mice missing a gene called PTCHD1 in a deep-seated brain structure have autism-like symptoms that ease with treatment.
Explore more from The Transmitter
Frameshift: Raphe Bernier followed his heart out of academia, then made his way back again
After a clinical research career, an interlude at Apple and four months in early retirement, Raphe Bernier found joy in teaching.

Frameshift: Raphe Bernier followed his heart out of academia, then made his way back again
After a clinical research career, an interlude at Apple and four months in early retirement, Raphe Bernier found joy in teaching.
Organoid study reveals shared brain pathways across autism-linked variants
The genetic variants initially affect brain development in unique ways, but over time they converge on common molecular pathways.
Organoid study reveals shared brain pathways across autism-linked variants
The genetic variants initially affect brain development in unique ways, but over time they converge on common molecular pathways.
Single gene sways caregiving circuits, behavior in male mice
Brain levels of the agouti gene determine whether African striped mice are doting fathers—or infanticidal ones.
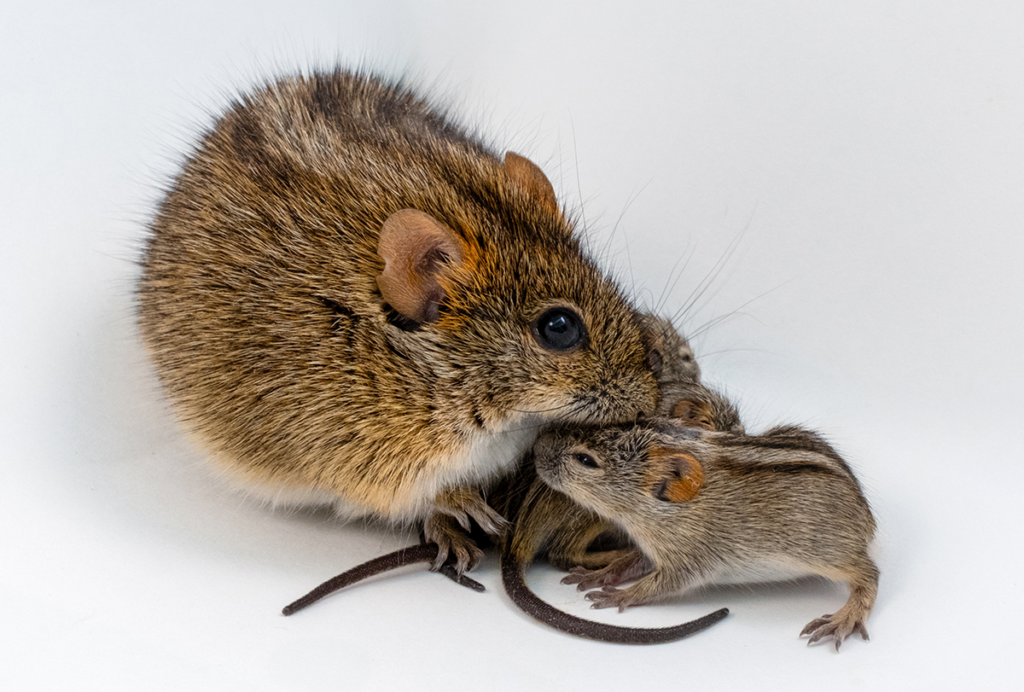

Single gene sways caregiving circuits, behavior in male mice
Brain levels of the agouti gene determine whether African striped mice are doting fathers—or infanticidal ones.


